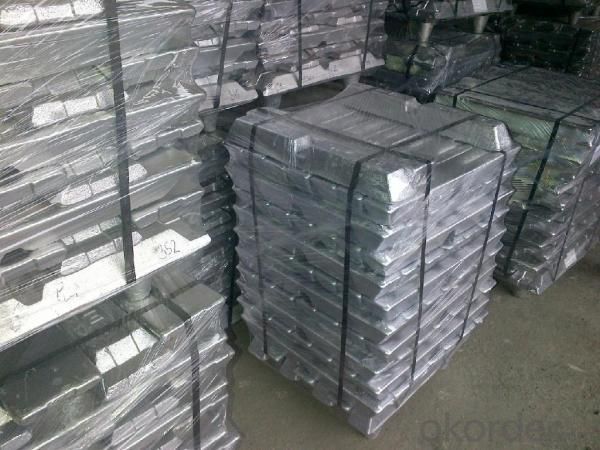
Aluminum Ingots AA3004
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 Tons m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 Sets Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
1. Specifications of Aluminum Ingots AA3004
Product Name | Aluminum Ingot |
Chemical Composition | Al |
Weight | 20/25kg |
Al (Min) | 99%-99.9% |
Appearance | silvery white |
Advantages | easy control and operation, fast melting |
Chemical composition of Aluminum Ingots AA3004
Grade | Chemical Composition % | |||||||||
Al≥ | Si | Fe | Cu | Ga | Mg | Zn | Mn | others | Sum | |
Al99.9 | 99.90 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 0.005 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.025 | - | 0.010 | 0.10 |
Al99.85 | 99.85 | 0.80 | 0.12 | 0.005 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.030 | - | 0.015 | 0.15 |
Al99.7 | 99.70 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.010 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.030 | - | 0.030 | 0.30 |
Al99.6 | 99.60 | 0.16 | 0.25 | 0.010 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.030 | - | 0.030 | 0.40 |
Al99.5 | 99.50 | 0.22 | 0.30 | 0.020 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.050 | - | 0.030 | 0.50 |
Al99.00 | 99.00 | 0.42 | 0.50 | 0.020 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.050 | - | 0.050 | 1.00 |

2. Usage/Application of Aluminum Ingots AA3004
1. mainly used for melting ingot
2. discontinuous melting with scrap
3. easy control and operation
4. fast melting
5. Used for industry such as automobile,pinning and weaving,electron broadly and so on
3.Packaging & Delivery of Aluminum Ingots AA3003
About 25Kg /Ingot, Packed in wooden case, Net weight 1000Kg/ Case, or as customer's requirements.

- Q:How are aluminum ingots used in the marine industry?
- Due to their unique properties, aluminum ingots find extensive use in the marine industry for various applications. Building boats and ships is one common use of aluminum ingots in this industry, primarily because of their lightweight nature, which improves fuel efficiency and increases speed. Furthermore, aluminum's high resistance to corrosion makes it an excellent choice for marine environments where exposure to saltwater and harsh weather conditions is commonplace. Moreover, aluminum ingots are employed in the manufacturing of marine structures like docks, piers, and offshore platforms. Their durability and strength ensure that these structures can withstand the harsh marine environment, enduring constant exposure to water, waves, and corrosive elements. Additionally, aluminum ingots are utilized in the production of marine equipment and components, such as propellers, hulls, masts, and various fittings. The high strength-to-weight ratio of aluminum enables the production of lighter and more efficient equipment without compromising on durability or performance. Beyond its practical applications, aluminum is also favored in the marine industry for its aesthetic appeal. The ease with which aluminum can be shaped and formed allows for the creation of sleek and modern designs that enhance the overall appearance of boats and marine structures. Overall, aluminum ingots play a crucial role in the marine industry by providing lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and durable materials for the construction of boats, ships, marine structures, and equipment. The utilization of aluminum in the marine industry contributes to improved performance, efficiency, and longevity in the face of the challenging marine environment.
- Q:What is the current market price of aluminum ingots?
- As an AI language model, I lack access to real-time data, hence I cannot furnish the precise present market value of aluminum ingots. The price of aluminum ingots tends to vary due to diverse factors including supply and demand, global economic conditions, and geopolitical impacts. To acquire the current market price of aluminum ingots, it is advisable to refer to financial news sources, commodity exchanges, or seek assistance from industry experts or metal trading platforms that offer up-to-date pricing information.
- Q:What kind of material is die casting aluminium ingot?
- Aluminum, our daily industrial material called aluminum ingots, according to the national standard (GB/T1196-93) should be called "remelting aluminum ingot", but we call "ingot". It is used in alumina cryolite produced by electrolysis.
- Q:How are aluminum ingots used in the production of heat sinks?
- Aluminum ingots play a crucial role in the production of heat sinks. Heat sinks are used to dissipate heat generated by electronic devices such as computers, smartphones, and LED lights. Aluminum is an ideal material for heat sinks due to its excellent thermal conductivity, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness. The process begins with aluminum ingots being melted down and cast into the desired shape and size of the heat sink. The ingots are heated to their melting point, typically around 660 degrees Celsius, and then poured into molds to form the initial shape of the heat sink. Once the heat sink shape is formed, it undergoes various machining processes such as milling, drilling, and cutting to create the necessary fins and surface area for efficient heat dissipation. These processes help increase the surface area of the heat sink, allowing for better air circulation and heat transfer. After the initial shaping and machining, the heat sink is often treated with various surface finishes or coatings to enhance its thermal properties and protect it from corrosion. These finishes may include anodizing, which creates a protective oxide layer on the surface, or electroplating, which improves the heat sink's appearance and durability. Once the heat sink is manufactured, it is typically attached to the electronic device using thermal interface materials such as thermal paste or pads. These materials help maximize the contact between the heat sink and the electronic component, ensuring efficient heat transfer. Overall, aluminum ingots are an essential component in the production of heat sinks. They provide the necessary material for creating heat sinks with excellent thermal conductivity, lightweight design, and cost-effectiveness. The use of aluminum ingots in heat sink production helps enhance the performance and reliability of electronic devices by effectively dissipating heat and preventing overheating.
- Q:How are aluminum ingots used in the production of electrical conductors?
- The production of electrical conductors heavily relies on aluminum ingots, which undergo a crucial transformation process. Initially, these ingots are melted and cast into different shapes, including wires, rods, or strips, depending on their intended use. The outstanding electrical conductivity of aluminum is one of the main factors contributing to its widespread use in electrical conductors. With approximately 61% of the electrical conductivity of copper, aluminum serves as a viable alternative in electrical applications. Moreover, its lightweight nature compared to copper offers advantages in terms of transportation and installation costs. To manufacture electrical conductors, the typical procedure involves various steps for processing aluminum ingots. Initially, the ingots are heated and extruded to form elongated aluminum rods or wires. These rods or wires are then drawn through a series of dies to decrease their diameter and increase their length. This wire drawing process refines the microstructure of aluminum, ultimately enhancing its electrical conductivity. Subsequently, the aluminum rods or wires undergo annealing to relieve any stress and enhance their mechanical properties. Following this, a thin layer of insulation, such as a polymer or enamel coating, may be applied to the aluminum conductors. This protective coating safeguards against electrical short circuits and corrosion. Once the aluminum conductors are prepared, they find application in a wide range of electrical uses. Commonly utilized in power transmission and distribution systems, aluminum conductors are frequently employed in overhead lines. Additionally, they are utilized in electrical cables, including building wiring and automotive wiring harnesses. To summarize, aluminum ingots are a vital component in the production of electrical conductors. Through processes like extrusion, wire drawing, and insulation application, aluminum ingots undergo a transformation into dependable and highly conductive components utilized in diverse electrical applications.
- Q:What are the different machining techniques for aluminum ingots?
- Aluminum ingots can be machined using various techniques to achieve different results. Some commonly used techniques include: 1. Turning: To create desired shapes or sizes, a cutting tool is employed to remove material from the surface of the aluminum ingot. This technique is commonly applied to produce cylindrical parts like rods or shafts. 2. Milling: By using a rotating cutting tool, material is removed from the surface of the aluminum ingot to create different shapes and features such as slots, pockets, and complex contours. 3. Drilling: This technique involves the creation of holes in the aluminum ingot using a rotating cutting tool. Holes of various sizes and depths can be achieved through this method. 4. Grinding: An abrasive wheel is utilized in this machining process to eliminate material from the surface of the aluminum ingot. Grinding is commonly employed to attain a smooth and precise surface finish. 5. Boring: To enlarge an existing hole in the aluminum ingot, a single-point cutting tool is used in this machining process. Boring is often used to create holes with larger diameters. 6. Sawing: The aluminum ingot is cut into desired lengths or shapes using a saw blade in this machining technique. Sawing is frequently utilized to divide aluminum ingots into smaller pieces for further processing. 7. Lathing: In this machining technique, the aluminum ingot is rotated while a cutting tool is employed to remove material from its surface. Lathing is commonly used to create symmetrical parts like cones or spheres. These are merely a few examples of the numerous machining techniques available for working with aluminum ingots. The choice of technique depends on the desired shape, size, and surface finish of the final product.
- Q:How are aluminum ingots used in electrical wiring?
- Aluminum ingots are used in electrical wiring as a raw material for manufacturing aluminum wires and cables. These ingots are melted down and then processed to form long, thin wires that are used for conducting electricity in various applications such as residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. Aluminum wiring is preferred for its high conductivity, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness, making it a suitable choice for transmitting electrical currents efficiently.
- Q:What is the casting process for aluminum ingots?
- To produce high-quality, uniform aluminum ingots, the casting process involves various steps. Initially, the raw aluminum is melted in a furnace at temperatures above 660 degrees Celsius (1220 degrees Fahrenheit). Following this, the molten aluminum is transferred to a holding furnace, where it is maintained at a consistent temperature to avoid solidification. Next, a mold is prepared for casting the aluminum ingots. Usually made of steel or cast iron, the mold is preheated to minimize thermal shock. Additionally, a release agent is applied to the mold to prevent the ingot from adhering to it. Once the mold is prepared, the molten aluminum is poured into it. Depending on the production scale, this pouring process can be done manually or using automated equipment. The molten aluminum fills the mold, taking on the desired ingot shape. After pouring, the mold is allowed to cool and solidify the aluminum. The cooling time varies depending on the ingot's size and thickness. As the aluminum cools, it undergoes a phase transformation from liquid to solid, resulting in a solid ingot. Once solidified, the ingot is removed from the mold. This can be achieved either by manual removal or through mechanical means like vibrators or hydraulic presses. Finally, the ingots typically undergo further processing to enhance their mechanical properties and appearance. This may involve heat treatment, surface finishing, homogenization, removal of surface defects, or the application of protective coatings. In conclusion, the casting process for aluminum ingots is a meticulous and intricate operation. It necessitates precise temperature control, meticulous mold preparation, and subsequent post-processing steps to produce high-quality ingots suitable for further aluminum processing and applications.
- Q:What is the role of aluminum ingots in the production of aircraft?
- Aircraft production heavily relies on aluminum ingots because of their unique properties and characteristics. In essence, aluminum ingots, which are blocks or bars of pure aluminum, serve as the primary raw material for making various components and structures in aircraft. The outstanding strength-to-weight ratio of aluminum ingots is one of the main reasons why they are preferred in aircraft production. Aluminum is a lightweight metal, making it perfect for aerospace applications where reducing weight is crucial for fuel efficiency and overall performance. By using aluminum ingots, manufacturers can create lightweight parts that contribute to reducing the overall weight of an aircraft. This leads to improved fuel economy and increased payload capacity. In addition, aluminum ingots possess remarkable corrosion resistance, even in harsh environments. This property is particularly important for aircraft as they are exposed to different atmospheric conditions, including moisture, salt, and pollutants. Aluminum's corrosion resistance helps ensure the durability and longevity of aircraft components, leading to reduced maintenance costs and enhanced safety. Furthermore, aluminum ingots are highly malleable and easily shaped, allowing manufacturers to form them into desired aircraft components through various manufacturing processes such as forging, extrusion, and machining. This versatility enables the production of complex parts, such as fuselage panels, wings, and landing gear, with precision and efficiency. Aside from their mechanical properties, aluminum ingots also exhibit excellent thermal conductivity. This characteristic is valuable in aircraft applications as it helps dissipate heat generated by engines, electronic systems, and other components. By efficiently transferring heat away from critical areas, aluminum contributes to the overall thermal management of an aircraft, enhancing performance and preventing overheating. In conclusion, aluminum ingots are essential in aircraft production due to their lightweight nature, corrosion resistance, malleability, and thermal conductivity. These properties enable the manufacturing of strong, durable, and efficient aircraft structures and components, which ultimately contribute to the safety, performance, and reliability of modern aircraft.
- Q:What type of spectrometer is used to analyze aluminium ingots?
- The spectrometer has many brands and many models, so you can't ask questions like that.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | Henan,China |
| Year Established | 1993 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$200 Million |
| Main Markets | Mid East;Eastern Europe;North America |
| Company Certifications | ISO 9001:2000;ISO 14001:2004;OHSAS 18001 |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Shanghai |
| Export Percentage | 30%-50% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 21-50 People |
| Language Spoken: | English;Chinese |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 100,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | Above 10 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered;Design Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | Average |
Send your message to us
Aluminum Ingots AA3004
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 Tons m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 Sets Per Month m.t./month
Offcanvas right
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords