Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - Fireclay Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
General Information of Fireclay Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
Made as per international standards, FIREF fireclay based mortar for hot blast stove is known for its low thermal conductivity, high refractoriness, and excellent thermal shock resistance.
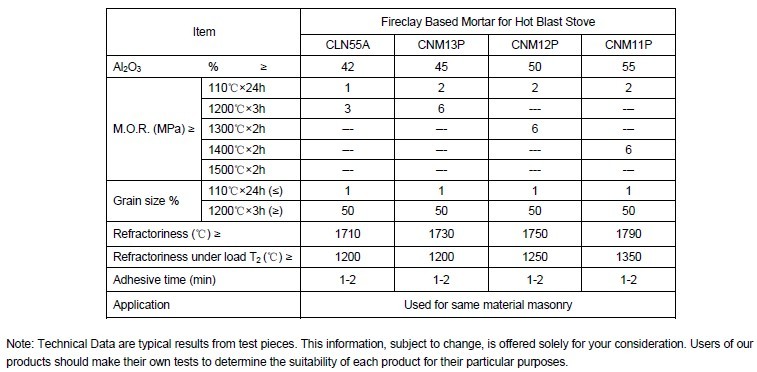
Technical data of Fireclay Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
Production line and packing of Fireclay Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove


Feature of Fireclay Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
Low thermal conductivity
High refractoriness
Excellent thermal shock resistance
Excellent mechanical strength
Application of Fireclay Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
FIREF fireclay based mortar for hot blast stove can be used together with the same material fireclay bricks.
Production Flow of Fireclay Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove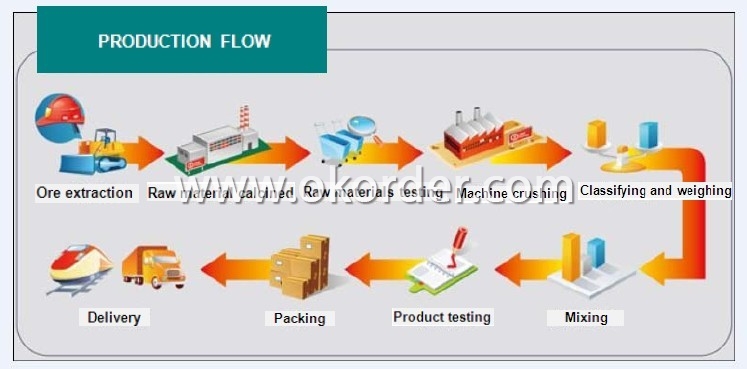
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall efficiency of iron and steel production?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the overall efficiency of iron and steel production. These refractories, which are made from a single material, provide exceptional thermal insulation, resistance to high temperatures, and excellent mechanical strength. By lining the furnaces, ladles, and other equipment used in the production process, monolithic refractories help in maintaining and regulating the required high temperatures for melting, refining, and shaping iron and steel. This insulation reduces heat loss, minimizes energy consumption, and ensures a more efficient and cost-effective production process. Additionally, the mechanical strength of monolithic refractories allows for better protection against wear and tear, resulting in increased equipment lifespan and reduced downtime for repairs and maintenance. Overall, the use of monolithic refractories significantly contributes to the efficiency, productivity, and sustainability of the iron and steel production industry.
- Q: In iron and steel industry, the main raw materials for blast furnace ironmaking are iron ore, coke and limestone. What's the use of limestone here?
- At high temperatures, limestone (calcium carbonate) breaks down into lime (calcium oxide, which is useful) and carbon dioxide.
- Q: How can the lifespan of monolithic refractories be extended?
- The lifespan of monolithic refractories can be extended through proper installation techniques, regular maintenance, and careful handling.
- Q: What are the factors affecting the thermal conductivity of monolithic refractories?
- The factors affecting the thermal conductivity of monolithic refractories include the composition and structure of the refractory material, the porosity and density of the material, the presence of any impurities or defects, the temperature at which the material is being used, and the presence of any external factors such as pressure or moisture.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories different from traditional refractory bricks?
- Monolithic refractories are different from traditional refractory bricks because they are not pre-fabricated into brick shapes. Instead, they are supplied as a ready-mix or ready-to-use material that can be directly applied on-site. This eliminates the need for complex brick-laying processes and allows for a more flexible and efficient installation. Monolithic refractories also have superior thermal shock resistance and can withstand higher temperatures, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the reduction of downtime in iron and steel plants?
- Monolithic refractories contribute to the reduction of downtime in iron and steel plants by providing superior thermal insulation and resistance to high temperatures, reducing the risk of equipment failure and unplanned shutdowns. Their ability to withstand extreme conditions, such as molten metal and slag, allows for extended operational periods without frequent maintenance or replacement. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer quick and easy installation, repair, and maintenance, minimizing the time required for downtime and ensuring a more efficient and productive operation in iron and steel plants.
- Q: Can monolithic refractories be used for the lining of reheating furnaces and walking beam furnaces?
- Yes, monolithic refractories can be used for the lining of reheating furnaces and walking beam furnaces. Monolithic refractories are versatile and can be shaped to fit the specific requirements of these furnaces. They offer excellent thermal insulation, high temperature resistance, and durability, making them suitable for withstanding the extreme conditions within these furnaces. Additionally, monolithic refractories can be easily installed, repaired, and replaced, making them a practical choice for lining these types of furnaces.
- Q: What are the recommended storage and handling practices for monolithic refractories?
- To ensure optimal performance and longevity of monolithic refractories, it is crucial to adhere to recommended storage and handling practices. Take note of the following key practices: 1. Storage: Store monolithic refractories in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated area. Protect the storage facility from moisture, extreme temperatures, and direct sunlight. Ideally, use pallets or racks to prevent contact with the ground and minimize the risk of damage. 2. Handling: Handle monolithic refractories with care to avoid physical damage. Use appropriate lifting equipment, such as forklifts or cranes, to lift and move the refractories. This will prevent excessive stress or strain on the material. Avoid dropping or dragging them, as this can cause cracks or fractures. 3. Packaging: Inspect the packaging for any signs of damage or moisture before accepting the delivery. Damaged packaging may indicate potential damage to the refractory material. Immediately inform the supplier if any anomalies are noticed. 4. Moisture control: Protect monolithic refractories from direct contact with water or excessive humidity during storage and handling. Moisture absorption can reduce performance and structural integrity. If refractories become wet, thoroughly dry them before use to eliminate absorbed moisture. 5. Stack height: Consider the stack height when storing monolithic refractories. Excessive stacking can apply pressure on lower layers, leading to deformation or cracking. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for maximum stack height to ensure structural integrity. 6. Regular inspection: Regularly inspect the refractory material for any signs of damage or degradation during storage and handling. Look for cracks, spalling, or any visible abnormalities. If any issues are identified, consult the manufacturer or a refractory expert to determine if the material is still suitable for use. By adhering to these recommended storage and handling practices, you can minimize the risk of damage to monolithic refractories, optimize their performance, extend their service life, and ensure their effectiveness in high-temperature applications.
- Q: What are the specific requirements of monolithic refractories for continuous casting applications?
- To withstand the extreme temperatures and thermal shock conditions experienced during continuous casting, monolithic refractories have specific requirements. First and foremost, these refractories must possess high thermal conductivity, enabling them to efficiently transfer heat away from the molten metal and maintain a stable casting temperature. This is crucial in preventing the formation of defects such as cracks, hot spots, and uneven solidification in the cast product. Secondly, monolithic refractories for continuous casting applications need to exhibit high refractoriness. This means they can endure the high temperatures of the molten metal without melting or deforming, ensuring the refractories can provide a protective lining and maintain their structural integrity throughout the casting process. In addition, these refractories must demonstrate excellent resistance to thermal shock. The continuous casting process involves rapid cooling and heating cycles, resulting in significant temperature differentials and inducing thermal stresses. Monolithic refractories with low thermal expansion and high thermal shock resistance can endure these conditions without cracking or spalling. Moreover, good erosion and corrosion resistance are vital requirements for monolithic refractories in continuous casting applications. The molten metal and slag can be highly corrosive and abrasive, causing wear and chemical attack on the refractory lining. Therefore, refractories with high resistance to erosion and corrosion are essential to ensure the longevity and stability of the lining. Lastly, monolithic refractories for continuous casting applications should possess good workability and ease of installation. This allows for efficient and precise lining installation, minimizing downtime during maintenance or repairs. Overall, the specific requirements for monolithic refractories in continuous casting encompass high thermal conductivity, refractoriness, thermal shock resistance, erosion and corrosion resistance, as well as good workability. Fulfilling these requirements guarantees that the refractories effectively safeguard the casting equipment and maintain the quality of the cast products.
- Q: What are the considerations for selecting monolithic refractories for reheating furnaces?
- There are several key considerations when selecting monolithic refractories for reheating furnaces. Firstly, the refractory material must have excellent thermal conductivity to efficiently transfer heat to the steel being reheated. Additionally, it should possess high resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress to withstand the rapid temperature changes and mechanical forces experienced in the furnace. The refractory should also have low porosity to prevent the penetration of gases and slag, ensuring a longer service life. Other factors to consider include the refractory's resistance to corrosive environments, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness. Ultimately, choosing the right monolithic refractory is crucial to ensure optimal furnace performance and longevity.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Henan, China |
| Year Established | 2007 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 60 Million |
| Main Markets | Mid East; Eastern Europe; North America |
| Company Certifications | ISO 9001:2008 |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Tianjin |
| Export Percentage | 31% - 50% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 21-50 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 36,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | Above 5 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | Average |
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry - Fireclay Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords