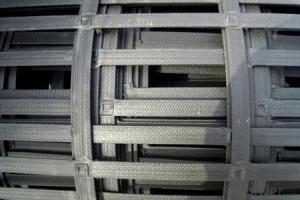
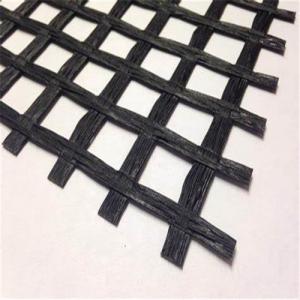
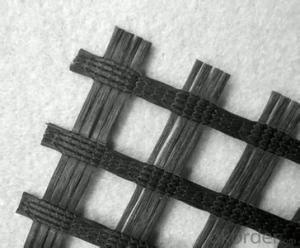
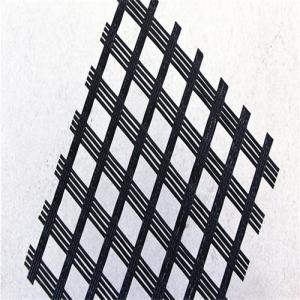
Tx160 Triaxial Geogrid
Tx160 Triaxial Geogrid Related Searches
Fridge With Freezer On Bottom Driveway Pillars With Lights Blu Ray Player With Recorder Blu Ray Player With Internet Geogrid In Retaining Walls 1708 Biaxial Fiberglass Tape Pullout Resistance Of Geogrid Geogrid Warp Knitting Machine Srw 3 Series Geogrid Biaxial Plastic GeogridHot Searches
Fiberglass Scaffolding For Sale Fiberglass Panels For Sale Fiberglass Greenhouses For Sale Geogrid Fabric For Sale Gas Powered Core Aerator For Sale Revolution 4 Propeller For Sale Alabaster Carving Stone For Sale Geogrid For Sale Near Me Tensar Geogrid For Sale Geogrid For Sale Ex Display Log Cabins For Sale Photoelectric Cells For Sale Athletic Lockers For Sale Cubicle Partitions For Sale Stearman Propeller For Sale Palram Greenhouses For Sale Gumbo Bowls For Sale Suzuki Propellers For Sale Freight Crates For Sale Outhouse Sheds For SaleTx160 Triaxial Geogrid Supplier & Manufacturer from China
Okorder.com is a professional Tx160 Triaxial Geogrid supplier & manufacturer, offers integrated one-stop services including real-time quoting and online cargo tracking. We are funded by CNBM Group, a Fortune 500 enterprise and the largest Tx160 Triaxial Geogrid firm in China.Hot Products
FAQ
- There are several factors that can affect the creep behavior of geogrids. These include the type and quality of the geogrid material, the load applied to the geogrid, the duration of the load, the temperature and moisture conditions, and the installation and construction methods used.
- Geogrids improve soil stability by providing reinforcement and confinement to the soil, helping to distribute and transfer loads more evenly. They interlock with the soil particles, increasing the shear strength and preventing soil movement and erosion. Additionally, geogrids can enhance the load-bearing capacity of the soil, allowing for more efficient construction and reducing the risk of slope failures or settlement.
- Yes, geogrids are generally resistant to biological fouling. The synthetic materials used in geogrids are not susceptible to decay or degradation caused by biological organisms such as bacteria, fungi, or algae. This resistance helps maintain the structural integrity and long-term performance of geogrids in various applications.
- Yes, geogrids can be used in ground stabilization for wastewater treatment plants. Geogrids are commonly used in civil engineering projects to reinforce soil and provide stability. In the case of wastewater treatment plants, geogrids can be used to reinforce the ground and prevent soil erosion, especially in areas with high water flow or heavy loads. They can improve the stability of the ground and ensure the longevity and effectiveness of the wastewater treatment infrastructure.
- Yes, geogrids can be used in foundation stabilization. They are commonly used in civil engineering and construction projects to reinforce soil and improve the stability of foundations. Geogrids are typically installed horizontally or vertically within the soil to distribute loads and prevent soil movement, thereby enhancing the overall stability and performance of foundations.
- Installation damage can have a significant impact on the performance of geogrids in long-term applications. Damage during installation, such as improper handling, stretching, or tearing, can reduce the structural integrity of the geogrid. This can result in decreased load-bearing capacity, reduced soil confinement, and potential failure of the geogrid system over time. It is crucial to ensure proper installation techniques and quality control measures to minimize installation damage and maintain optimal geogrid performance in long-term applications.