Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 MT m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
General Information of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
ALRE mullite based mortar for hot blast stove made as per international standards, is known for its low thermal conductivity, high refractoriness, and excellent thermal shock resistance.
Technical data of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
Item | High Alumina Mortar | |
Al2O3(%)≥ | 70 | |
M.O.R. (MPa) ≥ | 110℃×24h | 4 |
1200℃×3h | — | |
1300℃×2h | 6 | |
1400℃×2h | — | |
1500℃×2h | — | |
Grain size(%) | 110℃×24h (≤) | 1 |
1200℃×3h (≥) | 50 | |
Refractoriness (℃) ≥ | 1790 | |
Refractoriness Under Load(℃) ≥ | 1550 | |
Adhesive Time(min) | 1-2 | |
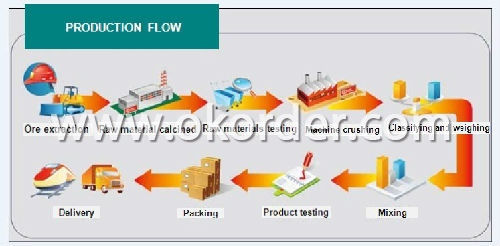
Production line and Packing of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove


Feature of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
Excellent thermal shock resistance
Excellent mechanical strength
Low thermal conductivity
High refractoriness
Application of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
ALRE tmullite based mortar for hot blast stove can be used widely for same material masonry.
Production Flow of Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
- Q: How are monolithic refractories different from traditional brick refractories?
- There are several differences between monolithic refractories and traditional brick refractories. Firstly, monolithic refractories are composed of a single, homogeneous material, whereas traditional brick refractories are made up of individual bricks that are pieced together. This variance in construction allows monolithic refractories to possess a more uniform and consistent structure, which can enhance their performance and durability. Secondly, installing monolithic refractories is typically easier compared to traditional brick refractories. Due to their composition, they can be poured or sprayed into place, eliminating the need for precise bricklaying and mortar application. This simplified installation process saves time and labor during construction or repair projects. Furthermore, monolithic refractories often exhibit superior resistance to thermal shock when compared to traditional brick refractories. The homogeneous structure of monolithic refractories enables them to expand and contract more uniformly under thermal stress, reducing the risk of cracking and failure. This characteristic makes monolithic refractories more suitable for applications with rapid temperature changes, such as in furnaces or kilns. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer better resistance to chemical attacks and erosion. Traditional brick refractories may have joints and gaps between bricks, which can become vulnerable to chemical reactions or erosion over time. Conversely, monolithic refractories possess a seamless structure that minimizes the risk of chemical penetration and erosion, enhancing their longevity and performance. In conclusion, monolithic refractories provide advantages in terms of uniformity, ease of installation, thermal shock resistance, and chemical resistance compared to traditional brick refractories. These disparities make monolithic refractories the preferred choice for numerous industrial applications that involve high temperatures and harsh environments.
- Q: What are the quality control measures for monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- In the iron and steel industry, the quality control measures for monolithic refractories are essential to ensure the efficiency and safety of the production process. These measures involve various inspections and tests throughout the manufacturing and installation stages. Firstly, the raw materials used for monolithic refractories undergo rigorous testing. This includes analyzing the chemical composition, particle size distribution, and impurity content. These tests ensure that the ingredients meet the required specifications and are suitable for the intended application. During the production process, quality control measures focus on monitoring the mixing and blending of the materials. This ensures a homogeneous mixture and avoids any inconsistencies in the final product. The density and viscosity of the refractory castables or plastics are also checked to maintain the desired physical properties. Once the monolithic refractories are manufactured, they undergo several tests to evaluate their performance characteristics. These tests can include determining the cold crushing strength, modulus of rupture, and thermal conductivity. These properties are critical to ensure the refractories can withstand the extreme temperatures and mechanical stress present in the iron and steel industry. In addition to laboratory testing, quality control measures involve on-site inspections during installation. This includes verifying the correct application techniques, such as proper vibration, curing, and drying procedures. It is important to ensure that the monolithic refractories are applied correctly to achieve optimal performance and longevity. Furthermore, regular sampling and monitoring of the refractories' performance during operation are carried out. This allows for the detection of any signs of degradation or wear, enabling proactive maintenance and replacement before any significant issues arise. Overall, the quality control measures for monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry involve comprehensive testing, monitoring, and inspection procedures. These measures aim to guarantee the reliability, durability, and efficiency of the refractories, ultimately contributing to the smooth operation of the iron and steel production processes.
- Q: What are the key trends in the use of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry?
- There are several key trends in the use of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry that are worth noting. Firstly, there is a growing demand for monolithic refractories due to their superior performance characteristics compared to traditional brick refractories. Monolithic refractories offer higher thermal shock resistance, better insulation properties, and improved resistance to chemical attacks. This has led to their increased usage in various applications within the iron and steel industry. Secondly, there is a shift towards the use of low-cement and ultra-low cement castables in monolithic refractories. These materials have a reduced cement content, resulting in improved refractory properties such as higher strength, better corrosion resistance, and increased resistance to thermal spalling. This trend is driven by the need to enhance the overall efficiency and durability of refractory linings in iron and steel manufacturing processes. Another important trend is the development of advanced monolithic refractories with enhanced sustainability and environmental performance. The iron and steel industry is under increasing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint and minimize environmental impact. As a result, there is a growing emphasis on the use of environmentally friendly binders and additives in monolithic refractories. These new materials not only offer excellent refractory properties but also contribute to the industry's sustainability goals. Furthermore, there is a rising focus on the development of monolithic refractories that can withstand extreme operating conditions. Iron and steel manufacturing processes involve high temperatures, aggressive chemical environments, and severe mechanical stresses. Therefore, there is a need for monolithic refractories that can endure these harsh conditions without compromising their performance. The industry is investing in research and development to create refractories that provide exceptional resistance to thermal shock, abrasion, and erosion. Lastly, there is an increasing adoption of digital and smart technologies in the monitoring and maintenance of monolithic refractories. With the advancements in sensor technology and data analytics, it is now possible to collect real-time data on the condition and performance of refractory linings. This allows for proactive maintenance, early detection of potential issues, and optimization of refractory usage, resulting in improved operational efficiency and cost savings. In conclusion, the key trends in the use of monolithic refractories in the iron and steel industry include the demand for superior performance, the shift towards low-cement and ultra-low cement castables, the development of sustainable materials, the focus on extreme operating conditions, and the adoption of digital and smart technologies for monitoring and maintenance. These trends reflect the industry's continuous efforts to enhance the efficiency, durability, and environmental sustainability of refractory linings in iron and steel manufacturing processes.
- Q: What are the key differences between acidic and basic monolithic refractories?
- The key differences between acidic and basic monolithic refractories lie in their chemical composition and the type of environments they can withstand. Acidic refractories are made of silica or alumina and can withstand acidic environments, such as those containing sulfur or phosphorus. On the other hand, basic refractories are made of magnesia or dolomite and are resistant to basic environments, such as those containing calcium oxide or alkalis. Additionally, acidic refractories have higher thermal shock resistance, while basic refractories have higher resistance to chemical attack.
- Q: What are the different techniques for installing monolithic refractories?
- Installing monolithic refractories can be accomplished using various techniques, each with its own advantages and suitability for different applications. Some commonly employed methods are as follows: 1. Casting: This involves creating a slurry by mixing the refractory material with water or a binder. The resulting mixture is then poured into molds or directly onto the prepared surface. Once set and hardened, it forms a solid monolithic structure. 2. Gunning: By utilizing a gunning machine, the refractory material is sprayed onto the surface. The material is combined with water or a binder to form a wet mix, which is then propelled onto the surface at high velocity. Gunning is commonly used for on-site repairs or lining larger areas. 3. Ramming: In this technique, the refractory material is compacted into place using a pneumatic or manual ramming tool. Prior to ramming, the material is typically preheated to decrease moisture content and enhance workability. Ramming is often employed for lining smaller areas or filling gaps between bricks or precast shapes. 4. Shotcreting: Similar to gunning, shotcreting involves using a dry mix of refractory material. The dry mix is combined with water or a binder just before being sprayed onto the surface using a high-pressure nozzle. Shotcreting is frequently used for lining larger areas or creating intricate shapes. 5. Troweling: This technique entails applying the refractory material onto the surface using a trowel or similar tool. The material used is typically a wet mix that is spread and smoothed manually. Troweling is commonly employed for patching or repairing small areas, as well as for adding finishing touches. 6. Vibrating: By using a vibrating tool or vibrator, the refractory material is compacted and any air pockets are eliminated. Vibrating is often used to improve the density and strength of the monolithic refractory after it has been installed using other techniques. It is essential to consider various factors, such as the type of refractory material, the size and shape of the area to be lined, and the specific requirements of the application when selecting the appropriate technique. Additionally, proper surface preparation and adherence to installation guidelines are crucial to ensure the effectiveness and longevity of the monolithic refractory.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the quality of iron and steel products?
- Enhancing the quality of iron and steel products is a crucial role played by monolithic refractories. These refractories consist of a single, solid structure that grants them high resistance against thermal and mechanical stresses. Their unique properties make them suitable for a range of high-temperature applications in the iron and steel industry. To start with, monolithic refractories excel in thermal insulation, maintaining a consistent temperature within furnaces and kilns. This temperature stability is vital for the proper heat treatment of iron and steel, ensuring ideal metallurgical properties and reducing the risk of defects. By preventing heat loss, monolithic refractories promote efficient energy utilization, resulting in cost savings and environmental benefits. In addition, monolithic refractories demonstrate remarkable endurance in the face of harsh operating conditions. The iron and steel manufacturing process involves extreme temperatures, aggressive chemical environments, and mechanical stresses. Monolithic refractories exhibit exceptional resistance to these conditions, ensuring durability and longevity. Their ability to resist thermal shock prevents cracking or spalling, which can lead to contamination and compromised product quality. Furthermore, monolithic refractories provide excellent corrosion resistance, shielding iron and steel products from chemical reactions with molten metal, slag, and other aggressive substances. This resistance not only preserves the integrity of the refractory lining but also prevents contamination of the metal, resulting in improved product quality. Monolithic refractories also offer flexibility in design and installation. They can be shaped, cast, or gunned into various complex geometries, allowing for customization based on the specific requirements of the iron and steel production process. This versatility ensures optimal lining performance, maximizing efficiency and product quality. In conclusion, monolithic refractories significantly contribute to the quality of iron and steel products. Their thermal insulation properties, resistance to harsh operating conditions, corrosion resistance, and design flexibility all play a vital role. By providing a reliable and durable lining in high-temperature applications, monolithic refractories help guarantee consistent and high-quality output in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: What are monolithic refractories and how are they different from other refractory materials?
- Monolithic refractories are a type of refractory material that are composed of a single, homogeneous structure, as opposed to being made up of multiple separate pieces. They are different from other refractory materials, such as bricks or tiles, which are assembled together to form a lining. Monolithic refractories are typically made from a combination of aggregates, binders, and additives, which are mixed together and applied in a plastic or semi-plastic state. This allows for easier installation, as they can be shaped and formed to fit the specific dimensions of the furnace or kiln. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer benefits such as better thermal shock resistance, reduced joints and seams, and improved overall performance due to their seamless nature.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories perform in high-temperature environments?
- Monolithic refractories are highly effective in high-temperature environments due to their unique characteristics. These refractories are made from a single, continuous composition, as opposed to being composed of multiple bricks or tiles. This monolithic structure provides several advantages when it comes to performance in high-temperature conditions. Firstly, monolithic refractories have excellent thermal shock resistance. This means that they can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling. High temperatures can cause significant stress on materials, but the monolithic structure allows for better expansion and contraction, reducing the risk of damage. Additionally, monolithic refractories have high resistance to chemical attack. In high-temperature environments, there are often aggressive chemical agents present that can corrode and erode traditional refractory materials. However, the monolithic composition is usually designed to be chemically inert, providing a protective barrier against these corrosive elements. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer superior strength and durability at high temperatures. Their single composition ensures a dense and compact structure, making them less prone to cracking or breaking under extreme thermal conditions. This strength allows them to maintain their integrity and performance even in the most demanding environments. Furthermore, monolithic refractories can be easily installed and repaired. Unlike traditional refractories, which require precise brick or tile placement, monolithic materials can be poured or sprayed into place, conforming to any shape or size. This flexibility makes installation faster and more cost-effective, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Overall, monolithic refractories excel in high-temperature environments due to their thermal shock resistance, chemical inertness, durability, and ease of installation. Their ability to withstand extreme heat and harsh conditions makes them a preferred choice for industries such as steel, cement, glass, and petrochemicals, where high temperatures are common.
- Q: What are monolithic refractories?
- Monolithic refractories, in contrast to individual bricks or precast shapes, are refractory materials that are manufactured as a single unit. They can be shaped and installed without the need for joints or mortar, making them convenient for lining furnaces, boilers, kilns, and other high-temperature industrial equipment. These refractories consist of a carefully selected mixture of refractory aggregates, binders, and additives. This combination provides desired properties such as high temperature resistance, thermal shock resistance, and chemical durability. Aggregates like alumina, magnesia, zirconia, and silica are used, while binders such as clay, cement, or phosphate hold the aggregates together. One advantage of monolithic refractories is their ability to adapt to complex shapes and designs, allowing for customized linings that meet specific equipment requirements. They can be applied through pouring, gunning, ramming, or spraying onto the surface to be lined, leading to quick and efficient installation. This eliminates the need for time-consuming bricklaying and jointing, reducing installation time and labor costs. Monolithic refractories also possess superior thermal conductivity, enabling them to withstand high temperatures and sudden temperature changes. They offer excellent insulation properties, preventing heat loss and improving energy efficiency in industrial processes. Additionally, these refractories exhibit good resistance to chemical attack from molten metals, slags, gases, and other corrosive substances found in various industrial environments. This makes them highly suitable for applications in steel, cement, glass, petrochemical, and non-ferrous metals industries. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are a versatile and efficient solution for high-temperature applications. Their ability to be shaped and installed without joints or mortar, combined with their excellent thermal conductivity and chemical resistance, make them a valuable choice for lining industrial equipment operating under extreme conditions.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories different from traditional refractory bricks?
- Monolithic refractories are different from traditional refractory bricks because they are not pre-fabricated into brick shapes. Instead, they are supplied as a ready-mix or ready-to-use material that can be directly applied on-site. This eliminates the need for complex brick-laying processes and allows for a more flexible and efficient installation. Monolithic refractories also have superior thermal shock resistance and can withstand higher temperatures, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Henan, China |
| Year Established | 2007 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 200 Million |
| Main Markets | North America;Asia;Western Europe;Africa;Russia;Middle East |
| Company Certifications | ISO 9001:2008 |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Tianjin |
| Export Percentage | 20% - 30% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 10-20 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 150,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | Above 10 |
| Contract Manufacturing | Installation guide, OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | High; Average |
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:Mullite Based Mortar for Hot Blast Stove
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 MT m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords