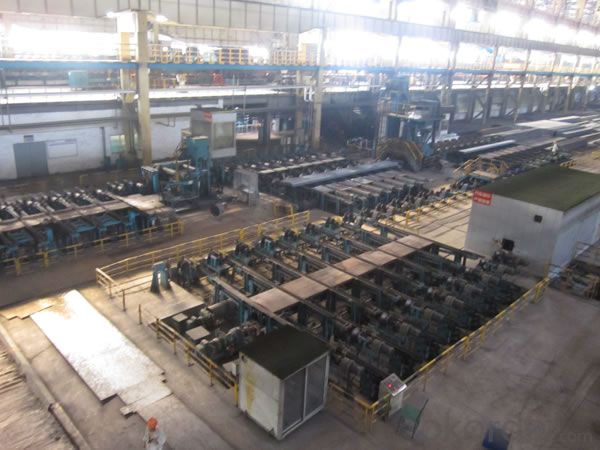
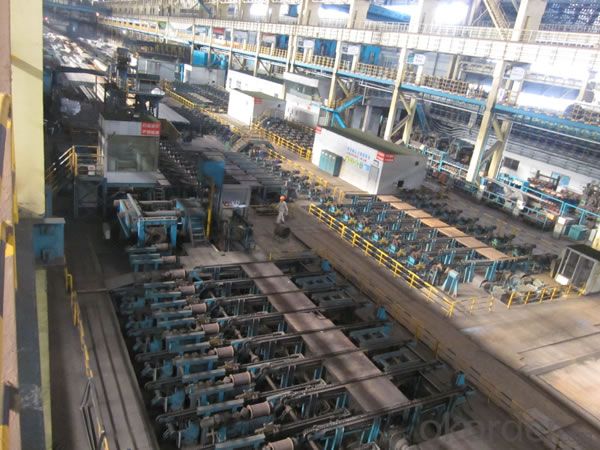
Prime square alloy steel billet 80mm Q235
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Prime square alloy steel billet 80mm Q235
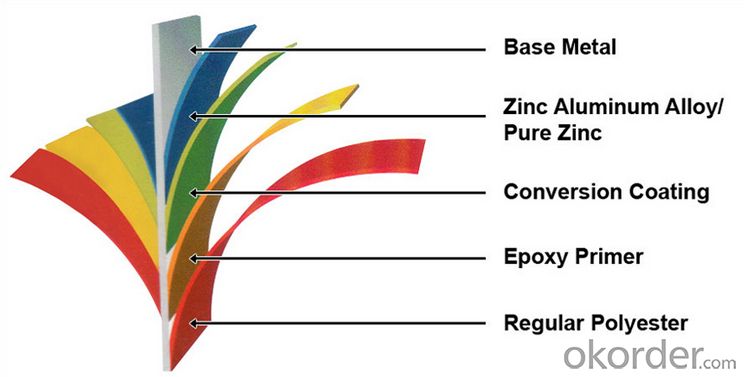
Description of Prime square alloy steel billet 80mm Q235
1. Prepainted steel coil is coated with organic layer, which provides higher anti-corrosion property and a longer lifespan than that of galvanized or galvalume steel sheets.
2. The base metals for prepainted steel coil consist of cold rolled, HDGI Steel, electro-galvanized and hot-dip alu-zinc coated steel. The finish coats of prepainted steel coil can be classified into groups as follows: polyester, silicon modified polyesters, polyvinylidene fluoride, high-durability polyester, etc.
3. The production process has evolved from one-coating-and-one-baking to double-coating-and-double-baking, and even three-coating-and-three-baking.
4. The color of the prepainted steel coil has a very wide selection, like orange, cream-colored, dark sky blue, sea blue, bright red, brick red, ivory white, porcelain blue, etc.
5. The prepainted steel coils can also be classified into groups by their surface textures, namely regular prepainted sheets, embossed sheets and printed sheets.
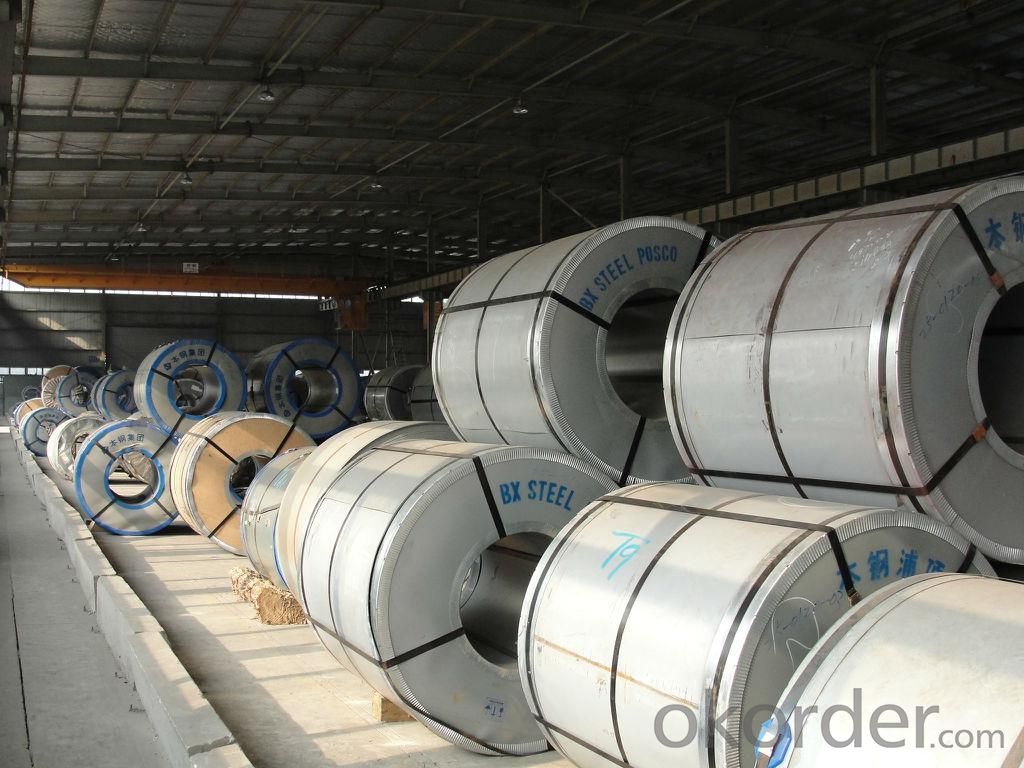

Main Feature of Prime square alloy steel billet 80mm Q235
Uncoated CR steel sheet
With the features of in line with the international highest standards in demension and shape, excellent surface finish and properties, the products are mainly used in home appliance and automobile industries.
Galvanized steel sheet(include HDG and EG)
With the features of good corrosion resistance, the products are mainly used in automobile, home appliance, electronics, building and machinery manufacture industries, etc.
Precoated steel sheet
With the features of enviromental protection and good processablility, long lasting surface durability, rich in colors, the products are maily used in building, home appliance and furniture industries, etc.
Applications of Prime square alloy steel billet 80mm Q235
A. Corrugated design makes it excellent waterproof performance
B. Materials as prepainted steel sheets, galvanized steel sheets, galvalume (Al-Zn coated sheets) are available to make corrugated sheet.
C.Those material are durable, anti-corrosion in bad weather for 20-30 years based on it's Zinc(Galvanized) coating or AZ (Galvalume) coating.
D. Different shape of the sheet make it suitable for any style of buildings.
E.Easy to install, no need special tools to fix the sheet.
F.Light weight due to high strength to weight ratio of steel. Light weight means easier handling lower shipping costs, easier installation
G. Different color is availbe base on the RAL Standard make your building more beautiful.
H. We will provide the best solutions if you don't have a exact idea of the specification you want for the steel sheet based on your weather conditions, engineering structure, construction budget and so on.
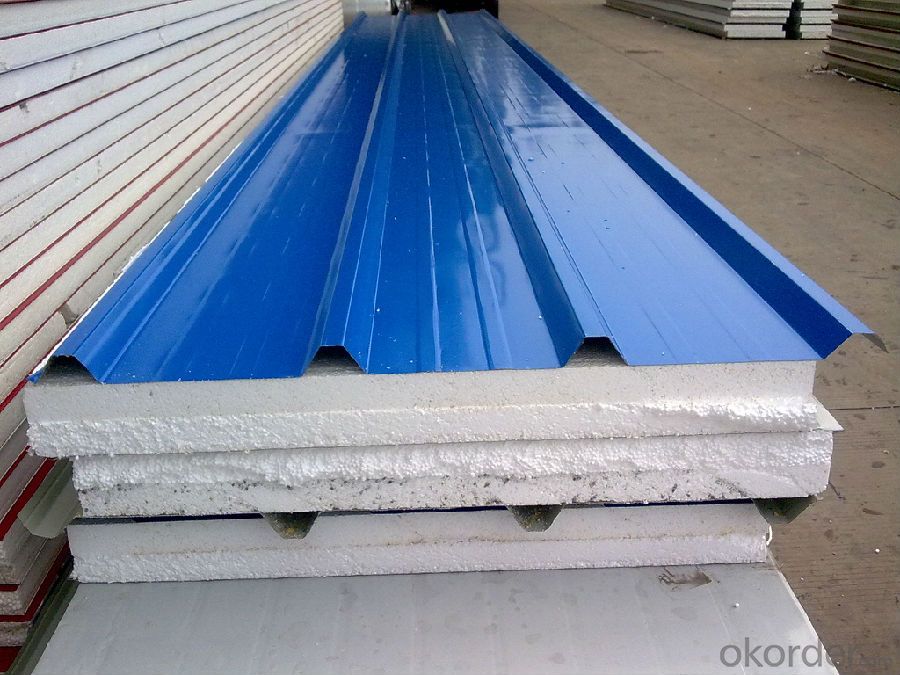

Specifications of Prime square alloy steel billet 80mm Q235
Product | Billet |
Material Grade | SGCC / SGCH / DX51D+AZ, etc |
Thickness | 0.6-3.0mm |
Width | 500-1500mm |
Tolerance | Thickness: +/-0.02mm , Width:+/-2mm |
Zinc-coating | Z30-150g/m2 |
Technique | Raw material: Hot rolled steel coil --> Cold rolled_>hot dipped galvalume |
Surface | Dried, Chromated, Unoiled |
Spangle | Regular spangle , small spangle, zero spangle |
ID | 508MM 610MM |
Coil weight | 1-25MT |
Export package | Cardboard inner sleeves, Waterproof paper, galvanized steel covered and steel strip packed |
FAQ of Prime square alloy steel billet 80mm Q235
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
we always fix steel produce in container well to make it safe arrive at destination port
we always provide best and professional forward service for our buyer
we always apply 14days free detention for our buyers container in destination
we provide one set After-sales service for our buyer
we provide China inland steel market price report
we help our buyer become number one in local market .
- Q: Are steel billets used in the manufacturing of oil and gas pipelines?
- Yes, steel billets are commonly used in the manufacturing of oil and gas pipelines. Steel billets are semi-finished products that are typically produced through a process called continuous casting, where molten steel is solidified into a rectangular shape. These billets serve as the starting material for various steel products, including pipes used in the oil and gas industry. The manufacturing process of oil and gas pipelines involves several steps, one of which is the production of seamless or welded steel pipes. Steel billets are heated and then rolled into tubes or pipes through a process called pipe making. For seamless pipes, the heated billet is pierced to form a hollow shell, which is then elongated and shaped into a pipe. Welded pipes are created by rolling and welding a flat plate of steel to form a tube. The use of steel billets in pipeline manufacturing is preferred due to the excellent mechanical properties of steel, including its strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. These properties make steel an ideal material for pipelines that need to withstand high-pressure environments and harsh conditions. Additionally, steel billets can be customized in terms of size, shape, and composition to meet the specific requirements of each pipeline project. In conclusion, steel billets play a crucial role in the manufacturing of oil and gas pipelines. They serve as the raw material that is transformed into seamless or welded pipes, which are then used to transport oil and gas across long distances. The use of steel ensures the reliability and integrity of these pipelines, making them essential components of the oil and gas industry.
- Q: What types of steel are commonly used for billets?
- There are several types of steel that are commonly used for billets, depending on the specific application and desired properties. One common type is carbon steel, which is an alloy of iron and carbon. Carbon steel billets are widely used because of their high strength, durability, and affordability. They are suitable for a variety of applications, including construction, automotive, and machinery industries. Another type of steel used for billets is alloy steel. Alloy steel billets are made by adding various alloying elements such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum to carbon steel. These alloying elements enhance the strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance of the steel, making it suitable for more demanding applications like aerospace, oil and gas, and power generation. Stainless steel is also commonly used for billets, especially in applications where corrosion resistance is critical, such as in marine environments or food processing industries. Stainless steel billets are made by adding chromium and sometimes other elements like nickel or molybdenum to carbon steel. This combination of elements provides excellent resistance to corrosion, high temperatures, and chemicals. Finally, tool steel is another type of steel used for billets, primarily in the manufacturing of tools and dies. Tool steel billets are made with specific alloying elements like tungsten, vanadium, or cobalt, which give them exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and heat resistance properties. These billets are essential for producing precision tools and components used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. In summary, the types of steel commonly used for billets include carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, and tool steel. The choice of steel depends on the specific application requirements, such as strength, corrosion resistance, or hardness.
- Q: How are steel billets cast into shape?
- Steel billets are cast into shape through a process called continuous casting. This involves pouring molten steel into a water-cooled copper mold, which allows the steel to solidify and form a continuous billet. The billet is then further shaped and molded into its desired form through rolling or forging processes.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the corrosion resistance of carbon steel billets?
- The main factors affecting the corrosion resistance of carbon steel billets are the composition of the steel, the presence of impurities or alloying elements, the surface condition and finish, the environment (including humidity, temperature, and exposure to corrosive agents), and the protective coatings or treatments applied to the billets.
- Q: How are steel billets cleaned before further processing?
- Prior to further processing, steel billets undergo a series of steps to eliminate impurities and contaminants. The initial step involves subjecting the billets to a high-pressure water jet to effectively remove loose scale and dirt from the surface. This water jetting process effectively eliminates most loose particles and prepares the surface for further cleaning. Following the initial water jetting, the billets are submerged in an acid bath. This acid bath can consist of a variety of chemicals, such as hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, or a combination of both. The purpose of the acid bath is to eliminate any remaining scale or oxide layers from the billets' surface. The acid reacts with these impurities, dissolving them and leaving behind a clean surface. Once the acid cleaning is completed, the billets undergo a thorough rinsing with water to ensure the removal of any traces of acid. This rinsing process is vital to prevent any acid residue from affecting the final product's quality. After rinsing, the billets are dried either using hot air or in a furnace to eliminate any moisture. This drying process is essential in preventing surface rusting or corrosion on the billets. Overall, the cleaning of steel billets prior to further processing is a critical step in guaranteeing the quality and integrity of the final product. It effectively eliminates impurities, scale, and oxide layers from the surface, resulting in a clean and uniform surface for subsequent processing operations.
- Q: What are the main characteristics of high-quality steel billets?
- The main characteristics of high-quality steel billets include superior chemical composition, uniform and refined microstructure, precise dimensions, and excellent surface quality. Firstly, high-quality steel billets have a superior chemical composition. This means that they are made from carefully selected raw materials and have the right balance of elements to ensure optimal strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. The chemical composition is crucial in determining the overall quality and performance of the steel billets. Secondly, high-quality steel billets have a uniform and refined microstructure. This means that the grains within the steel are evenly distributed and have been properly refined during the manufacturing process. A uniform and refined microstructure enhances the strength and toughness of the steel, making it more resistant to cracking, deformation, and other forms of mechanical stress. In addition, high-quality steel billets have precise dimensions. They are manufactured to strict tolerances, ensuring that they have the correct length, width, and thickness. Precise dimensions are important as they allow for easy and accurate machining, forging, or rolling of the billets into the desired end products. This ensures that the final products made from the billets have consistent and accurate dimensions. Lastly, high-quality steel billets have excellent surface quality. They are free from defects such as cracks, scale, or other surface imperfections. A smooth and clean surface allows for better heat transfer, improved weldability, and enhanced overall appearance of the final products. It also ensures that the billets can be easily inspected and processed without any hindrances. Overall, high-quality steel billets possess superior chemical composition, uniform and refined microstructure, precise dimensions, and excellent surface quality. These characteristics are essential in producing steel billets that meet the highest standards of strength, durability, and reliability, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of transmission towers?
- Steel billets are an essential component in the production of transmission towers. These billets, which are semi-finished steel products, serve as the raw material for the construction of these towers. To begin, the steel billets are first heated at extremely high temperatures in a furnace. This heating process, known as hot rolling, helps to soften the billets and make them more malleable, allowing them to be easily shaped and formed into the desired structure of the transmission tower. Once the billets have been heated, they are then passed through a series of rolling mills, where they are shaped into long, cylindrical sections known as steel bars. These bars are then further processed and cut to the required length and dimensions, depending on the specific design and requirements of the transmission tower. After the bars have been cut and shaped, they undergo a process called galvanization. This involves coating the steel bars with a layer of zinc, which provides corrosion resistance and protects the tower from environmental elements such as moisture and rust. Finally, the galvanized steel bars are assembled and welded together to form the intricate framework of the transmission tower. The strength and durability of the steel billets used in this process ensure that the tower can withstand the heavy loads and extreme weather conditions it is subjected to. Overall, steel billets play a crucial role in the production of transmission towers as they provide the necessary strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance required for these structures. Their ability to be shaped and formed into the desired dimensions, along with their durability, make them an ideal material for the construction of transmission towers.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the overall weight reduction of a structure?
- There are several ways in which steel billets contribute to reducing the overall weight of a structure. Firstly, through a process called continuous casting, steel billets can be precisely shaped and sized, resulting in lighter and more compact billets. This, in turn, decreases the weight of the structure. Secondly, advanced alloys and compositions can be used to make steel billets with high strength-to-weight ratios. These alloys are specifically designed to provide the same level of strength and durability as traditional steel, but with a lower weight. By incorporating these lightweight steel billets into the construction of a structure, the overall weight can be significantly reduced without sacrificing strength and performance. In addition, steel billets can be employed in the manufacturing of complex shapes and structures using techniques such as extrusion and forging. These methods allow for the creation of intricate designs and structures, eliminating the need for additional components and reducing the overall weight of the structure. Furthermore, steel billets can be used in the construction of lightweight structural elements such as beams, columns, and trusses. These elements can be designed to have hollow sections or thinner profiles, which reduces the amount of steel needed while still maintaining structural integrity. This results in a substantial decrease in the overall weight of the structure. In conclusion, steel billets contribute to weight reduction in structures by enabling the production of lighter and more compact components, utilizing advanced alloys with high strength-to-weight ratios, allowing for the creation of complex shapes and structures, and facilitating the construction of lightweight structural elements.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the overall recyclability of a structure?
- The overall recyclability of a structure is greatly enhanced by steel billets, which play a vital role. These semi-finished steel products are created by melting iron ore and other raw materials in a blast furnace. Steel billets possess various characteristics that contribute to a structure's recyclability, thanks to their composition and manufacturing process. Foremost, steel is one of the most recycled materials worldwide. Steel billets can be recycled endlessly without compromising their quality or integrity. Consequently, when a structure reaches the end of its lifespan, the steel components can be effortlessly dismantled, and the steel billets can be melted down to produce new steel products. This ability to recycle steel billets reduces the necessity for extracting and refining new iron ore, thereby conserving natural resources and minimizing the environmental impact associated with mining activities. Moreover, the recycling process of steel billets requires significantly less energy compared to producing steel from raw materials. Recycling steel billets consumes around 75% less energy than manufacturing steel from scratch. This energy efficiency not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also contributes to cost savings during the manufacturing process. By utilizing recycled steel billets in structure construction, we can mitigate the carbon footprint and promote sustainable practices within the construction industry. Additionally, the utilization of steel billets in structures provides practical advantages. Steel is renowned for its strength, durability, and resilience, making it an ideal material for constructing robust and long-lasting structures. By incorporating steel billets, structures can be designed to withstand various environmental conditions, such as earthquakes and hurricanes, guaranteeing the safety and longevity of the building. This aspect of longevity is crucial in terms of recyclability since it allows the structure to fulfill its purpose for an extended period before being recycled. In conclusion, steel billets significantly contribute to a structure's overall recyclability. Their ability to be recycled endlessly, reduced energy consumption during the recycling process, and practical advantages like strength and durability make steel billets an exceptional choice for constructing sustainable and recyclable structures. By incorporating steel billets, we can foster a circular economy, conserve natural resources, reduce emissions, and create a more sustainable future for the construction industry.
- Q: How is the quality of steel billets ensured during the manufacturing process?
- The quality of steel billets is ensured through a combination of rigorous testing and adherence to established industry standards throughout the manufacturing process. There are several key steps involved in ensuring the quality of steel billets: 1. Raw Material Inspection: The first step is to carefully inspect the raw materials, usually iron ore and/or scrap metal, to ensure they meet the required specifications. This includes checking for impurities and verifying the chemical composition. 2. Melting and Refining: The raw materials are then melted in a furnace, and any impurities are removed through refining processes such as desulphurization and degassing. This helps improve the quality of the steel by reducing unwanted elements and enhancing its overall purity. 3. Continuous Casting: Once the steel is refined, it is then cast into billet form using a continuous casting process. This process ensures a consistent size and shape of the billets, which is important for further processing. 4. Non-Destructive Testing: During and after the continuous casting process, various non-destructive testing techniques are employed to check the integrity of the billets. These include ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, and visual inspection, among others. These tests help identify any defects or imperfections that may compromise the quality of the billets. 5. Heat Treatment: Depending on the desired properties of the final steel product, the billets may undergo heat treatment processes such as annealing, quenching, or tempering. These processes further enhance the strength, hardness, and other mechanical properties of the steel. 6. Final Inspection: The finished steel billets undergo a final inspection to ensure they meet the required specifications. This includes checking their dimensions, surface quality, and mechanical properties. Samples from each batch are typically subjected to destructive testing to confirm their strength and other properties. 7. Traceability and Documentation: Throughout the manufacturing process, it is crucial to maintain proper traceability and documentation of all quality-related activities. This includes recording test results, maintaining batch records, and ensuring proper identification and labeling of the billets. By following these stringent procedures and conducting various tests, manufacturers can ensure that the quality of steel billets is maintained at every stage of the manufacturing process. This helps to guarantee that the final steel products made from these billets will meet the required standards and perform as intended in various applications.
Send your message to us
Prime square alloy steel billet 80mm Q235
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords































