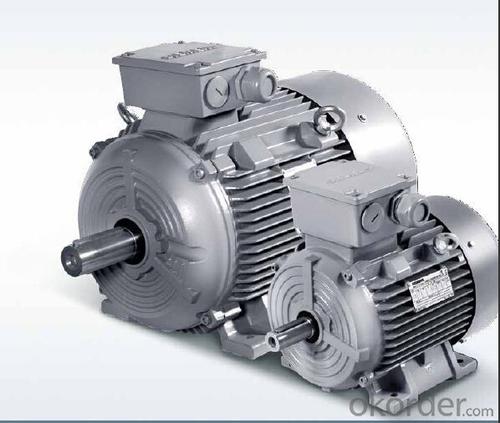
Siemens ILE0001 Series High Low Voltage AC Motor
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
| part name | brand | model | Voltage | protection | cooling | |
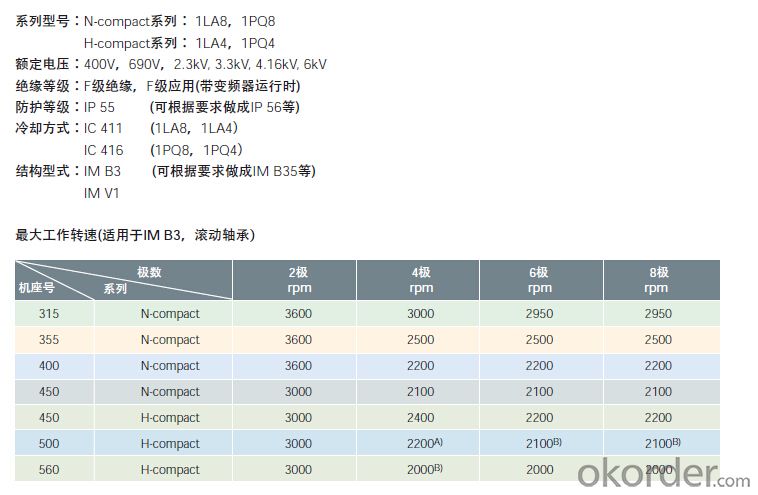
| motor | Siemens | 1LA8 | 1PQ8 | 400V,690V,2.3KV,4.16KV,6KV | IP55 | IC411 (1LA8,1LA4) |
| IC416 (1PQ8,1PQ4) | ||||||




- Q: My motor is designed for 40deg ambient temp with F class (Amb.40deg+105K Rise+10K Hot spot allowance) insulation. But my customer wants to use it at 50Deg. As per our spec. motor should be de-rated the max. power should be 93% of the rated power. Means customer has to reduce his application's OP torque about 7%. If my customer doesn't accept reduce the app. torque, can I go for H class (Amb.40deg+125K Rise+10K Hot spot allowance) insulation. Will the 20K additional temp. rise cushion compensate the increase of 10deg in Ambient? What will be the winding temp. according to the ambient temp rise about 10Deg (50Deg)C 20Deg C (60deg)? Pls help
- In theory the heat dissipation is linear, so an increase in ambient of 10C (aka 10K) will cause the winding temperature to increase by the same amount. Yes, you can use a higher insulation class throughout to allow the motor to run hotter. If you are not the motor manufacturer, ask the manufacturer what they would recommend.
- Q: I have AC motor with star/triangle that blow the fuse after 30 seconds it started
- Bluto B also has a good point. There is a centrifugal switch that is supposed to cut out the low speed starter windings on may AC motors, and if that were stuck, it could cause excess drain.
- Q: Or does it only work with a DC motor?
- A permanent magnet motor is a DC motor. You'll do a lot better with an automotive alternator. The voltage regulator, (needed), is built in and they are fitted with pulleys for speed multiplication, (also needed).
- Q: I sucked at physics in undergrad and I suck at physics even more now. Thanks.
- Looks like you need to solve for torque. 6 is a distance - your radius is 3 inches. 3 inches times 2.54 cm per inch = 7.62 cm, or 0.0762 metres. 50 kg is a mass. To convert mass to force in Newtons, multiply by the acceleration due to gravity of 9.8 m/s^2 = 490 Newtons. To get Joules (energy), multiply force by distance: 490 N * 0.0762 m = 37.338 Joules. We're missing a time value. How fast do you want the motor to turn? You might also be able to solve this by answering how far and how fast do you need to lift the mass? Divide the work in joules by the time in seconds to get the wattage of the motor. Power = work / time. Divide the power by the AC rms voltage to get the current rating.
- Q: motor control
- Electrical drives are electrical motor controls that control motor speed. For many years, most electrical drives used DC motors, but AC motor drives have now become the dominant type. The most common AC motor speed controls are variable frequency drives (VFDs) that control the speed of 3-phase induction motors. In the most common type of VFD, mains power is rectified to provide DC power. The DC power is then converted to 3-phase AC power using electronic switching circuits in an inverter configuration. The inverter controls both the frequency and the voltage supplied to the motor using pulse width modulation to control the voltage. The voltage supplied to the motor must be proportional to the frequency. To operate at half of normal speed, the motor must receive half of the mains frequency and half of the mains voltage. The motor can produce its full rated torque at reduced speed, but the power is reduced because power is proportional to torque multiplied by speed. Electrical drives are electronic power conversion devices. The electronic circuits operate at 3-phase mains voltage and carry the full motor current. Thus their power rating is the same as the motor power rating. Their efficiency is typically 95% to 98%, but that means they must dissipate 2% to 3% of the motor power as heat which can be quite a lot of heat.
- Q: How does it go from off to one direction to off to the other direction? How does the switch work?
- Usually a two direction motors are three phase motors thou it can be single phase motor but with three phase motor its easy to control. This if it works on AC currant. It also can be DC that is easer to control. 3 phases AC motor you can reverse the direction of rotation by switching two phases instead of U V W you have to make it U W V or any other combination. And it will reverse you can achieve this with a switch to give an order to a contactor to do the switching. Note that you may need a time delay to make the switching to have the motor at complete stop before reversing. Single-phase motor is very complicated process I think no one do this. A DC motor is easy you just switch the + to – and the – to + then it will reverse this can be achieved by a change over switch. Also you can use the change over switch for the 3-phase motor.
- Q: Is the permanent magnet synchronous linear motor AC motor or direct current motor?
- Permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) is usually referred to as brushless DC motor with back electromotive force, trapezoidal wave and armature current as square wave. The back electromotive force and armature current are both sine waves, which are called permanent magnet synchronous motors.
- Q: will a1/2 hp ac motor power a smalll car air conditioner compressor?
- I don't see why not as long as you have the pulleys geared correctly. You might want to incorporate a delay circuit for the clutch. Have it to where the motor reaches full speed before the clutch engages.
- Q: Haven't connected it yet.
- 90W. DC, but what supply voltage? If you were supplied a diode, that should have been connected also. If needing that, it's not an AC/DC type motor, just DC. Even if voltage OK, it would smoke on AC.
- Q: AC motors are designed to operate at +/- ____ Percent of their rated potential difference, and +/- _____ percent of their rated frequency?
- To approach the question the way it is asked would be to say few. Only synchronous A/C motors operate at a fixed speed based on the number of poles and the frequency of the power supply. A synchronous speed can be in increments of 3600 RPM or 2500 RPM depending on the frequency. Induction A/C motors will operate at the synchronous speed when there is no applied load and will begin to slow down slightly as load is applied. That slip is usually around 2- 3% when the nominal design horsepower is produced. . For example, an 1800 RPM synchronous motor will operate at 1800 RPM when fully loaded. A common induction motor will operate between 1800 and 1750 RPM. Most motors are manufactured to specific horsepower ratings at their design speeds and so cataloged. When a device needs a motor and it's design horsepower is known, the motor selected will be the next larger size. For instance a direct drive pump may be rated at 17.5 horsepower non-overloading (maximum) at 1750 RPM. There are no standard motors made to that specific horsepower so a 20 horsepower motor will be selected and will run efficiently at that partial load. Depending on the motor cooling system and the motor wiring insulation design, some will have transient service factors of 10-15% above the full load rating, but prolonged operation in an overloaded condition will shorten the motor life. In the larger sizes, motors can be custom built to closely match a non-standard horsepower within the normal speed range.
Send your message to us
Siemens ILE0001 Series High Low Voltage AC Motor
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords





















