Geogrid Gravel Driveway
Geogrid Gravel Driveway Related Searches
Geogrid For Gravel Driveway Geogrid Driveway Geogrid Grass Driveway Driveway Geogrid Gravel Geogrid Geogrid Gravel Geogrid For Driveway Geogrid Fabric Driveway Geogrid For Gravel Roads Geogrid Driveway Installation Geogrid For Driveways Geogrid Walkway Geogrid For Gravel Geogrid Driveway Cost Geogrid Road Grass Geogrid Geogrid Pavement Geogrid Parking Geogrid Grass Geogrid Paving Geogrid Grass Pavers Geogrid Road Base Asphalt Geogrid Geogrid For Roads Geogrid Road Construction Geogrid Parking Lot Geogrid For Road Construction Road Base Geogrid Geogrid Slope Geogrid LayerGeogrid Gravel Driveway Supplier & Manufacturer from China
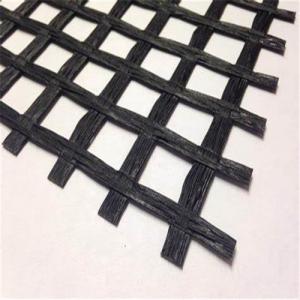
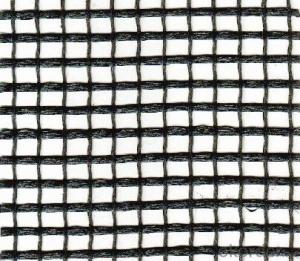
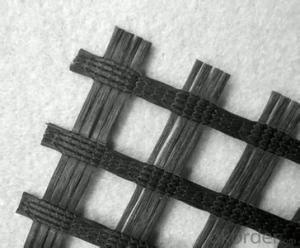
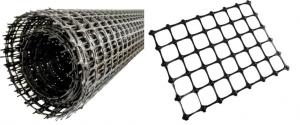
Geogrid Gravel Driveway is a type of reinforced ground system that utilizes geogrids and gravel to create a strong and stable surface for various applications. This innovative product combines the strength of geogrids with the affordability and ease of installation of gravel, making it an ideal solution for a wide range of projects. From residential driveways to commercial parking lots, Geogrid Gravel Driveway offers a cost-effective and durable option for ground reinforcement.The Geogrid Gravel Driveway system is particularly useful in areas where soil stability is a concern, as it helps to distribute the load evenly across the surface, preventing ruts and sinkholes from forming. This product is also highly adaptable, making it suitable for a variety of terrains and climates. Whether it's a simple driveway or a complex construction project, Geogrid Gravel Driveway can provide the necessary support and stability needed for a successful outcome.
Okorder.com is a leading wholesale supplier of Geogrid Gravel Driveway products, offering a vast inventory to meet the needs of contractors, builders, and homeowners alike. With a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, Okorder.com ensures that each order is delivered promptly and in excellent condition. By partnering with Okorder.com, customers can take advantage of competitive pricing and reliable service, making the process of purchasing and installing Geogrid Gravel Driveway a seamless experience.
Hot Products