steel structure workshop warehouse building design, manufacture and installation
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Technical Parameters
Item Name | steel structure workshop warehouse building |
Main Material | Q235/Q345 Welded H Beam and Hot Rolled Section Steel |
Surface | Painted or Hot Dip Galvanized |
Roof & Wall Panel | EPS Sandwich panel /Single Corrugated Steel Sheet/ Colour sheet with Glass-wool, for customers choose |
Window | PVC Steel or Aluminum Alloy |
Door | Sliding Door or Rolling Up Door |
Service | Design, Fabrication and Installation |
We can make quotation according to customer's drawing or requirement; (size by length/width/height and wind speed), offering a free design drawing and all detailed drawings for installation. | |
Design software: Auto CAD,PKPM,MTS,3D3S, Tarch, Tekla Structures(Xsteel)V12.0.etc | |
Packing | According to customer's requirement |
Load into 40/20GP,40HQ or 40OT |
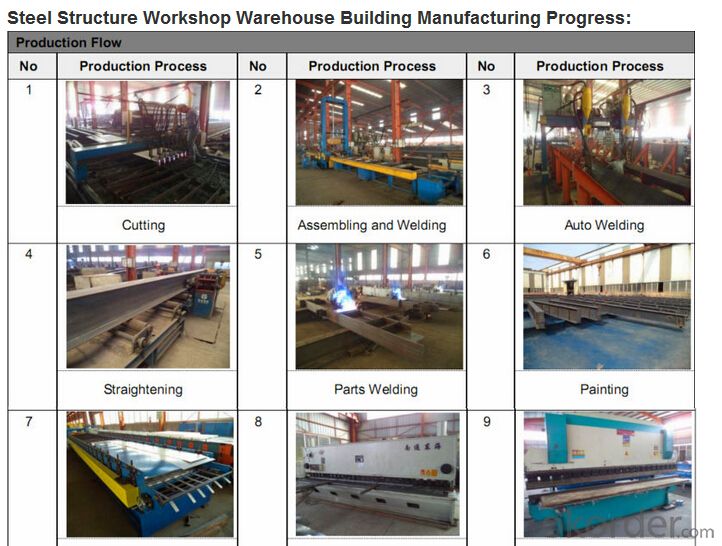


- Q:How are steel structures designed for fireproofing?
- Steel structures are designed for fireproofing through various measures. One common approach is the application of fire-resistant coatings or paints on the steel surfaces, which provide a protective layer that delays heat transfer and prevents the steel from reaching critical temperatures. Additionally, steel structures may incorporate fire-resistant materials, such as intumescent coatings or fireproof insulation, to further enhance their fire resistance. Moreover, the design of steel structures takes into consideration factors like fire compartmentalization, adequate ventilation, and the inclusion of fire-resistant barriers to limit the spread of fire and smoke. These combined strategies ensure that steel structures maintain their structural integrity and protect occupants during a fire event.
- Q:How do steel structures resist loads such as gravity, wind, and seismic forces?
- Steel structures resist loads such as gravity, wind, and seismic forces due to their inherent strength and flexibility. The strength of steel allows it to bear heavy loads, while its flexibility enables it to bend and deform under extreme forces without collapsing. Additionally, steel structures are designed with various techniques such as bracing, trusses, and moment-resisting frames to distribute and dissipate these forces, ensuring structural stability and safety.
- Q:How are steel structures used in mining and mineral processing facilities?
- Steel structures are extensively used in mining and mineral processing facilities due to their strength, durability, and versatility. These structures are used in various applications throughout mining operations, from the extraction of minerals to their processing and transportation. In mining facilities, steel structures are commonly utilized for the construction of mine shafts, tunnels, and galleries. These structures provide the necessary support and stability required for underground mining operations. Steel beams, columns, and trusses are employed to create sturdy frameworks that can withstand the immense pressure and weight of the overlying rock and soil. Steel is also widely used in the construction of processing plants and equipment in mineral processing facilities. Processing plants are responsible for the extraction, separation, and refining of valuable minerals from mined ore. Steel structures are used to house various machinery, such as crushers, mills, flotation cells, and smelters, which are crucial in the processing of minerals. These structures provide a safe and stable environment for the operation of heavy equipment and ensure the efficiency of the mineral processing operations. Additionally, steel structures are utilized in the transportation and storage of minerals within mining facilities. Conveyor systems, chutes, and hoppers made of steel are commonly used to transport and store bulk materials such as coal, iron ore, and copper concentrate. These structures are designed to withstand the abrasive nature and weight of the materials being transported, ensuring a smooth and efficient flow of minerals throughout the facility. Furthermore, steel structures are employed in the construction of infrastructure and support facilities within mining sites. Buildings such as offices, workshops, laboratories, and warehouses are often made of steel due to its cost-effectiveness, speed of construction, and adaptability. Steel provides a flexible and customizable solution, allowing for the creation of structures that meet specific requirements and can be easily modified or expanded as needed. Overall, steel structures play a vital role in mining and mineral processing facilities by providing the necessary support, durability, and functionality required for these operations. From underground mining to processing plants and infrastructure, steel is the material of choice due to its strength, versatility, and ability to withstand the harsh conditions of the mining industry.
- Q:What are the disadvantages of using steel in structures?
- Using steel in structures has several drawbacks: 1. Expensive: Steel tends to be more costly than alternative construction materials like wood or concrete. The initial expense of steel and its fabrication can be higher, making it less cost-effective for certain projects. 2. Susceptible to Corrosion: Steel is prone to corrosion when exposed to moisture or chemicals. Without proper maintenance and protective coatings, steel structures can rust and deteriorate over time, compromising their strength and durability. 3. Heavy Weight: Steel is a heavyweight material, which can present challenges during construction. It requires specialized equipment and expertise to handle and assemble steel components, making the construction process more complex and potentially more costly. 4. Negative Environmental Impact: The production of steel involves significant energy consumption and the emission of greenhouse gases. The mining and extraction of iron ore, as well as the manufacturing processes, contribute to air and water pollution, making steel production environmentally harmful. 5. Fire Vulnerability: While steel is generally fire-resistant, it can lose strength and collapse under high temperatures. In the event of a fire, additional fireproofing measures may be necessary for steel structures, adding to the overall project cost. 6. Design Limitations: Steel has inherent design limitations due to its properties. For example, steel structures typically have height and span restrictions compared to other building materials. This can restrict architectural flexibility and limit design possibilities for large-scale structures. 7. Thermal Conductivity: Steel is an efficient heat conductor, leading to quick heat transfer. This can result in thermal bridging and energy loss in buildings, necessitating additional insulation and energy-efficient measures to address this issue. Overall, while steel offers numerous advantages such as strength and versatility, it is crucial to consider these disadvantages when selecting it as a construction material for structures.
- Q:What is the role of steel guardrails in a structure?
- Steel guardrails play a vital role in ensuring the safety and protection of structures. Their main function is to establish a barrier or boundary, effectively preventing unintended falls or collisions. They find wide-ranging applications in highways, bridges, parking lots, rooftops, and balconies. A key objective of steel guardrails is to direct and redirect vehicles on roads and highways. They are strategically positioned along road edges to deter vehicles from drifting off or crossing into opposing lanes, thereby reducing the risk of accidents and safeguarding the well-being of drivers and passengers. In the event of a collision, the guardrails absorb the impact and aid in preventing the vehicle from veering off the road or crashing into oncoming traffic. Likewise, steel guardrails are indispensable for providing protection on bridges and elevated structures. They serve as a protective barrier, ensuring the safety of pedestrians and workers by preventing inadvertent falls. Rooftop and balcony guardrails also function as a safety precaution, warding off accidental falls. In addition to their protective role, steel guardrails contribute to the aesthetic appeal of a structure. They can be designed in a variety of styles and finishes to harmonize with the architectural design or blend seamlessly with the surroundings. Overall, the function of steel guardrails in a structure is to guarantee safety, protection, and guidance. Their presence helps avert accidents, shields individuals from falls or collisions, and upholds the structural integrity of buildings and infrastructure.
- Q:What are the design considerations for steel platforms?
- Some design considerations for steel platforms include the load-bearing capacity of the steel, the structural integrity, the type and thickness of the steel used, the dimensions and layout of the platform, the required safety features such as guardrails and non-slip surfaces, the accessibility for maintenance and inspections, and the overall aesthetic appeal.
- Q:How are steel structures used in elevators and escalators?
- Steel structures are used in elevators and escalators primarily for their strength and durability. The steel framework provides a rigid and robust support system for the moving parts and components of elevators and escalators. Steel is able to withstand heavy loads and maintain structural integrity, ensuring safe and reliable operation. Additionally, steel's versatility allows for the creation of complex and intricate designs, enabling the construction of efficient and space-saving elevator and escalator systems.
- Q:What is the difference between rigid connection and hinge in steel structure?. Are all high strength bolts connected just now?
- If the steel column base section reduced, ribbed or not and anchor bar closer to the section is more biased hinge. Whether the beam has been joined or not, the simpler way is to see if the flange is welded. If welding is partial to the line, if it is not welded, it will hinge on the hinge.
- Q:What are the considerations for steel structure maintenance and repair?
- There are several important considerations for steel structure maintenance and repair. Firstly, regular inspections are crucial to identify any signs of damage or deterioration. This can be done by trained professionals who are familiar with the specific requirements of steel structures. Inspections should cover all components of the structure, including connections, welds, and support systems. Any issues should be addressed promptly to prevent further damage or potential safety hazards. Secondly, proper cleaning and maintenance routines play a key role in the longevity of steel structures. Regular cleaning removes dirt, debris, and corrosion-inducing substances, such as salt or chemicals, which can compromise the integrity of the steel. Cleaning should be done using appropriate methods and products to avoid scratching or damaging the surface of the steel. Another consideration is the need for protective coatings. Steel structures are often coated with paint or specialized coatings to provide protection against corrosion. These coatings should be periodically inspected and maintained to ensure they remain intact and effective. Any areas with peeling, chipping, or other signs of coating failure should be promptly addressed to prevent corrosion from occurring. Furthermore, it is important to assess and address any structural issues that may arise. Over time, steel structures can experience fatigue, stress, or other forms of damage. These issues may require repair or reinforcement, which should be done by qualified professionals following industry standards and codes. In addition to inspections and repairs, it is crucial to monitor and control the environmental conditions surrounding the steel structure. Exposure to excessive moisture, temperature fluctuations, or corrosive chemicals can accelerate the deterioration of steel. Implementing measures such as proper drainage, ventilation, and corrosion inhibitors can help mitigate these risks. Lastly, documentation and record-keeping are essential for effective maintenance and repair of steel structures. Keeping a comprehensive record of inspection reports, maintenance activities, repairs, and any modifications made to the structure can help in tracking the history of the structure, identifying recurring issues, and planning future maintenance activities. Overall, steel structure maintenance and repair involve regular inspections, proper cleaning, protective coatings, addressing structural issues, controlling environmental conditions, and maintaining detailed records. By considering these factors, the lifespan and performance of steel structures can be significantly extended.
- Q:What are the considerations when designing steel structures for cleanrooms and laboratories?
- When designing steel structures for cleanrooms and laboratories, several considerations need to be taken into account. Firstly, the steel used should have a high resistance to corrosion, as these environments often involve exposure to chemicals or cleaning agents. Additionally, the design should incorporate proper ventilation systems to maintain air quality and control the flow of contaminants. The structure should also be designed to be easily cleanable, ensuring that surfaces are smooth and free from crevices where dirt or bacteria can accumulate. Furthermore, attention should be given to the layout and positioning of equipment and utilities to ensure efficient and safe operations within the space. Lastly, the design should comply with industry standards and regulations related to cleanroom and laboratory environments to ensure the overall safety and functionality of the facility.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
steel structure workshop warehouse building design, manufacture and installation
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords

























