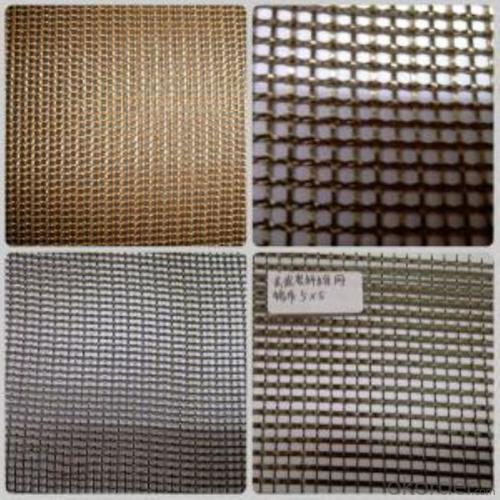
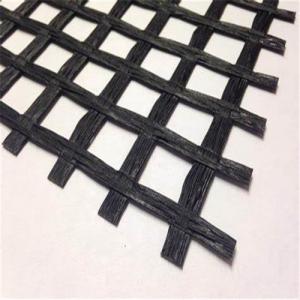
Geogrid from Basalt Fiber for Road and Buildings
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 8000 m³
- Supply Capability:
- 1000000 m³/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
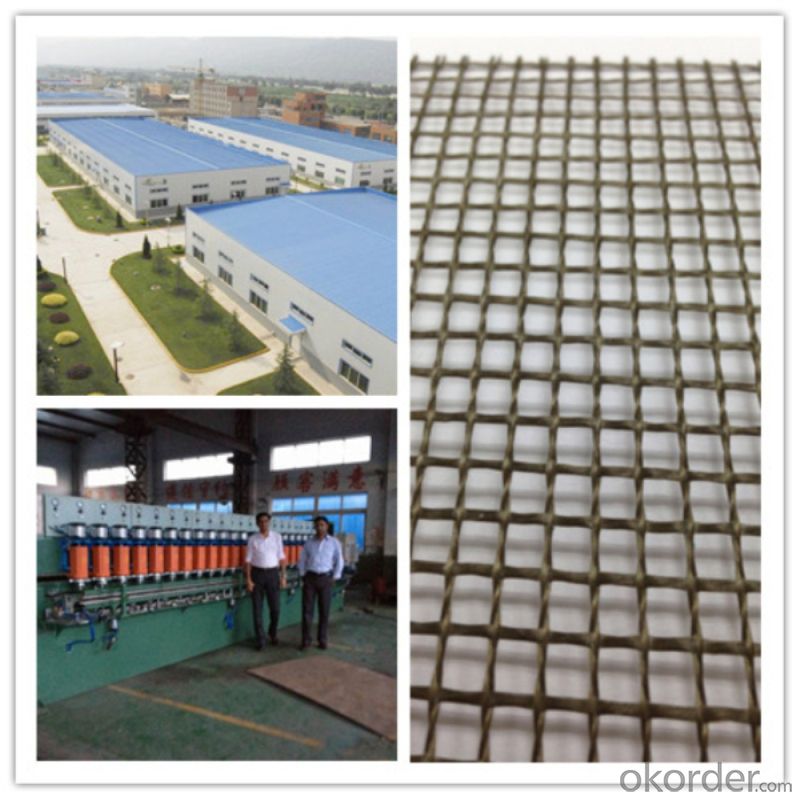
Basalt Fiber Geogrid Introduction
Continuous basalt fiber geogrid is made by impregnating woven basalt fiber scrim with asphalt and then drying to be made.
In the normal temperature, the ratio of the elastic modulus between the basalt fiber concrete and the asphalt concrete is 24: 1.
Advantages of Basalt Fiber Geogrid
Basalt fibre concrete has the excellent resistance to deformation, the elongation at break is about 3.1%. Basalt Fiber owns the high-temperature resistance, frost resisting resistance (-260~650 ℃), the same thermal expansion coefficient with the asphalt concrete, the high tensile strength, ultraviolet resistance, the stable chemical resistance, ageing resistance. The stirring temperature of the asphalt concrete is up to 190℃. The high-temperature Basalt fiber is the best alternative of the polyester fiber. It can satisfy the asphalt stirring temperature (190 ℃), and it is the excellent construction material for reinforced cement & concrete, and it has the outstanding penetration resistance.
Basalt geogrid/geotextile is more durable than metallic and glass-fiber reinforcement due to basalt fiber’s excellent performance.
Specifications of Basalt Fiber Geogrid
Item No. | Weight (g/m2) | Size (mm) | Thickness (mm) | Width (mm) | Roll Length (m) |
CMAX-250 | 250 | 5X5 | 0.6-0.7 | 300-2000 | 50m~100m |
CMAX-120 | 165 | 10X10 | 0.7-0.8 | 300-2000 | 50m~100m |
CMAX-300 | 350 | 25X25 | 0.8-0.9 | 300-2000 | 50m~100m |
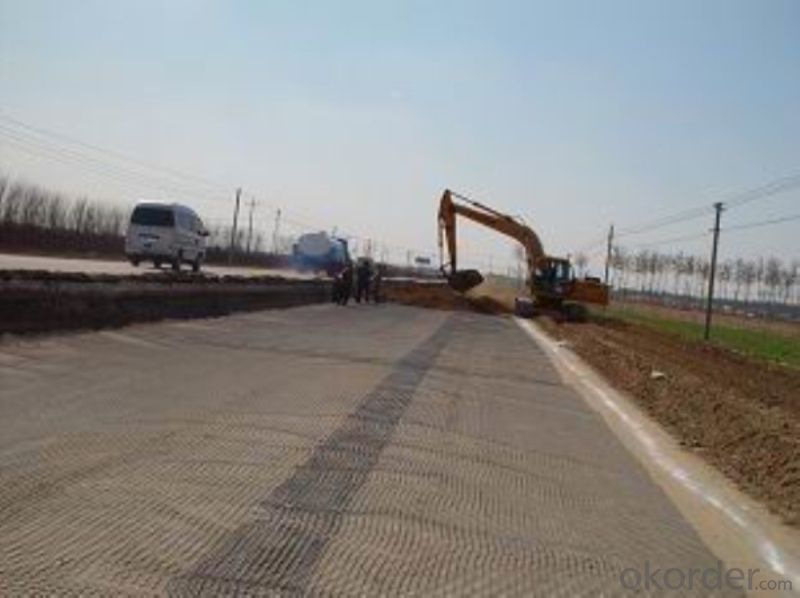
Application of Basalt Fiber Geogrid:
-laying of cement concrete pavement
-the reinforcement of the piers, dams,road and buildings
-building surface drywall joints
-cement mortar or concrete pouring
FAQ:
1. Which payment do you accept?
For you convinience, our payment can be L/C,TT
2. Is free sample available?
We can supply free samples. You'll just need to pay for express cost.
3. How about your quality?
We have strict quality control system, we make testing on incoming raw material and finished products. Your third party testing is also welcomed. With high quality, our products are used on government projects at home and abroad. Our product quality is accepted by clients from all over the world.
4. When will you reply my request?
You are our expected customer, we’ll reply your request within 24hours. Please feel free to contact us at any time.
Photo of Basalt Fiber Geogrid:
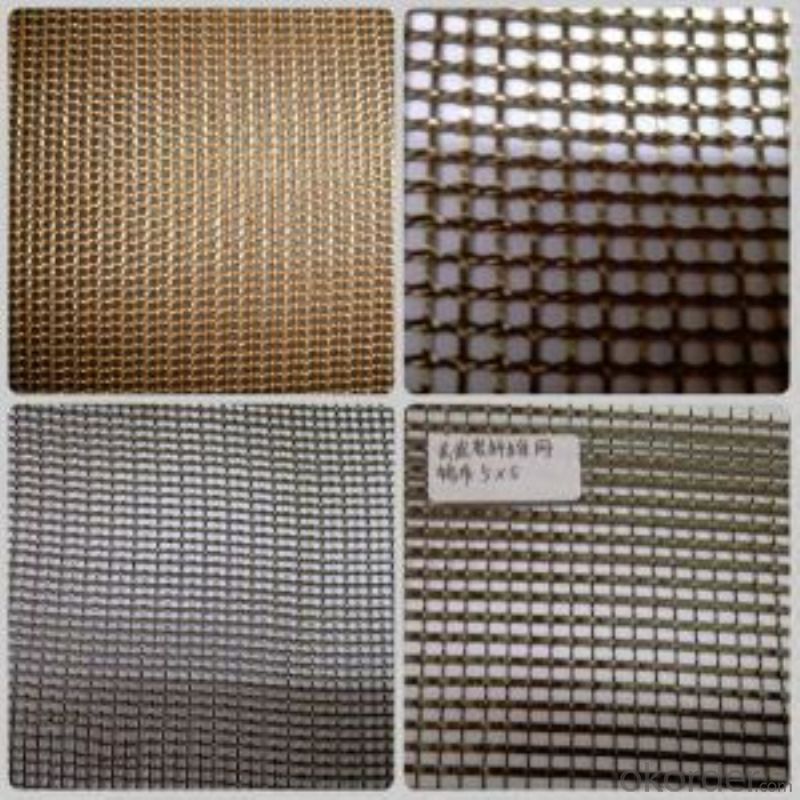
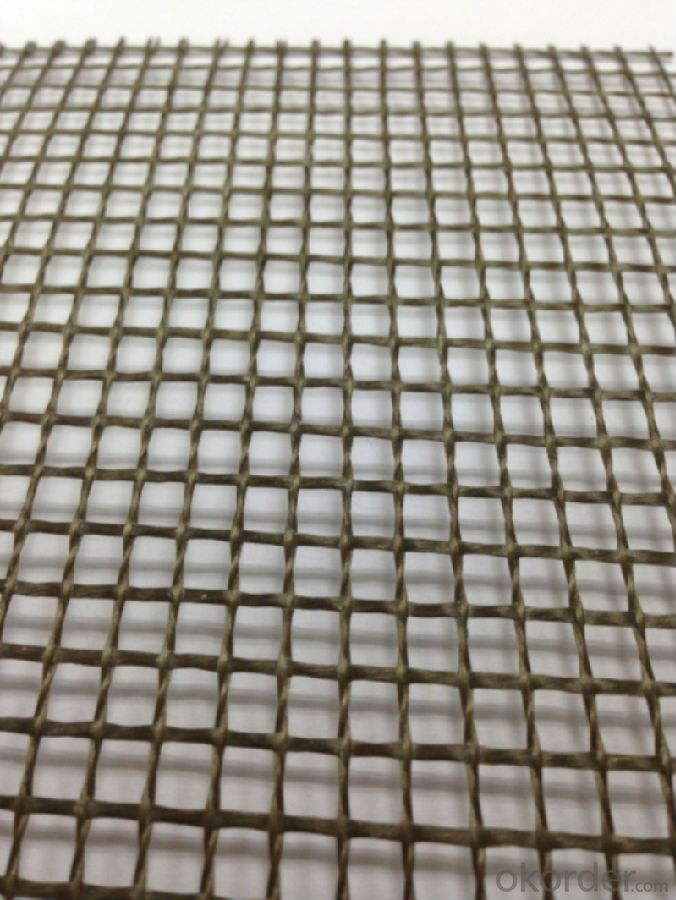
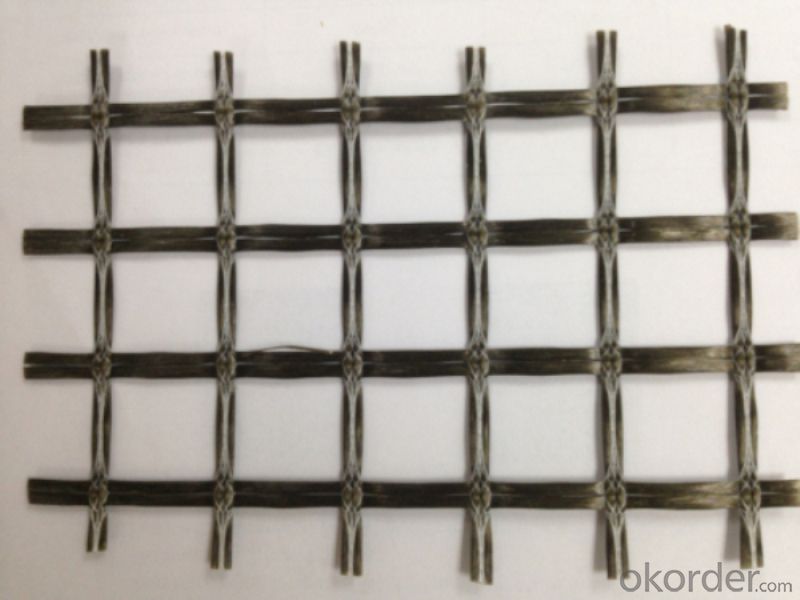









- Q: Modified asphalt and basalt asphalt
- Modified asphalt, is the original asphalt processing to change its original performance after the asphalt composite materials, modified asphalt is the rubber, resin and polymer, ground rubber powder and other materials improver on the asphalt For processing operations and other measures. Basalt asphalt, is the improvement of basalt fiber used in asphalt processing, basalt fiber is a new type of inorganic green green high-performance fiber material, he is the oxide of silicon dioxide and asphalt with high temperature fusion formation.
- Q: Basalt fiber reinforced steel and steel which expensive
- Basalt fibrous tendons are more expensive, not basalt fiber reinforced, basalt fiber similar to fiberglass, basalt fiber tendon is a fiber reinforced plastic ribs.
- Q: The world's most famous columnar basalt
- The dense lava flow is cooled, contracted at a vertical angle, and decomposed in the direction perpendicular to the lava flow direction to form a distinctive geometry, which is the formation of a columnar basalt, which has a regular hexagonal shape, Even close to the artificially manufactured specifications.The world's most famous pillar basaltic structure includes: the Irish coast "Giant's Causeway" (Giant's Causeway), the largest and widely recognized by the United States Wyoming's "Devil Tower" (Devil's Tower).
- Q: Basalt and limestone Which rocks are not suitable for building materials? why
- Paint, the airport runway stone used in the best materials, strong pressure, feed, rubber, basalt stone with wear-resistant, high-quality limestone by ultra-fine grinding, the crushing value is low, with strong compressibility, poor electrical conductivity , The main raw material of calcium carbide, is an indispensable flux limestone in the metallurgical industry, low crushing value, bonding, is the development of rail transport and road transport the best cornerstone, corrosion resistance, paint, and internationally recognized , Is widely used in paper making. Limestone is the manufacture of cement, asphalt adhesion basalt stone, less draft water is the repair of highways, railways, lime, sealed, corrosion resistance, medicine, asphalt adhesion, etc., polishing and other products in the manufacture If it is easy to weather, and moisture aspects of consideration, corrosion! The latter is not suitable
- Q: How to remove moisture from porous basalt asphalt mixture
- Porous basalt asphalt mixture how to remove the water to strengthen the management of materials to reduce the water within the basalt aggregate to facilitate drying quality. Such as the accumulation of storage sites filled with shelter, to prevent water, etc., especially the fine aggregate should pay attention.
- Q: Quartz stone and basalt which hard
- Quartz stone Mohs hardness of 7. Is a physical and chemical properties are very stable mineral resources, quartz stone is the quartz stone plate manufacturers of its production of a short plate, because the main component of its quartz content of up to 93% or more, so called Quartz.
- Q: Basalt and granite are the same?
- Granite is a volcanic eruption of the lava and is subject to considerable pressure in the molten state uplift to the crustal surface of the tectonic rocks in the crustal surface formation, slowly moving down.
- Q: How to distinguish between basalt and rhyolite in the wild
- The rhyolite is composed of potassium feldspar and quartz, and the crystal shape is square plate, with glass luster, but cleavage. Is a gray, pink or brick red rock with a plaque structure and a stripe structure.
- Q: Basalt and the difference between Andesite
- The contents of CaO, Fe2O3 + FeO and MgO are slightly lower than those of intrusive rocks. The content of CaO, Fe2O3 + FeO and MgO is slightly lower than that of intrusive rocks. The content of CaO, Fe2O3 + FeO and MgO is slightly lower than that of intrusive rocks. Mineral composition is mainly composed of basic feldspar and pyroxene, secondary minerals are olivine, amphibole and biotite, etc., the rocks are dark, usually black, sometimes gray and dark purple and so on. Has a patchy structure. Stomatal structure and almond structure are common. Basaltic bulk density of 2.8 ~ 3.3g / cm3, dense compress strength is very large, up to 300MPa, sometimes higher, the existence of vitreous and stomatal strength is reduced. Basaltic durability is very high, joint and more, and with brittle, and thus difficult to take large stone, due to the common pores and almond structure, although the basaltic surface is widely distributed, but can be made no small stone.
- Q: Granite, limestone and basalt from the color and appearance how to distinguish
- The basalt has a clear bubble look, because he is the product of the volcanic eruption, the granite is relatively smooth, there are many products such as muscovite feldspar quartz, marble is not the first two hard, with the geological hammer ringing sound, limestone with hydrochloric acid to see No bubbles.
Send your message to us
Geogrid from Basalt Fiber for Road and Buildings
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 8000 m³
- Supply Capability:
- 1000000 m³/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords