Hot Rolled Heavy Steel Rails for Rails of Tren GB38KG, GB43KG
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
OKorder is offering Hot Rolled Heavy Steel Rails for Rails of Tren GB38KG, GB43KG at great prices with worldwide shipping. Our supplier is a world-class manufacturer of steel, with our products utilized the world over. OKorder annually supplies products to European, North American and Asian markets. We provide quotations within 24 hours of receiving an inquiry and guarantee competitive prices.
Product Applications:
Hot Rolled Heavy Steel Rails for Rails of Tren GB38KG, GB43KG is suitable for the laying of main trunk line of the curves and the orbit of the tunnel, can also be used for tower crane and other crane track. For example: railway, subway, transportation track, express, curve way, tunnel way.
Product Advantages:
OKorder's Hot Rolled Heavy Steel Rails for Rails of Tren GB38KG, GB43KG are durable, strong, and resist corrosion. And they are made of high quality of steel billets.
Main Product Features:
· Premium quality
· Prompt delivery & seaworthy packing (30 days after receiving deposit)
· Corrosion resistance
· Can be recycled and reused
· Mill test certification
· Professional Service
· Competitive pricing
Specificaions of Hot Rolled Heavy Steel Rails for Rails of Tren GB38KG, GB43KG
Production Standard: GB2585-81
Material: 50Mn, U71Mn
Grade | Element(%) | ||||
C
| Mn | S
| P
| Si
| |
50Mn |
0.48—0.56 |
0.70—1.00 |
≤0.035 |
≤0.035
|
0.17-0.37 |
U71Mn | 0.65—0.76 | 1.10—1.40 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.030 | 0.15-0.35 |
Sizes: 38kg, 43kg, 45kg, 50kg, 60kg
Length: 10m, 12m, 12.5m or as the requriement of the clients
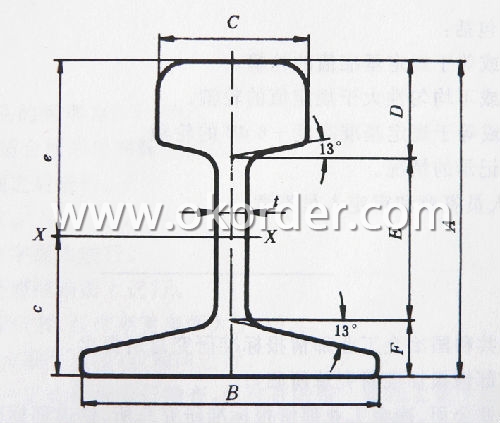
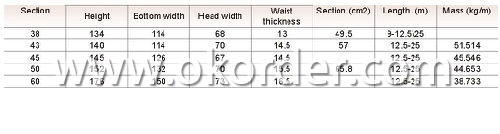
Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
Payment terms: 30% advance payment by T/T, 70% payment against the copy of the B/L; 100% L/C at sight, etc.

Packaging & Delivery of Hot Rolled Heavy Steel Rails for Rails of Tren GB38KG, GB43KG
1. Packing: it is nude packed in bundles by steel wire rod
2. Bundle weight: not more than 3.5MT for bulk vessel; less than 3 MT for container load

3. Marks:
Color marking: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: there will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.
4. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
5. Delivered by container or bulk vessel

6. Delivery Time: All the Ms Heavy Steel Rail will be transpoted at the port of Tianjin, China within 30 days after receiving the advance payment by T/T or the orginal L/C at sight.
Production flow of Hot Rolled Heavy Steel Rails for Rails of Tren GB38KG, GB43KG
Material prepare (billet) —heat up—rough rolling—precision rolling—cooling—packing—storage and transportation
Inspection of Hot Rolled Heavy Steel Rails for Rails of Tren GB38KG, GB43KG
We will send the MTC of the factory to the clients dirrectly which contain the anlisis of the heat, chemiqul composition, phisical characteristicas, etc.
And our inspectors will arrive at the factory to meke the inspection of the size, length, weight and quantity before the transportation from the factory.


FAQ:
Q1: How do we guarantee the quality of Hot Rolled Heavy Steel Rails for Rails of Tren GB38KG, GB43KG?
A1: We have established an advanced quality management system which conducts strict quality tests at every step, from raw materials to the final product. At the same time, we provide extensive follow-up service assurances as required.
Q2: What is the normal tolerance of Hot Rolled Heavy Steel Rails for Rails of Tren GB38KG, GB43KG?
A2: Normally 3%-5%, but we can also produce the goods according to the customers' requests.
Q3: The products are invoicing on theoritical weight or on actual weight?
A3: We can do it in both manners, according to the customers' request.
- Q:How are steel rails designed to handle thermal expansion?
- Steel rails are equipped with a combination of factors to handle thermal expansion. Firstly, the material chosen for steel rails is carefully selected to have a low coefficient of thermal expansion. This selection ensures that the steel is less likely to expand or contract with temperature changes. By opting for a material with a low coefficient of thermal expansion, the rail becomes more resilient to the stresses caused by thermal fluctuations. In addition to material selection, rail design also plays a vital role in managing thermal expansion. Typically, small gaps known as expansion joints are incorporated between the rails. These gaps allow the rail to freely expand and contract without causing excessive stress or buckling. The length of these expansion joints is precisely calculated to provide sufficient space for expansion while also maintaining the rail system's integrity and stability. Furthermore, the rail fastening system is designed to accommodate thermal expansion. The fasteners that secure the rail in place are often designed to allow slight movement, enabling the rail to expand and contract without causing any damage. This flexibility in the fastening system helps minimize the stresses or strains on the rail caused by thermal expansion. Overall, the design of steel rails takes into consideration the potential for thermal expansion. It incorporates features such as material selection, expansion joints, and flexible fastening systems to ensure that the rail can handle temperature-induced changes without compromising its structural integrity.
- Q:Can steel rails withstand extreme temperatures?
- Yes, steel rails can withstand extreme temperatures. Steel is known for its exceptional strength and durability, making it suitable for various applications, including railway tracks. Steel rails are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, both high and low. Steel has a high melting point, which means it can resist high temperatures without deforming or melting. Additionally, steel has excellent thermal conductivity, allowing it to quickly dissipate heat and prevent excessive expansion or contraction. This property helps steel rails maintain their structural integrity even in extreme temperature conditions. Furthermore, steel is also resistant to cold temperatures, preventing it from becoming brittle or prone to cracking in freezing conditions. Overall, steel rails are specifically engineered to withstand extreme temperatures and provide a reliable and safe transportation system.
- Q:How are steel rails manufactured?
- Steel rails are manufactured through a process called steelmaking, which involves melting iron ore and adding various alloys to create the desired steel composition. This molten steel is then poured into molds to form the rail shape and cooled to solidify. The rails are then cut to the required length, heat-treated for strength, and undergo various finishing processes such as straightening, grinding, and surface treatment before being ready for installation.
- Q:Are steel rails used in heritage or tourist railways?
- Yes, steel rails are commonly used in heritage or tourist railways. Steel rails are preferred due to their durability, strength, and ability to withstand heavy train traffic, making them suitable for preserving historical railways or providing scenic rides for tourists.
- Q:What are the different methods of fastening steel rails to sleepers?
- There are several methods of fastening steel rails to sleepers, including clip and bolt fastening systems, elastic fastening systems, and direct fixation systems. Clip and bolt fastening systems involve using specially designed clips that attach the rail to the sleeper with bolts. Elastic fastening systems utilize rubber pads or pads with steel springs to provide flexibility and reduce vibrations. Direct fixation systems eliminate the need for separate fastening components by directly attaching the rail to the sleeper using various methods such as welding or adhesive bonding.
- Q:How are steel rails protected against soil erosion?
- Steel rails are protected against soil erosion through various measures. One commonly used method is the installation of ballast, which is a layer of crushed stones or gravel placed below and around the rails. The ballast acts as a drainage system, allowing water to flow freely through it and preventing the accumulation of water around the rails. This helps to minimize the risk of soil erosion caused by water runoff. Additionally, retaining walls and embankments are often constructed along railway tracks to prevent soil erosion. These structures provide stability to the surrounding soil, preventing it from being washed away by rainwater or other external forces. Retaining walls can be made of concrete, stone, or other materials that are resistant to erosion. Another technique used to protect steel rails against soil erosion is the implementation of erosion control measures such as slope stabilization and vegetation cover. Slope stabilization involves the use of erosion control blankets or geotextiles, which are placed on the slopes adjacent to the railway tracks to prevent soil displacement. Vegetation cover, on the other hand, involves planting grass or other types of vegetation along the railway corridor. The roots of these plants help bind the soil, reducing the risk of erosion. Regular maintenance and inspections are also essential to prevent soil erosion. Rail operators often conduct routine inspections to identify any signs of erosion or instability along the tracks. If any issues are detected, appropriate measures are taken to address them promptly, such as repairing or reinforcing the affected areas. Overall, a combination of ballast, retaining walls, erosion control measures, and regular maintenance helps to ensure that steel rails are adequately protected against soil erosion. These measures contribute to the longevity and safety of railway infrastructure.
- Q:What are the safety measures taken for pedestrians near steel rail tracks?
- Safety measures taken for pedestrians near steel rail tracks include the following: 1. Pedestrian crossings: Pedestrian crossings are marked and designated at appropriate locations near rail tracks. These crossings are often equipped with warning signs, road markings, and sometimes, pedestrian signals to ensure that pedestrians can safely cross the tracks. 2. Railway gates/barriers: At certain high-risk areas, railway gates or barriers are installed to prevent pedestrians from accessing the tracks when trains are approaching. These gates are usually automated and are triggered by the presence of an approaching train. 3. Warning signs and signals: Various warning signs and signals are placed near rail tracks to alert pedestrians of the potential danger. These signs may include messages such as "Railroad Crossing" or "Look Both Ways Before Crossing" to encourage pedestrians to be cautious. 4. Safety education and awareness campaigns: Local transportation authorities often conduct safety education campaigns to raise awareness among pedestrians about the risks associated with rail tracks. These campaigns provide information on safe crossing techniques, the importance of paying attention to warning signs, and the consequences of trespassing on railway property. 5. Fencing and barriers: Fencing and barriers are installed along the railway tracks to prevent pedestrians from accessing the tracks at unauthorized locations. These physical barriers help to deter pedestrians from walking on or near the tracks, reducing the risk of accidents. 6. Speed restrictions: Speed restrictions are enforced on trains passing through areas with high pedestrian activity. This helps to minimize the chances of accidents, as slower-moving trains are more likely to stop in time in case of an emergency or an unexpected pedestrian presence. 7. Regular maintenance and inspection: Railway authorities regularly inspect and maintain the rail tracks to ensure that they are in good condition and free from any hazards that could pose a risk to pedestrians. This includes checking for loose or damaged rails, repairing any defects, and removing any debris near the tracks. Overall, safety measures for pedestrians near steel rail tracks aim to prevent accidents and promote the safe movement of pedestrians in close proximity to rail infrastructure. By implementing these measures, the risk of pedestrian accidents and injuries can be significantly reduced.
- Q:How are steel rails protected against track settlement?
- Various methods are employed to protect steel rails against track settlement. One commonly used approach involves the implementation of ballast, which consists of crushed stones or gravel that is placed beneath and around the rails. By offering stability and evenly distributing the weight of the trains, ballast prevents excessive settlement. To further safeguard against settlement, the rails themselves are designed to be sturdy and long-lasting, with appropriate spacing and alignment. This design ensures that the weight of the trains is evenly distributed along the entire length of the rails, thus minimizing the chances of settlement. Regular inspections and maintenance are also conducted to identify any signs of settlement or deformation. In certain instances, engineers may employ additional techniques such as under-sleeper pads or resilient fasteners to enhance protection against settlement. Under-sleeper pads are made of rubber or polyurethane and are placed between the rail and the sleeper. These pads help absorb vibrations and reduce the impact of settlement. On the other hand, resilient fasteners are specifically designed to allow some movement of the rail, compensating for settlement and reducing stress on the track structure. Overall, a combination of proper design, regular maintenance, and the use of ballast, under-sleeper pads, and resilient fasteners effectively safeguard steel rails against track settlement. These measures are crucial for maintaining the safety and stability of the tracks, reducing the risk of derailments, and ensuring smooth and efficient rail operations.
- Q:Are steel rails recyclable?
- Yes, steel rails are recyclable. Steel is a highly recyclable material, and steel rails can be melted down and reused to produce new steel products. Recycling steel rails not only helps conserve natural resources but also reduces the environmental impact associated with the production of new steel.
- Q:How do steel rails handle the effects of heavy impacts (e.g., derailments, collisions)?
- Steel rails are designed to handle heavy impacts such as derailments and collisions quite effectively. The high strength and durability of steel allow the rails to withstand immense forces without breaking or bending. Additionally, the continuous welded design of the rails ensures that they remain securely connected, minimizing the risk of separation during impacts. Moreover, steel rails are regularly inspected and maintained to identify any potential weaknesses or defects, ensuring their ability to handle heavy impacts and maintain the safety and integrity of the railway system.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Heavy Steel Rails for Rails of Tren GB38KG, GB43KG
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords





























