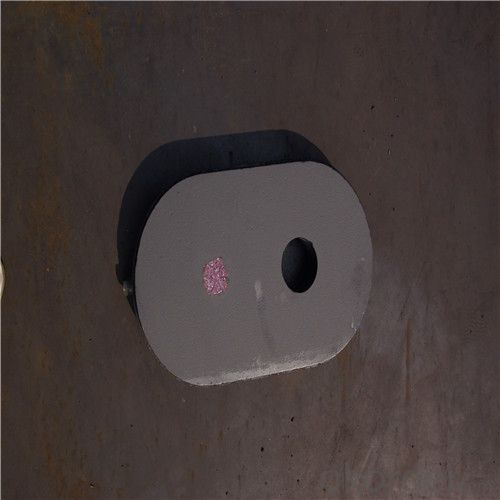
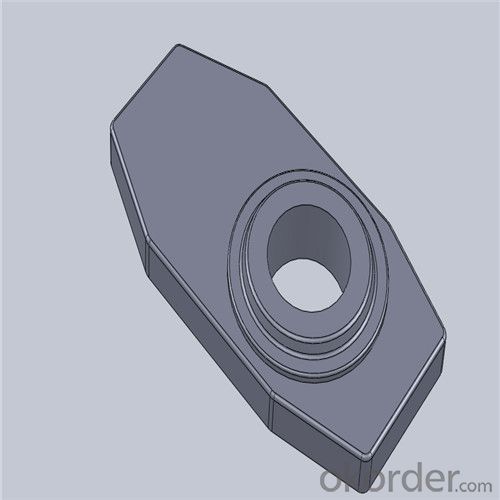
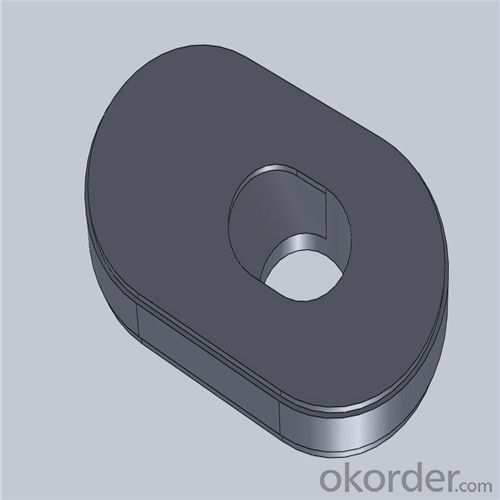
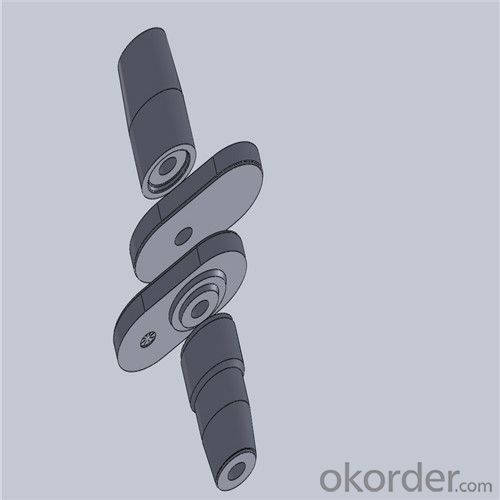
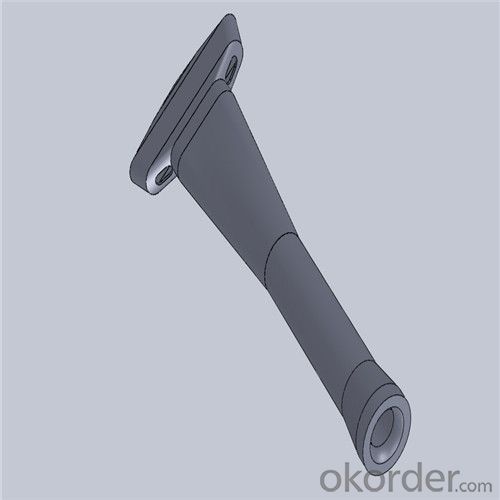
Monolithic Refractories High Performance Ladle Sliding Gate for Steel Industry
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for High Performance Refractory Ladle Slide Gate
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Shape: | Plate | Material: | Alumina Block |
| SiO2 Content (%): | N/A | Al2O3 Content (%): | 80-90% | MgO Content (%): | N/A |
| CaO Content (%): | N/A | Refractoriness (Degree): | 1770°< Refractoriness< 2000° | CrO Content (%): | N/A |
| SiC Content (%): | N/A | Model Number: | CS80 | Brand Name: | |
| Product name: | High performance refractory ladle slide gate | Model No.: | cs80 | Brand name: | CMAX |
| Quality: | Al-C or Al-Zr-C | Service life: | 4-6 heats | Apparent porosity: | 7% Max |
| Bulk density:: | 3.1 MIN | C.C.S: | 120MPA | MOQ: | 100 pcs for trial |
| Delivery time: | 60 working days upon receipt of deposit |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Inner carton packing, outer wooden case suitable for long term sea shipping |
| Delivery Detail: | three months working days upon receipt of deposit |
Specifications
Surface flatness less than 0.05mm
High mechanical strength
Erosion resistance
Oxidation resistance
Thermal shock stability
Using the raw materials of tabular alumina, zirconia-corundum, carbon and other high-grade additives, after sintering to obtain characteristics of oxidation resistance, scour strength, erosion resistance, thermal shock resistance, shape stable and long service life, made our products the preferred materials for the large and medium-sized steel ladle, refining ladle, series of alloy steel ladle, and tundish. Our high performance sintering sliding gates include alumina carbon , Al2O3-ZrO2-C, etc, can meet the needs of different steel grade.
General Chemical Analysis for refractory ladle slide gate :
slide gate plate widely including Alumina carbon and Alumina Zirconia Carbon slide gate plate, MgO and MgO-spinel slide gate plate,nonoxides bonding slide gate plateand unburned slide gate plate.
Alumina -Zirconia-Carbon material
| Al-Zr-C Material | |||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) |
| 85 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
Composite type: Al-Zr-C for working line, outer Al-C material
| Al-Zr-C & Al-C Material | ||||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S | |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) | |
| Inner side (Working face) | 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| Outside | 90 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 3 | |


About us


Sample is on your request.
Welcome to visit our factory~
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall efficiency of iron and steel production?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the overall efficiency of iron and steel production. These refractories, which are made from a single material, provide exceptional thermal insulation, resistance to high temperatures, and excellent mechanical strength. By lining the furnaces, ladles, and other equipment used in the production process, monolithic refractories help in maintaining and regulating the required high temperatures for melting, refining, and shaping iron and steel. This insulation reduces heat loss, minimizes energy consumption, and ensures a more efficient and cost-effective production process. Additionally, the mechanical strength of monolithic refractories allows for better protection against wear and tear, resulting in increased equipment lifespan and reduced downtime for repairs and maintenance. Overall, the use of monolithic refractories significantly contributes to the efficiency, productivity, and sustainability of the iron and steel production industry.
- Q: What are the key trends in the use of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- It is worth noting that there are several notable trends in the use of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry. First and foremost, there is an increasing demand for monolithic refractories due to their superior performance characteristics in comparison to traditional brick refractories. Monolithic refractories provide higher thermal shock resistance, superior insulation properties, and improved resistance to chemical attacks. As a result, they are being used more extensively in various applications within the iron and steel industry. Secondly, there is a shift towards the utilization of low-cement and ultra-low cement castables in monolithic refractories. These materials contain a reduced amount of cement, leading to enhanced refractory properties such as increased strength, better corrosion resistance, and improved resistance to thermal spalling. This trend is driven by the need to enhance the overall efficiency and longevity of refractory linings in iron and steel manufacturing processes. Another significant trend is the development of advanced monolithic refractories that prioritize sustainability and environmental performance. The iron and steel industry is facing mounting pressure to reduce its carbon footprint and minimize its impact on the environment. Consequently, there is a growing emphasis on the use of environmentally friendly binders and additives in monolithic refractories. These novel materials not only offer excellent refractory properties but also contribute to the industry's sustainability objectives. Moreover, there is an increasing focus on the development of monolithic refractories capable of withstanding extreme operating conditions. Iron and steel manufacturing processes involve high temperatures, aggressive chemical environments, and severe mechanical stresses. Consequently, there is a need for monolithic refractories that can withstand these harsh conditions without compromising their performance. The industry is investing in research and development to create refractories that exhibit exceptional resistance to thermal shock, abrasion, and erosion. Lastly, there is a growing adoption of digital and smart technologies for the monitoring and maintenance of monolithic refractories. Advances in sensor technology and data analytics have made it possible to collect real-time data on the condition and performance of refractory linings. This enables proactive maintenance, early detection of potential issues, and optimization of refractory usage, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and cost savings. In conclusion, the use of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry is witnessing key trends such as the demand for superior performance, the shift towards low-cement and ultra-low cement castables, the development of sustainable materials, the focus on extreme operating conditions, and the adoption of digital and smart technologies for monitoring and maintenance. These trends reflect the industry's continuous efforts to enhance the efficiency, durability, and environmental sustainability of refractory linings in iron and steel manufacturing processes.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories recycled or disposed of at the end of their lifespan?
- Monolithic refractories, which are commonly used in high-temperature industrial applications, can be recycled or disposed of at the end of their lifespan through several methods. The chosen method depends on the specific type of monolithic refractory and its composition. One common approach to recycling monolithic refractories is through a process known as reclamation. Reclamation involves collecting used refractory materials and processing them to remove any impurities or contaminants. The reclaimed refractory material can then be crushed, ground, or milled to produce a fine powder that can be used as a raw material in the production of new refractories. Another method of recycling monolithic refractories is through thermal treatment. This involves subjecting the used refractory material to high temperatures in a controlled environment, such as a kiln or furnace. The heat helps to break down the refractory material, removing any binders or impurities. The resulting material can then be reused as a raw material or incorporated into other applications, such as aggregates for construction. In cases where recycling is not feasible, monolithic refractories can be disposed of in specialized facilities designed for handling and treating hazardous waste. These facilities ensure that the refractory material is properly contained and treated to minimize any potential environmental impact. This disposal method is typically used for refractories that contain hazardous substances or cannot be recycled due to their composition. It is important to note that the proper disposal or recycling method for monolithic refractories should comply with local regulations and guidelines. These regulations aim to ensure the safe handling, treatment, and disposal of these materials, taking into consideration their potential environmental and health impacts. Therefore, it is crucial for industries and businesses to work closely with waste management professionals and follow the appropriate procedures to responsibly manage monolithic refractories at the end of their lifespan.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories prevent heat loss through convection?
- Monolithic refractories prevent heat loss through convection by providing a continuous and dense structure that minimizes the movement of air or gases, thereby reducing the transfer of heat through convection currents.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the reduction of heat loss in iron and steel plants?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in reducing heat loss in iron and steel plants through their high thermal insulation properties. These refractories are designed to withstand extreme temperatures and provide excellent resistance to thermal shock and erosion. By lining the walls, roofs, and floors of various equipment and structures in the plants, monolithic refractories help to create a barrier that prevents heat from escaping into the surrounding environment. This insulation not only conserves energy but also ensures efficient heat transfer within the plant, leading to improved productivity and cost-effectiveness.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories prevent thermal radiation in the iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in preventing thermal radiation in the iron and steel industry. Thermal radiation refers to the transfer of heat energy through electromagnetic waves, and it can be a significant challenge in this industry due to the high temperatures involved. Monolithic refractories, which are single-piece refractory materials, are designed to have excellent thermal insulation properties. They have low thermal conductivity, which means they are not good conductors of heat. This property allows them to act as a barrier against thermal radiation. When used in the iron and steel industry, monolithic refractories are typically applied as linings in furnaces, ladles, and other equipment that are exposed to extremely high temperatures. These linings serve as a protective layer, preventing the heat from escaping and reducing the amount of thermal radiation emitted. Additionally, monolithic refractories have high emissivity, which refers to their ability to absorb and re-emit thermal radiation. This property allows them to effectively capture and contain the heat within the equipment, minimizing the amount of radiation that escapes into the surroundings. By preventing thermal radiation, monolithic refractories help to maintain the desired temperatures within the iron and steel production process. This is crucial for achieving efficient and controlled operations, as well as ensuring the quality of the final products. Furthermore, the use of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry also contributes to energy savings. By reducing the heat loss through thermal radiation, less energy is required to maintain the desired temperatures, resulting in lower energy consumption and cost savings. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are essential in preventing thermal radiation in the iron and steel industry. Their excellent thermal insulation properties, low thermal conductivity, and high emissivity make them effective barriers against heat transfer through radiation. By minimizing heat loss and ensuring controlled temperatures, monolithic refractories contribute to efficient operations, high-quality products, and energy savings.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories enhance the performance of ladle and tundish covers?
- Monolithic refractories enhance the performance of ladle and tundish covers by providing high thermal conductivity, excellent resistance to thermal shock, and superior mechanical strength. These properties ensure efficient heat insulation, minimize heat loss, and prevent cracking or damage due to rapid temperature changes. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer good corrosion resistance, prolonging the lifespan of the ladle and tundish covers and improving their overall performance.
- Q: Can monolithic refractories be used for the lining of ladle refining furnaces and VOD converters?
- Indeed, ladle refining furnaces and VOD converters can benefit from the utilization of monolithic refractories. These refractories, which consist of a single, uniform material, can be molded and installed in various settings, particularly those involving extreme temperatures such as ladle refining furnaces and VOD converters. The advantage of monolithic refractories lies in their simplicity of application and repair. They can be either cast or gunned in place, offering flexibility in terms of lining design and installation. The lining of ladle refining furnaces and VOD converters requires materials capable of withstanding high temperatures, chemical reactions, and mechanical stresses. Monolithic refractories are well-suited for these demanding applications due to their exceptional resistance to thermal shock and chemical attack. In the case of ladle refining furnaces, monolithic refractories are used to line the vessel in which molten metal is contained and processed. By doing so, these refractories help to maintain the desired temperature and safeguard the ladle from the corrosive effects of both molten metal and slag. Additionally, they serve as insulation to minimize heat loss and enhance energy efficiency. VOD converters, on the other hand, are employed in the steelmaking process to reduce the carbon content of molten steel. Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in lining the converter's vessel and ensuring the maintenance of the required temperature for the decarburization reaction. Furthermore, they provide protection against the corrosive impact of molten metal and slag, thereby guaranteeing the converter's durability and performance. To summarize, monolithic refractories possess outstanding characteristics that make them an excellent choice for lining ladle refining furnaces and VOD converters. Their versatility, ease of installation, and ability to withstand high temperatures and chemical attack render them perfectly suited for these critical applications within the steel industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the performance of iron and steel furnaces?
- Monolithic refractories, unlike traditional brick-based refractories, offer several advantages that enhance the performance of iron and steel furnaces. Firstly, their seamless design eliminates joints and seams, reducing the risk of thermal shock and leakage, leading to improved insulation and energy efficiency. Additionally, monolithic refractories have higher thermal conductivity and superior resistance to chemical attacks, ensuring longer furnace life and reduced maintenance costs. Their ability to be easily shaped and installed also allows for better lining optimization, promoting better heat transfer and uniform temperature distribution within the furnace. Ultimately, monolithic refractories contribute to increased productivity, reduced downtime, and overall improved performance of iron and steel furnaces.
- Q: What are the typical properties of monolithic refractories used in iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories used in the iron and steel industry typically possess high thermal conductivity, excellent resistance to thermal shock, and high mechanical strength. They are also known for their ability to withstand high temperatures and harsh chemical environments. Additionally, these refractories exhibit good erosion and abrasion resistance, low porosity, and high density, making them ideal for lining furnaces, ladles, and other equipment in the iron and steel production process.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories High Performance Ladle Sliding Gate for Steel Industry
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords