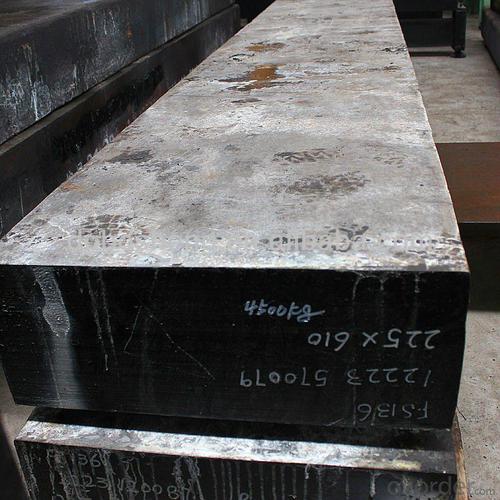
Prime square alloy steel billet 115mm Q235
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Prime square alloy steel billet 115mm Q235
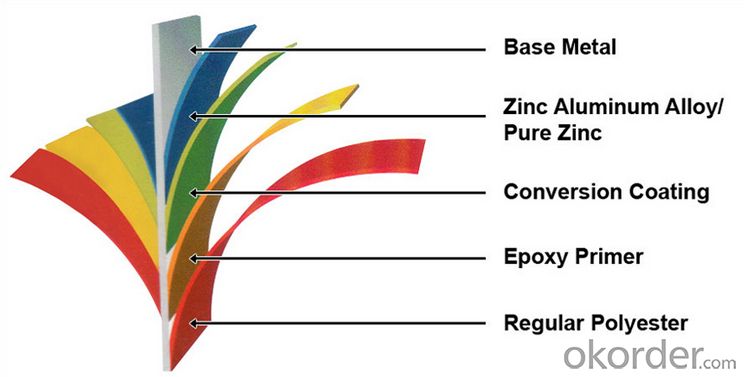
Description of Prime square alloy steel billet 115mm Q235
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.

Main Feature of Prime square alloy steel billet 115mm Q235
Uncoated CR steel sheet
With the features of in line with the international highest standards in demension and shape, excellent surface finish and properties, the products are mainly used in home appliance and automobile industries.
Galvanized steel sheet(include HDG and EG)
With the features of good corrosion resistance, the products are mainly used in automobile, home appliance, electronics, building and machinery manufacture industries, etc.
Precoated steel sheet
With the features of enviromental protection and good processablility, long lasting surface durability, rich in colors, the products are maily used in building, home appliance and furniture industries, etc.
Applications of Prime square alloy steel billet 115mm Q235
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.

Specifications of Prime square alloy steel billet 115mm Q235
Product | Billet |
Material Grade | SGCC / SGCH / DX51D+AZ, etc |
Thickness | 0.6-3.0mm |
Width | 500-1500mm |
Tolerance | Thickness: +/-0.02mm , Width:+/-2mm |
Zinc-coating | Z30-150g/m2 |
Technique | Raw material: Hot rolled steel coil --> Cold rolled_>hot dipped galvalume |
Surface | Dried, Chromated, Unoiled |
Spangle | Regular spangle , small spangle, zero spangle |
ID | 508MM 610MM |
Coil weight | 1-25MT |
Export package | Cardboard inner sleeves, Waterproof paper, galvanized steel covered and steel strip packed |
FAQ of Prime square alloy steel billet 115mm Q235
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
we always fix steel produce in container well to make it safe arrive at destination port
we always provide best and professional forward service for our buyer
we always apply 14days free detention for our buyers container in destination
we provide one set After-sales service for our buyer
we provide China inland steel market price report
we help our buyer become number one in local market .
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of steel cables?
- Steel billets are used in the production of steel cables by being heated and then passed through a series of rollers to shape them into thin, long strands. These strands are then twisted together to form the cables, which are used for various applications such as suspension bridges, elevators, and construction projects. The high strength and durability of steel billets make them ideal for producing strong and reliable steel cables.
- Q: What is the difference between carbon three plants and carbon four plants?
- Also known as C4 plants. Such as corn, sugar cane, sorghum, amaranth and so on.CO2 is the first product of the assimilation of photosynthetic carbon cycle in three carbon compounds 3- phosphoglycerate plants, known as carbon three plants (C3 plants), such as wheat, soybeans, cotton, tobacco, etc.. C3 plants have higher CO2 compensation points than C4 plants, so the survival rate of C3 plants is lower than that of C4 plants when the CO2 content is low.By contrast, the division of C3 plant cells is less definite than that of C4 plants, and CO2 uses less efficiently. To some extent, C3 plants may be considered as prokaryotes in plants, whereas C4 plants are more like eukaryotes".
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the energy efficiency of a structure?
- There are several ways in which steel billets contribute to the energy efficiency of a structure. Firstly, steel billets are a primary raw material for producing structural steel, which is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio. This quality allows steel structures to bear heavy loads without needing excessive amounts of material. As a result, structures made of steel are lighter and more energy efficient. The reduced weight leads to lower transportation costs and less energy consumption during construction. Moreover, steel billets can be easily molded and shaped into different forms, enabling the design and construction of more efficient and streamlined structures. The flexibility of steel as a construction material empowers engineers and architects to create innovative designs that maximize energy efficiency. For instance, steel can be used to construct long-span structures, which reduces the need for additional support columns and optimizes natural lighting and ventilation. Consequently, this decreases the reliance on artificial lighting and HVAC systems. Additionally, steel is highly durable and requires minimal maintenance throughout its lifespan. This durability not only extends the life of the structure but also reduces the energy and resources needed for repairs and replacements. Steel structures also possess excellent fire resistance properties, which contributes to energy efficiency by minimizing fire-related damages and the subsequent energy consumption associated with rebuilding or repairing. Lastly, steel is highly recyclable. At the end of a structure's life, steel components can be salvaged and recycled easily, decreasing the demand for new steel production and conserving natural resources. The recycling process for steel is energy-efficient compared to the production of new steel, further reducing the carbon footprint of the structure. In conclusion, steel billets enhance the energy efficiency of a structure through their high strength-to-weight ratio, design flexibility, durability, fire resistance, and recyclability. These properties enable the construction of lighter, more efficient structures that require less energy during construction, operation, and maintenance. Consequently, they minimize environmental impact.
- Q: What are the different methods of steel billet cutting and machining?
- There are several methods of cutting and machining steel billets, each with its own advantages and applications. Some of the most common methods include: 1. Sawing: This method involves using a saw blade to cut through the steel billet. It is a relatively simple and cost-effective method, suitable for cutting large quantities of billets into desired lengths. However, it may result in rough edges and require additional finishing processes. 2. Flame cutting: Also known as oxy-fuel cutting, this method uses a fuel gas combined with oxygen to create a high-temperature flame that melts and cuts through the steel billet. It is useful for cutting thick billets and can achieve a high level of precision. Flame cutting can be done manually or using automated machines. 3. Plasma cutting: This method employs a plasma torch to generate a high-velocity jet of ionized gas that melts and cuts through the steel billet. It is particularly effective for cutting through thick materials, as well as for intricate shapes and curves. Plasma cutting offers high cutting speeds and excellent precision. 4. Waterjet cutting: In this method, a high-pressure jet of water mixed with abrasive particles is used to cut through the steel billet. Waterjet cutting is versatile and can handle various materials, including steel, without generating heat-affected zones or causing distortion. It is ideal for cutting complex shapes and thin materials. 5. Laser cutting: Laser cutting involves using a high-powered laser beam to melt and vaporize the steel billet along a predefined path. This method offers exceptional precision and enables intricate and complex cuts. Laser cutting is commonly used for thin to medium thickness billets and is suitable for both small-scale and industrial applications. In addition to these cutting methods, there are various machining processes that can be applied to steel billets, such as milling, turning, drilling, and grinding. These processes involve removing material from the billet to achieve desired shapes, dimensions, and surface finishes. The choice of machining method depends on factors such as the complexity of the part, required tolerances, and production volume. Overall, the different methods of steel billet cutting and machining provide a range of options for manufacturers to effectively shape and process steel billets according to their specific requirements.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of consumer goods?
- Steel billets are a crucial raw material used in the manufacturing of consumer goods. These billets are primarily utilized as feedstock in various metalworking processes such as hot rolling, forging, and extrusion. By shaping and forming the steel billets into desired shapes, manufacturers are able to produce a wide range of consumer goods like automobiles, appliances, construction materials, and machinery components. The high strength and durability of steel make it an ideal choice for consumer goods, ensuring reliability and longevity in the final products.
- Q: Can steel billets be polished for improved surface finish?
- Yes, steel billets can be polished to achieve an improved surface finish. Polishing is a mechanical process that involves removing a thin layer of the material's surface to smooth out any imperfections or roughness. It can be done using various techniques such as abrasive polishing, chemical polishing, or electrochemical polishing. Polishing steel billets not only enhances their aesthetic appeal but also improves their functional properties. A polished surface reduces friction, which can be beneficial in applications where smooth movement or reduced wear is required. Additionally, a polished surface can improve the corrosion resistance of steel by creating a barrier against environmental factors. However, it is important to note that the extent to which a steel billet can be polished depends on its composition and properties. Some alloys may be more easily polished than others, and certain surface finishes may require more extensive polishing processes. It is also crucial to consider the desired application and the specific requirements for the steel billets before deciding on the appropriate polishing method.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of railway parts?
- Steel billets are an important raw material used in the production of railway parts. These billets are essentially semi-finished steel products that are cast into a specific shape and size, typically in a square or rectangular form. They serve as the starting point for the manufacturing process of various railway components. One of the primary applications of steel billets in the production of railway parts is for the manufacturing of rails. The billets are heated and then passed through a series of rolling mills to shape them into the desired rail profile. This process, known as rolling, involves applying pressure to the billet, which gradually elongates and shapes it into the rail section. The resulting rails are then cut to the required length and undergo further processes such as heat treatment and finishing to enhance their strength and durability. Apart from rails, steel billets are also used in the production of other crucial railway components such as wheels, axles, and various structural parts. For example, billets can be forged or machined to form the wheel blanks, which are subsequently processed to create the final wheel shape. Similarly, billets can be used to manufacture axles by forging and machining them into the desired dimensions and specifications. Additionally, steel billets may be employed in the fabrication of various structural parts used in railway infrastructure, including bridges, tunnels, and platforms. These billets are processed through different manufacturing techniques such as casting, forging, or machining to produce the required components. In summary, steel billets play a vital role in the production of railway parts. From manufacturing rails to wheels, axles, and structural components, these billets serve as the starting material that undergoes various shaping, heat treatment, and finishing processes to create the final railway components that ensure safe and efficient transportation.
- Q: What are the different types of casting processes used for shaping steel billets?
- Steel billets can be shaped using various casting processes. These methods include: 1. Continuous Casting: The most commonly used technique involves pouring molten steel into a continuously moving, water-cooled mold. The solidifying steel is continuously pulled out of the mold, resulting in a seamless billet. This process is efficient and allows for high production rates. 2. Centrifugal Casting: This method utilizes a rotating mold into which molten steel is poured. The centrifugal force evenly distributes the metal along the mold walls, creating a cylindrical billet. Centrifugal casting is known for producing high-quality, defect-free billets. 3. Ingot Casting: A traditional approach where molten steel is poured into a mold and left to solidify. The resulting solid steel, called an ingot, is then processed further to achieve the desired billet shape. Ingot casting offers flexibility in terms of billet size and shape. 4. Sand Casting: This process is suitable for manufacturing large and complex steel billets. It involves creating a mold using a mixture of sand and a binder. Molten steel is poured into the mold, and once it solidifies, the mold is removed to reveal the billet. While sand casting allows for custom-shaped billets, it is a slower and less precise method compared to others. 5. Investment Casting: Also known as lost-wax casting, this technique is ideal for intricate and complex billet shapes. Investment casting begins with the creation of a wax pattern in the desired shape. The wax pattern is then coated with a ceramic shell, and the wax is melted away, leaving behind a hollow mold. Molten steel is poured into the mold and solidifies, after which the ceramic shell is broken to retrieve the billet. Each casting process has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on factors such as desired billet shape, size, production volume, and quality requirements.
- Q: What are the different types of steel billets used in the aerospace industry?
- In the aerospace industry, various types of steel billets are used, including stainless steel, tool steel, and high-strength alloy steel. These types of steel are chosen for their specific properties, such as corrosion resistance, high temperature strength, and superior mechanical properties.
- Q: How are steel billets transported?
- Steel billets are typically transported using various modes of transportation such as trucks, trains, and ships. They are often loaded onto flatbed trucks or rail cars for land transportation, while larger quantities may be shipped in bulk on specialized vessels. Additionally, steel billets can also be transported using intermodal containers, allowing for seamless transfer between different modes of transport.
Send your message to us
Prime square alloy steel billet 115mm Q235
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords































