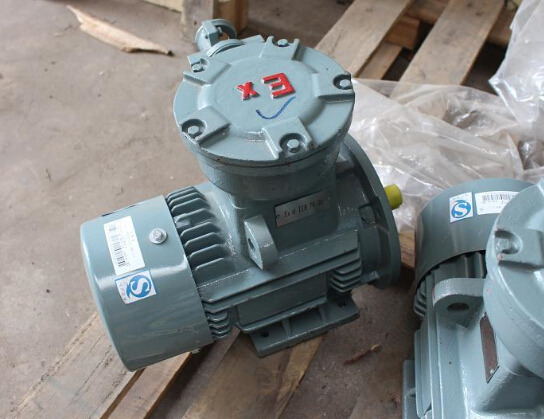
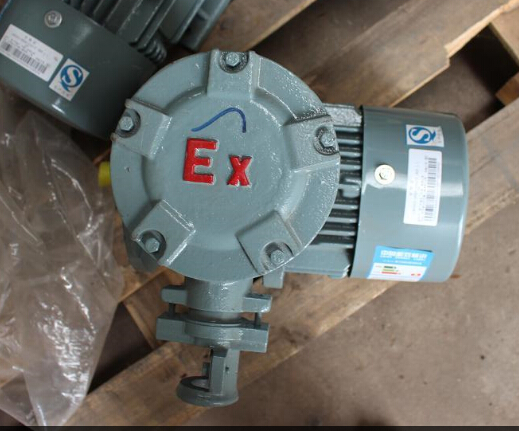
Siemens EX Series AC Motor
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like



- Q: Why asynchronous motor AC excitation, rather than DC excitation?
- Synchronous motor is also a kind of AC motor. Mainly used for generators, motors can also be used, generally used for larger power, speed does not require the adjustment of production machinery, such as large water pumps, air compressors and mine fans. In recent years, due to the development of permanent magnet materials and electronic technology, micro synchronous motor has been more and more widely used. One of the characteristics of synchronous motors is the steady running speed, N and stator current frequency f1 has a strict constant relationship, that is, n=60f1/p=n0 synchronous motor speed n and rotating magnetic field speed N0 the same. The name of "synchronization" comes from here. The stator of a synchronous motor goes without saying that the general rotor coil must be energized to keep it in sync with the stator. (the rotor of the micro synchronous motor can be made of permanent magnetic steel.)Asynchronous motor is different, the stator winding energized to generate rotating magnetic field, in the rotor to generate induction current, so that the motor rotation. Structure than synchronous motor simple
- Q: I have never seen such a motor with 3, 5, 7 poles etc. - always an even number. Why? Physically impossible?
- Convert a 8 poles into a 16 poles is almost impossible because it has limited space for addition 8 coils. Use thinner wire to achieve it result current reduction. WHY NOT USING SIMPLE GEARS COUPLING METHOD ?
- Q: Given that a car will need to run off stored power (Battery or fuel cell etc.), is it best to use the DC supply to run a DC motor, or drive a controller to run an AC motor to power the car. I'm disocunting running an AC generator as this would still need powering by an engine, which seems pointless.Which type of electric motor is most suited to powering a car and why?
- For smaller cars, with a power requirement of only a few dozen kW, it is is more efficient to use DC motors. Advantages: No DC to AC conversion with associated losses needed to run the motors. Wide rpm range. Torque can be controlled either with running the four individual wheel motors in parallel, or 2x2 series or all four in series. Another torque and power control is possible with pulse width control at a frequency of several hundred Hz. For larger vehicles such as trucks with a power requirement of 1 MW or more it would be more efficient to convert the battery DC power to variable frequency three phase power. This would have the following advantages: Lighter motors for the same power. More efficient conversion of DC to var. freq. 3-ph AC power than pulse control of large DC currents
- Q: why DC motors are always started through starters?
- Always? not in my experience. I suppose that depends on ones definition of starter if the definition includes anything that starts a motor, then the answer is obvious, if nothing starts the motor, then the motor doesn't start. Perhaps you could add some more information, like the size of the motor and it's application.
- Q: I am converting my '79 VW rabbit from ac to non-ac.Where do I find the bracket that holds the alternator low on the block.
- Check first with the auto-parts dept.at the dealership. They are fairly knowledgeable as to whether that is possible. Otherwise ask the service manager if that is possible to do. They may have a parts car out back of the dealership and you could get a used bracket there. Otherwise check out autosalvage yards for a 79 non ac car for the bracket.
- Q: g. the switch or what
- Blower motor.
- Q: What is the low power factor of AC motor in no-load operation?
- If it is an AC generator without no-load current, there will be no power factorIf AC motors were available, there could be two reasons
- Q: When I turn on the AC/heater/vent fan, it runs, but is very loud and there is very little air coming from the vents. What is the problem?
- blower motor
- Q: Is there a variable speed electric motor with enough horse power and torque that would run on 110 volts to put in a small car in place of the engine? I was thinking of using a generator to power it. This would change mpg to hours per gallon if the electric motor wasn't too expensive. It would be easy to mount to a standard transmission.
- There's a wacky photo of a car with a generator on top of the trunk powering a home air conditioner strapped to one of the windows. Must have been living in the car.
- Q: I have to do research for an engineering project and i can't even figure out what it ishelp!
- A motor that runs on alternating current as opposed to direct current. There are several types, also things like drills tend to have universal motors that will run on either.
Send your message to us
Siemens EX Series AC Motor
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords