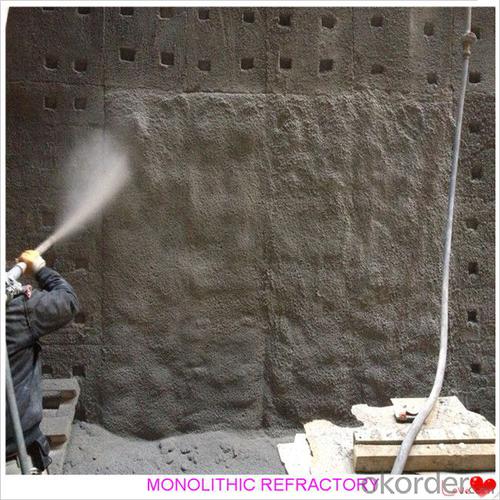
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - 42.5R Castable for Fireside and Industrial Furnace
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 3000000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
42.5R Castable For Fireplace and Industrial Furnace in Iron and Steel
Product Description:
42.5R castable is manufactured according to international standards. The product is famous for its excellent abrasion resistance and low thermal conductivity. Further, these can be provided in different specifications as required by the clients. The 42.5R castables are used high purity raw materials and additives as the main material, and made of under superfine powder adding technology.
Product Advantages:
The material has excellent structural stability and air tightness, and has high physical and chemical properties, also has a fine working ability.They should be used with the same material products.
Product Applications:
For feature of 42.5R castable, they have excellent abrasion resistance, thermal shock resistance, high-temperature resistance, anti-corrode and have high intensity.
Designed for refractory lining of blast furnace iron and slag runners, skimmers and soon
They can be used in troughs of small and mid size BFs and in all positions of the troughs where fast tapping is required.
Product Specifications:

FAQ:
1. How you can control your quality?
For each production processing, we have complete QC system for the chemical composition
and Physical properties. After production, all the goods will be tested, and the quality certificate
will be shipped along with goods.
2. What's your delivery time?
It usually needs about 20days- 45 days after receiving the deposit.
3. Do you provide free samples?
Yes, we can provide a free sample for testing, If we have sample in stock,
The quantity based on the material type, The buyer should bear all the shipping costs.
4. What's your payment terms?
We can accept 30% deposit, 70% balance before shipment for ordrs over $ 2000.
5. Can we visit your Company?
Yes, certainly. You are very welcome to China and we will be honored to have a customer and friend.
Product Picture:




- Q: How are monolithic refractories different from traditional brick refractories?
- There are several differences between monolithic refractories and traditional brick refractories. Firstly, monolithic refractories are composed of a single, homogeneous material, whereas traditional brick refractories are made up of individual bricks that are pieced together. This variance in construction allows monolithic refractories to possess a more uniform and consistent structure, which can enhance their performance and durability. Secondly, installing monolithic refractories is typically easier compared to traditional brick refractories. Due to their composition, they can be poured or sprayed into place, eliminating the need for precise bricklaying and mortar application. This simplified installation process saves time and labor during construction or repair projects. Furthermore, monolithic refractories often exhibit superior resistance to thermal shock when compared to traditional brick refractories. The homogeneous structure of monolithic refractories enables them to expand and contract more uniformly under thermal stress, reducing the risk of cracking and failure. This characteristic makes monolithic refractories more suitable for applications with rapid temperature changes, such as in furnaces or kilns. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer better resistance to chemical attacks and erosion. Traditional brick refractories may have joints and gaps between bricks, which can become vulnerable to chemical reactions or erosion over time. Conversely, monolithic refractories possess a seamless structure that minimizes the risk of chemical penetration and erosion, enhancing their longevity and performance. In conclusion, monolithic refractories provide advantages in terms of uniformity, ease of installation, thermal shock resistance, and chemical resistance compared to traditional brick refractories. These disparities make monolithic refractories the preferred choice for numerous industrial applications that involve high temperatures and harsh environments.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories perform in rotary kiln applications?
- Monolithic refractories perform exceptionally well in rotary kiln applications due to their high thermal shock resistance, excellent chemical resistance, and superior strength at high temperatures. Their ability to withstand extreme heat and harsh chemical environments makes them ideal for lining the interior of rotary kilns. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer easy installation and maintenance, ensuring efficient and reliable kiln operations.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories prevent thermal radiation in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories prevent thermal radiation in the iron and steel industry by providing a high level of insulation. They are specifically designed to withstand high temperatures and reduce heat transfer through radiation. By forming a protective barrier around the furnaces and other equipment, monolithic refractories minimize the loss of heat through thermal radiation, thereby improving energy efficiency and reducing energy consumption in the iron and steel production process.
- Q: What are the considerations for selecting monolithic refractories for ladles and tundishes?
- When it comes to choosing monolithic refractories for ladles and tundishes, there are a number of important factors to bear in mind. Firstly, it is crucial to select monolithic refractories that can withstand and maintain their strength and integrity at the extremely high temperatures experienced during metal casting processes. In addition, monolithic refractories with good thermal shock resistance are essential, as ladles and tundishes are subjected to rapid temperature changes during pouring and cooling. Such refractories can prevent cracking and spalling, ensuring the longevity and performance of these components. Erosion and corrosion resistance is another key consideration. Refractory linings can be eroded and chemically attacked by molten metal, slag, and other corrosive substances. Opting for monolithic refractories with excellent erosion and corrosion resistance can extend the service life of ladles and tundishes, reducing the need for maintenance and minimizing downtime. Mechanical strength is also important, as ladles and tundishes are frequently handled, transported, and subjected to mechanical stresses. Monolithic refractories with adequate mechanical strength can withstand these forces without cracking or breaking, thereby maintaining the structural integrity of these components. The method of applying monolithic refractories is another factor to think about. Depending on the size and shape of the ladles and tundishes, as well as the available equipment and expertise, different application methods such as gunning, casting, ramming, or spraying may be used. It is important to ensure that the selected monolithic refractories are compatible with the chosen application method. The thermal conductivity of monolithic refractories can impact heat transfer in ladles and tundishes. Opting for refractories with low thermal conductivity can help minimize heat loss and improve energy efficiency. While performance and durability are crucial, it is also important to consider the cost-effectiveness of the chosen monolithic refractories. This includes factors such as the initial cost of the refractories, installation and maintenance costs, and the expected service life. Striking a balance between performance and cost can help optimize the overall investment in ladles and tundishes. Overall, the selection of monolithic refractories for ladles and tundishes involves a combination of factors, including temperature resistance, thermal shock resistance, erosion and corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, application method compatibility, thermal conductivity, and cost-effectiveness. By carefully evaluating these factors, it is possible to choose the most suitable monolithic refractories that meet the specific requirements of ladles and tundishes in metal casting processes.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the efficiency of iron and steel production?
- Monolithic refractories play a critical role in improving the efficiency of iron and steel production processes. These refractories are renowned for their superior thermal properties, high resistance to mechanical stress, and outstanding resistance to chemical corrosion. One primary manner in which monolithic refractories enhance the efficiency of iron and steel production is by providing effective insulation. By lining furnaces and other high-temperature equipment, monolithic refractories prevent heat loss and ensure consistent maintenance of desired temperatures. This insulation helps reduce energy consumption by minimizing heat wastage, ultimately resulting in cost savings. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer exceptional resistance to thermal shock. In the iron and steel industry, frequent heating and cooling cycles are common, and conventional refractory materials may crack or fail under these conditions. However, monolithic refractories can endure rapid temperature fluctuations without failure, guaranteeing the longevity and reliability of the refractory lining. This resistance to thermal shock reduces downtime for repairs and maintenance, thereby increasing overall production efficiency. Furthermore, monolithic refractories exhibit significant resistance to chemical corrosion. In iron and steel production, various corrosive substances such as molten metal, slag, and gases are present. By utilizing monolithic refractories as lining materials, the underlying structures are protected from chemical attack, preventing erosion and prolonging the equipment's service life. This corrosion resistance reduces the need for frequent repairs or replacements, leading to cost savings and enhanced productivity. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer easy installation and repair. Unlike traditional refractories, which are often constructed brick by brick, monolithic refractories are applied as a single mass. This allows for faster installation and reduces the potential for weak points or joints that may compromise the overall efficiency of the refractory lining. Furthermore, when repairs or maintenance are necessary, monolithic refractories can be easily patched or replaced, minimizing downtime and ensuring seamless operation. To summarize, the use of monolithic refractories in iron and steel production contributes to increased efficiency in multiple ways. Their outstanding thermal insulation properties reduce energy consumption, while their resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion ensures reliable and long-lasting refractory linings. Additionally, their easy installation and repair capabilities further enhance productivity. Overall, monolithic refractories are an indispensable component in improving the efficiency and sustainability of iron and steel production processes.
- Q: What are the specific requirements of monolithic refractories for ladle purging applications?
- Monolithic refractories used for ladle purging applications need to have specific requirements such as high thermal shock resistance, excellent erosion resistance, and good insulating properties. They should also have low porosity to prevent excessive penetration of slag or metal, high strength to withstand the mechanical stresses during purging, and good chemical stability to resist the corrosive environment of the ladle. Additionally, they should have good workability for ease of installation and repair.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand chemical attack from molten metals and slag?
- Monolithic refractories are highly resistant to chemical attack from molten metals and slag due to their unique composition and structure. These refractories are typically made from a single, solid piece with no joints or seams, which minimizes the opportunity for chemical penetration. One of the key factors that enables monolithic refractories to withstand chemical attack is their high melting point. These materials are designed to have a melting point significantly higher than the temperature of the molten metal or slag they are exposed to. This prevents the refractory from melting or deforming when in contact with the hot molten substances. In addition to their high melting point, monolithic refractories are formulated with materials that have excellent chemical resistance. They are often composed of a combination of oxides, such as alumina, magnesia, and zirconia, which have a strong affinity for oxygen and form stable compounds. This allows the refractory to form a protective oxide layer on its surface when exposed to molten metals and slag, effectively shielding it from chemical attack. Furthermore, the dense and compact structure of monolithic refractories plays a crucial role in their resistance to chemical attack. The absence of joints and seams minimizes the chances of molten metals and slag infiltrating the refractory and causing chemical reactions. This dense structure also reduces the porosity of the material, making it less permeable to aggressive substances. Moreover, manufacturers often add specialized additives to monolithic refractories to enhance their chemical resistance. These additives can include fibers, binders, and corrosion inhibitors, which further improve the refractory's ability to withstand chemical attack. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are designed to withstand chemical attack from molten metals and slag through their high melting point, chemical-resistant composition, dense structure, and specialized additives. These properties allow them to maintain their integrity and performance even in the harshest environments, making them an ideal choice for applications involving high-temperature and corrosive substances.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand thermal cycling in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories are designed to withstand thermal cycling in the iron and steel industry due to their unique composition and properties. These refractories are made from a single, continuous material, unlike traditional refractory bricks that are made by stacking individual bricks together. One of the main reasons monolithic refractories are able to withstand thermal cycling is their ability to expand and contract without cracking or damage. This is due to their high thermal shock resistance, which is a measure of their ability to withstand rapid temperature changes. Monolithic refractories are specially formulated to have low thermal conductivity, allowing them to resist the transfer of heat and minimize thermal gradients within the material. In addition, monolithic refractories have excellent thermal stability, which means they can maintain their structural integrity and mechanical strength even at high temperatures. This is crucial in the iron and steel industry, where temperatures can reach extreme levels. The refractories are able to withstand repeated heating and cooling cycles without undergoing significant structural changes or degradation. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have good corrosion resistance, which is important in an environment where they come into contact with molten metal and various chemical agents. Their composition and special additives help to protect the refractory material from chemical attack, preventing erosion and prolonging their lifespan. The manufacturing process of monolithic refractories allows for easy installation and repair, as they can be applied as a liquid or a semi-liquid mixture. This reduces the risk of joints or weak points that could lead to thermal stress or failure during thermal cycling. Overall, the combination of high thermal shock resistance, low thermal conductivity, excellent thermal stability, corrosion resistance, and easy installation makes monolithic refractories highly durable and capable of withstanding the severe thermal cycling conditions in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand the thermal cycling in aluminum smelting applications?
- Monolithic refractories are able to withstand the thermal cycling in aluminum smelting applications due to their unique properties and design. These refractories are composed of a single, homogenous material without any joints or seams, which eliminates weak points that could be susceptible to thermal stress. Additionally, they have excellent thermal shock resistance and low thermal conductivity, allowing them to effectively handle the rapid temperature changes that occur during aluminum smelting processes. The monolithic refractories also have high refractoriness and chemical stability, enabling them to endure the harsh and corrosive conditions in aluminum smelting environments without significant degradation. Overall, the combination of these attributes allows monolithic refractories to withstand the extreme thermal cycling involved in aluminum smelting applications.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to reducing downtime in iron and steel plants?
- Monolithic refractories contribute to reducing downtime in iron and steel plants by providing enhanced durability and resistance to high temperatures, chemical corrosion, and mechanical wear. These refractories can be quickly and easily installed, repaired, or replaced, minimizing the time required for maintenance and reducing production interruptions. Their versatile and customizable nature allows for efficient lining of various equipment, such as furnaces, ladles, and converters, ensuring a continuous and uninterrupted production process.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - 42.5R Castable for Fireside and Industrial Furnace
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 3000000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords