Polystyrene Roof Panels
Polystyrene Roof Panels Related Searches
Modular Roof Panels Roof Polycarbonate Clear Flat Polycarbonate Roof Panels Recycled Polystyrene Pellets Curtain Panels Styrofoam Building Panels Conservatory Plastic Roof Panels Polycarbonate Sheet Roofing Exterior Polystyrene Insulation Curved Polycarbonate Panels Pp Roofing Sheets Solid Polycarbonate Roofing Structural Insulated Panels Polycarbonate Corrugated Roofing Frp Ceiling Panels Sequentia Corrugated Roof Panels Polyurethane Panels Australia Roof Insulation Materials Lightweight Structural Panels Pvc Decorative Wall and Ceiling Panels Corrugated Polycarbonate Roofing Stone Roof Tiles Architectural Exterior Wall Panels Fabricated Wall Panels Large Plastic Panels Urethane Insulation Panels Cieling Panels Aluminum Wall Panels Uv Coated Polycarbonate Panels Decorative Metal Ceiling PanelsPolystyrene Roof Panels Supplier & Manufacturer from China
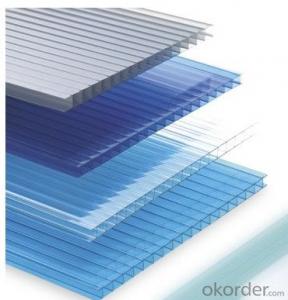
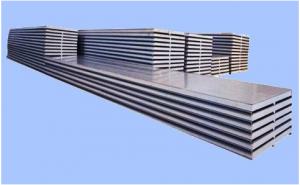
Polystyrene Roof Panels are a type of insulation material that is widely used in construction for their energy efficiency and lightweight properties. These panels are made from expanded polystyrene, a closed-cell foam that provides excellent thermal insulation, making them ideal for both residential and commercial buildings. They are known for their ability to reduce energy consumption by preventing heat loss during the winter and heat gain during the summer, thus contributing to a more comfortable and sustainable living environment.Polystyrene Roof Panels are utilized in various applications, including roofing, wall insulation, and flooring. They are particularly useful in areas with extreme temperature fluctuations, as they help maintain a stable indoor climate by reducing the need for heating and cooling systems. Additionally, these panels are appreciated for their moisture resistance, which prevents mold growth and ensures a healthier living space. They are also easy to install, making them a popular choice for DIY enthusiasts and professional contractors alike.
Okorder.com is a leading wholesale supplier of Polystyrene Roof Panels, offering a vast inventory of high-quality products at competitive prices. With a commitment to customer satisfaction, Okorder.com ensures that each order is delivered promptly and that customers receive the support they need to complete their projects successfully. Whether you are a builder looking for a reliable insulation solution or a homeowner aiming to improve your home's energy efficiency, Okorder.com is your go-to source for Polystyrene Roof Panels.
Hot Products