Ms Heavy Steel Rail 50Mn, U71Mn
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao Port,China
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25MT m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000000MT/YEAR m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specificaions of Ms Heavy Steel Rail 50Mn, U71Mn
Production Standard: GB2585-81
Material: 50Mn, U71Mn
Grade | Element(%) | ||||
C
| Mn | S
| P
| Si
| |
50Mn |
0.48—0.56 |
0.70—1.00 |
≤0.035 |
≤0.035
|
0.17-0.37 |
U71Mn | 0.65—0.76 | 1.10—1.40 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.030 | 0.15-0.35 |
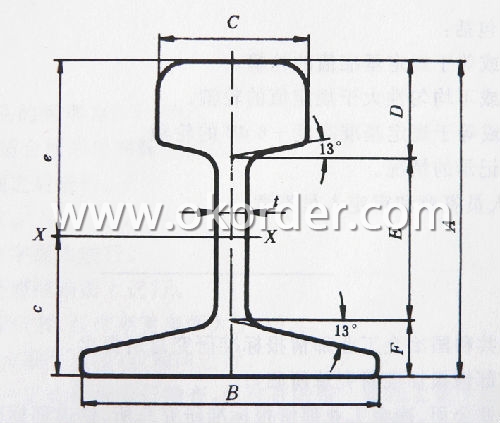
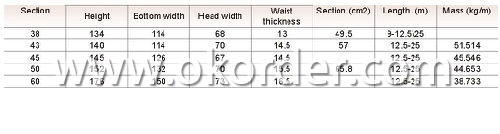
Sizes: 38kg, 43kg, 45kg, 50kg, 60kg
Length: 10m, 12m, 12.5m or as the requriement of the clients
Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
Payment terms: 30% advance payment by T/T, 70% payment against the copy of the B/L; 100% L/C at sight, etc.
Usage & Applications of Ms Heavy Steel Rail 50Mn, U71Mn
Heavy Steel Rail is suitable for the laying of main trunk line of the curves and the orbit of the tunnel, can also be used for tower crane and other crane track.
For example: railway, subway, transportation track, express, curve way, tunnel way.

Packaging & Delivery of Ms Heavy Steel Rai 50Mn, U71Mn
1. Packing: it is nude packed in bundles by steel wire rod
2. Bundle weight: not more than 3.5MT for bulk vessel; less than 3 MT for container load

3. Marks:
Color marking: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: there will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.
4. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
5. Delivered by container or bulk vessel

6. Delivery Time: All the Ms Heavy Steel Rail will be transpoted at the port of Tianjin, China within 30 days after receiving the advance payment by T/T or the orginal L/C at sight.
Production flow of Ms Heavy Steel Rail 50Mn, U71Mn
Material prepare (billet) —heat up—rough rolling—precision rolling—cooling—packing—storage and transportation
Inspection of Ms Heavy Steel Rail 50Mn, U71Mn
We will send the MTC of the factory to the clients dirrectly which contain the anlisis of the heat, chemiqul composition, phisical characteristicas, etc.
And our inspectors will arrive at the factory to meke the inspection of the size, length, weight and quantity before the transportation from the factory.


- Q:Can steel rails be used in shared rail corridors with other transportation modes?
- Yes, steel rails can be used in shared rail corridors with other transportation modes. Steel rails are commonly used in railways due to their durability and ability to withstand heavy loads. In shared rail corridors, steel rails can be integrated with other transportation modes such as light rail, trams, or freight trains, allowing for efficient and safe transportation of both passengers and goods.
- Q:Are steel rails prone to rail bending?
- Yes, steel rails are prone to rail bending, especially under heavy loads or extreme weather conditions.
- Q:What are the pros and cons of using steel rails in railway construction?
- Advantages of utilizing steel rails in railway construction encompass: 1. Endurance: Steel rails possess a remarkable level of endurance, enabling them to endure heavy loads and harsh weather conditions. This renders them highly suitable for long-term implementation in railway construction projects. 2. Robustness: Steel rails boast an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio that offers the necessary support and stability for trains to operate at high speeds. 3. Seamless ride: Steel rails provide a smooth and consistent surface for trains to travel on, minimizing vibrations and ensuring a comfortable journey for passengers. 4. Minimal upkeep: In comparison to other rail materials, steel rails demand relatively low maintenance. They have a longer lifespan and are less susceptible to wear and tear, reducing the need for frequent replacements or repairs. 5. Versatility: Steel rails can be effortlessly adapted and modified to suit different track configurations, making them suitable for a wide range of railway designs and layouts. Disadvantages of employing steel rails in railway construction include: 1. Cost: The manufacturing and installation of steel rails can be more expensive compared to other rail materials like concrete or wood. This can contribute to higher overall construction costs for railway projects. 2. Corrosion: Steel is prone to corrosion, especially in humid or coastal environments. Regular maintenance and protective coatings are necessary to prevent rust formation and ensure the longevity of steel rails. 3. Noise pollution: Steel rails can generate noise when trains traverse them, particularly at higher speeds. This can be a concern for nearby residents and necessitates additional noise reduction measures, such as the installation of sound barriers or the use of noise-dampening track components. 4. Weight restrictions: While steel rails are strong, there are limitations regarding weight. Extremely heavy or concentrated loads can cause deformation or damage to the rails, requiring careful planning and monitoring of freight transportation. 5. Environmental impact: Steel production has significant environmental implications, including greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. The utilization of steel rails contributes to these impacts, although efforts are underway to develop more sustainable and eco-friendly production processes.
- Q:How do steel rails handle expansion and contraction?
- Steel rails handle expansion and contraction through a combination of thermal expansion joints, proper maintenance, and careful design. These rails are designed with gaps or spaces between them to allow for thermal expansion during hot weather and contraction during cold weather. Additionally, regular maintenance and inspection are carried out to ensure that the rails remain aligned and securely fastened, minimizing the effects of expansion and contraction.
- Q:What are the different rail profiles used in steel rail manufacturing?
- Steel rail manufacturing commonly utilizes several different rail profiles that are designed to meet specific requirements and demands of various types of railway tracks. 1. The most prevalent rail profile used worldwide is the flat-bottomed rail (FB). It boasts a flat base and two symmetrical inclined sides, providing stability and suitability for high-speed trains and heavy freight traffic. 2. In the past, the bullhead rail profile was widely employed and still exists in some older railway systems. Resembling the shape of a bull's head, it possesses a rounded top surface and a flat base. Nowadays, bullhead rail is primarily utilized in heritage railways or preserved lines. 3. The double-headed rail profile allows for the rail to be flipped and used on both sides due to its two symmetrical heads. It is commonly employed when trains travel in both directions on a single track, eliminating the necessity for separate left and right-hand rails. 4. The vignoles rail, also referred to as T-section rail, is characterized by its flat base and two sloping sides meeting at the top. Owing to its strength and ability to withstand heavy loads, vignoles rail is extensively used in modern railway systems. 5. The grooved rail profile features a groove or channel along its top surface. It is commonly utilized in tram or light rail systems, as the groove accommodates the flanges on the wheels, aiding in keeping the trains on track. Each rail profile possesses unique advantages and is selected based on factors such as the type of railway system, train speed, load capacity, and the specific requirements of the track. Manufacturers carefully evaluate these factors to determine the most suitable rail profile for each application.
- Q:What is the impact of heavy axle loads on steel rail performance?
- Heavy axle loads can have a significant impact on steel rail performance. The continuous application of heavy loads over time can lead to increased wear and fatigue on the rail, resulting in accelerated degradation and reduced lifespan. This can result in higher maintenance costs, more frequent repairs, and potentially increased risk of rail failure. Additionally, heavy axle loads can also cause increased stress on the rail infrastructure, leading to potential issues such as rail buckling or track misalignment. Therefore, it is crucial to carefully manage and monitor axle loads to ensure the long-term performance and safety of steel rails.
- Q:What is the process of electrifying steel rails?
- The process of electrifying steel rails involves the installation and implementation of an overhead electric power supply system, commonly known as an overhead catenary system. This system consists of a series of wires, known as catenary wires, that are suspended above the tracks and connected to a power source. To begin the process, the existing infrastructure needs to be assessed to determine its suitability for electrification. This includes evaluating the condition of the rails, bridges, tunnels, and other structures along the rail line. If necessary, upgrades or modifications may be required to ensure safety and compatibility with the electric system. Once the infrastructure is deemed suitable, the next step is to install the overhead catenary system. This involves erecting support structures, such as poles or gantries, along the trackside to hold the catenary wires in place. These structures are strategically placed to ensure the wires are properly tensioned and positioned above the tracks. After the support structures are in place, the catenary wires are installed. These wires carry the electric current that powers the trains. The wires are typically made of a combination of copper and aluminum to provide both durability and conductivity. They are strung along the support structures, ensuring proper spacing and alignment to allow for the safe movement of trains underneath. Once the catenary wires are installed, they are connected to a power source. The power can be supplied from various sources, such as an electrical grid or dedicated power stations. Transformers and substations may be required to convert and distribute the power to the catenary wires. With the power source connected, the electrification system is tested to ensure it functions correctly and safely. This includes conducting tests on the catenary wires, power distribution, and train operation. Any issues or deficiencies are addressed and resolved before the system is fully operational. Once all necessary tests and inspections are completed, the steel rails are considered electrified and ready for use. Trains can now draw power from the catenary wires, providing a more efficient and environmentally friendly mode of transportation. Regular inspections and maintenance are conducted to ensure the continued safe and efficient operation of the electrified rail system.
- Q:What are the different rail profiles used in railways?
- There are several different rail profiles used in railways, including the flat-bottomed rail, the bullhead rail, and the vignole rail. Each profile has its own unique design and characteristics, which affect factors such as stability, durability, and track maintenance requirements.
- Q:Are steel rails affected by heavy loads or overloading?
- Yes, steel rails can be affected by heavy loads or overloading. Excessive weight or overloading can cause the rails to deform, bend, or even crack, leading to potential safety hazards and increased maintenance requirements. It is essential to adhere to the recommended load limits and ensure proper maintenance to prevent any long-term damage to the steel rails.
- Q:What are the advantages of continuous welded steel rails?
- Continuous welded steel rails have several advantages. Firstly, they provide a smoother and more comfortable ride for trains, reducing vibrations and noise. This improves passenger comfort and overall safety. Secondly, the continuous welding eliminates the need for track joints, which reduces maintenance requirements and enhances the overall durability of the rail system. Additionally, the absence of joints decreases the risk of derailments and increases the speed at which trains can safely travel. Lastly, continuous welded steel rails offer better electrical conductivity, ensuring efficient power transmission for electric trains and reducing the risk of power loss. Overall, these advantages make continuous welded steel rails a preferred choice for modern rail systems.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | Shandong, China |
| Year Established | 1993 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 20 Million |
| Main Markets | Exported to Thailand, India, Brazil, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Japan, Vietnam and many other countries and regions |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Qingdao; Rizhao |
| Export Percentage | 41% - 50% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 21-30 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 10,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | 2 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | Average |
Send your message to us
Ms Heavy Steel Rail 50Mn, U71Mn
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao Port,China
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25MT m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000000MT/YEAR m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords




























