Alumina Magnesium Castable for Ladle and Tundish
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
General Information of Alumina Magnesium Castable for Ladle and Tundish
Made as per international standards, FIREF alumina magnesium castable for ladle and tundish has been widely accpeted by the customers for its excellent corrosion resistance, long operating life and high refractoriness. Further, they can be provided in different specifications as required.
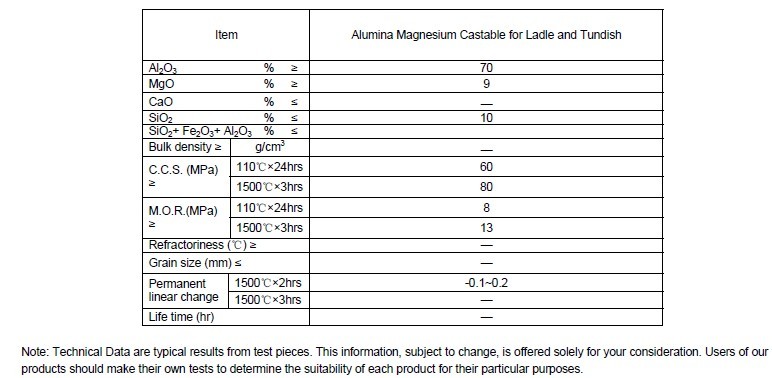
Technical data of Alumina Magnesium Castable for Ladle and Tundish
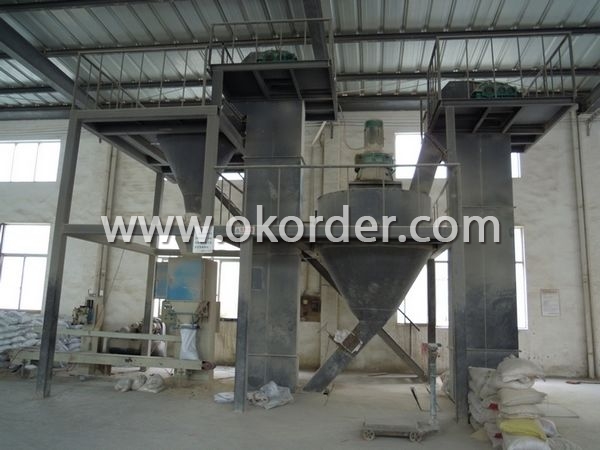
Production line and packing of Alumina Magnesium Castable for Ladle and Tundish


Feature of Alumina Magnesium Castable for Ladle and Tundish
Excellent corrosion resistance
Long operating life
High refractoriness
Application of Alumina Magnesium Castable for Ladle and Tundish
FIREF alumina magnesium castable for ladle and tundish can be used widely in Ladle and Tundish of iron and steel industry.
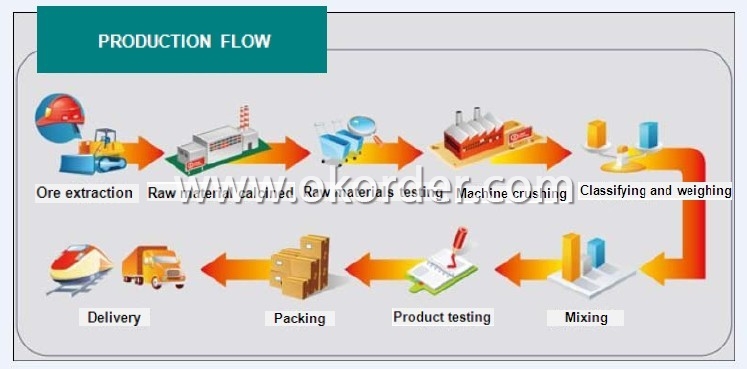
Production Flow of Alumina Magnesium Castable for Ladle and Tundish
- Q:How do monolithic refractories withstand chemical attack from molten metals and slag?
- Monolithic refractories are highly resistant to chemical attack from molten metals and slag due to their unique composition and structure. These refractories are typically made from a single, solid piece with no joints or seams, which minimizes the opportunity for chemical penetration. One of the key factors that enables monolithic refractories to withstand chemical attack is their high melting point. These materials are designed to have a melting point significantly higher than the temperature of the molten metal or slag they are exposed to. This prevents the refractory from melting or deforming when in contact with the hot molten substances. In addition to their high melting point, monolithic refractories are formulated with materials that have excellent chemical resistance. They are often composed of a combination of oxides, such as alumina, magnesia, and zirconia, which have a strong affinity for oxygen and form stable compounds. This allows the refractory to form a protective oxide layer on its surface when exposed to molten metals and slag, effectively shielding it from chemical attack. Furthermore, the dense and compact structure of monolithic refractories plays a crucial role in their resistance to chemical attack. The absence of joints and seams minimizes the chances of molten metals and slag infiltrating the refractory and causing chemical reactions. This dense structure also reduces the porosity of the material, making it less permeable to aggressive substances. Moreover, manufacturers often add specialized additives to monolithic refractories to enhance their chemical resistance. These additives can include fibers, binders, and corrosion inhibitors, which further improve the refractory's ability to withstand chemical attack. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are designed to withstand chemical attack from molten metals and slag through their high melting point, chemical-resistant composition, dense structure, and specialized additives. These properties allow them to maintain their integrity and performance even in the harshest environments, making them an ideal choice for applications involving high-temperature and corrosive substances.
- Q:What are the typical applications of monolithic refractories in blast furnaces?
- Monolithic refractories are commonly used in blast furnaces for various applications, including lining the hearth, taphole, and slag line, as well as repairing cracks and erosion in the furnace lining. They are also used to create a protective barrier against high temperatures, chemical reactions, and mechanical stresses inside the blast furnace.
- Q:What are the main causes of monolithic refractory failure in the iron and steel industry?
- There are several main causes of monolithic refractory failure in the iron and steel industry. One of the primary causes is thermal cycling. The extreme temperatures experienced in iron and steel manufacturing processes, such as melting, casting, and heat treating, subject the refractory lining to significant thermal stress. This repeated expansion and contraction of the material can lead to cracking, spalling, or even complete disintegration of the refractory. Another common cause of failure is chemical attack. The iron and steel industry involves the use of various chemicals, including molten metal, slag, and gases, which can react with the refractory lining. This chemical interaction can cause erosion, corrosion, or chemical decomposition of the refractory material, leading to its failure over time. Mechanical stress is also a significant factor in monolithic refractory failure. The heavy machinery and equipment used in iron and steel production can generate vibrations, shocks, and impacts that can weaken or damage the refractory lining. Additionally, improper installation or design can result in mechanical stress concentration points, making the refractory more susceptible to failure. Furthermore, improper maintenance and operational practices can contribute to refractory failure. Inadequate cooling or heating procedures, improper drying and curing of the refractory, and insufficient cleaning and inspection can all impact the longevity and performance of the material. Lack of regular maintenance and timely repairs can exacerbate small issues, leading to more significant failures over time. Lastly, the choice of refractory material and its quality can play a significant role in failure. Selecting an inappropriate refractory for the specific application or using low-quality materials can result in premature failure. It is crucial to consider factors such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress when choosing the refractory lining to ensure its suitability and durability in the iron and steel industry. In summary, the main causes of monolithic refractory failure in the iron and steel industry are thermal cycling, chemical attack, mechanical stress, improper maintenance and operational practices, and the choice and quality of refractory material. Addressing these factors through proper installation, regular maintenance, and careful material selection can help mitigate refractory failures and improve the overall efficiency and productivity of iron and steel production processes.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories resist erosion from molten metals and slags?
- Monolithic refractories are designed to resist erosion from molten metals and slags through various mechanisms. Firstly, monolithic refractories are made from high-quality materials such as alumina, magnesia, and silica. These materials have excellent resistance to high temperatures and chemical attack, making them capable of withstanding the corrosive nature of molten metals and slags. Secondly, monolithic refractories have a dense structure that prevents the penetration of molten metals and slags. The dense matrix of the refractory material acts as a physical barrier, limiting the contact between the molten material and the refractory itself. Furthermore, monolithic refractories can also contain additives or binders that enhance their erosion resistance. These additives can include silicon carbide, graphite, or other materials that provide additional strength and resistance to erosion. In addition, monolithic refractories can be designed with specific shapes and features to minimize erosion. For example, the refractory lining in a furnace may be designed with curved shapes or baffles to redirect the flow of molten metals and slags, reducing their impact on the refractory surface. Overall, the combination of high-quality materials, dense structure, additives, and tailored designs allows monolithic refractories to effectively resist erosion from molten metals and slags. This resistance ensures the durability and longevity of refractory linings in industrial applications where high temperatures and corrosive environments are present.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories perform in reheating furnace applications?
- Monolithic refractories are highly effective in reheating furnace applications due to their exceptional thermal stability, strength, and resistance to thermal shock. These refractories are designed to withstand high temperatures, rapid temperature changes, and harsh operating conditions commonly found in reheating furnaces. One of the key advantages of monolithic refractories in reheating furnace applications is their ability to provide a seamless lining. Unlike traditional brick refractories, which require extensive installation and joints, monolithic refractories can be easily applied as a single, homogeneous layer. This eliminates the risk of thermal stress and cracking at joints, ensuring a more reliable and durable lining. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer excellent thermal insulation properties, which help to conserve energy and reduce heat loss in the reheating furnace. This not only improves the overall efficiency of the furnace but also reduces operational costs. Moreover, monolithic refractories exhibit high mechanical strength, allowing them to withstand the mechanical stress and abrasion caused by the movement of the furnace charge. They also have good resistance to chemical attack from gases, slags, and molten metals commonly encountered in reheating furnace operations. Furthermore, monolithic refractories can be easily repaired or patched, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous furnace operation. Their ability to be easily shaped and molded to fit various furnace geometries also makes them highly versatile and adaptable to different reheating furnace designs. Overall, monolithic refractories offer exceptional performance in reheating furnace applications by providing superior thermal stability, strength, and resistance to thermal shock. Their seamless lining, thermal insulation properties, and resistance to mechanical and chemical stress make them an ideal choice for ensuring reliable and efficient furnace operation.
- Q:What are the factors affecting the lifespan of monolithic refractories?
- The lifespan of monolithic refractories can be significantly affected by several factors. 1. Operating temperature is a critical factor. While monolithic refractories are designed to withstand high temperatures, prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures can cause thermal shock and lead to premature failure. 2. Thermal cycling, which refers to frequent temperature fluctuations, can also shorten the lifespan of monolithic refractories. The refractory material expands and contracts, creating stress that can result in cracking and degradation over time. 3. The chemical environment where the monolithic refractories are used plays a crucial role in their lifespan. Exposure to corrosive gases, acids, alkalis, or molten metals can cause chemical reactions that degrade the refractory material. 4. Mechanical stress, such as abrasion, impact, and vibration, can weaken monolithic refractories and reduce their lifespan. This is particularly important in industries with high mechanical activity, such as steelmaking or cement production. 5. Proper installation and regular maintenance are essential for maximizing the lifespan of monolithic refractories. Inadequate installation techniques or neglecting maintenance can result in weak joints, inadequate anchoring, or the growth of cracks, leading to premature failure. 6. The quality and composition of the monolithic refractory material greatly impact its lifespan. Higher-quality materials with better resistance to temperature, chemical attacks, and mechanical stress tend to have longer lifespans. 7. The design of the refractory lining and its engineering considerations, such as thickness, shape, and reinforcement, also influence the lifespan of monolithic refractories. A proper design can distribute stress more evenly, reduce thermal gradients, and improve overall performance and durability. 8. The way monolithic refractories are operated and handled can affect their lifespan. Factors such as rapid temperature changes, improper cooling or heating procedures, or excessive thermal cycling can all contribute to premature failure. In conclusion, various factors such as temperature, thermal cycling, chemical environment, mechanical stress, installation and maintenance practices, quality of refractory material, design and engineering considerations, and operating conditions all impact the lifespan of monolithic refractories. Proper management and consideration of these factors are essential for maximizing their lifespan.
- Q:What are the typical properties of monolithic refractories used in iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories used in the iron and steel industry generally possess several key properties that make them suitable for the harsh operating conditions in these industries. Firstly, monolithic refractories have excellent thermal shock resistance. They can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling, which is crucial in the iron and steel industry where the heating and cooling processes can be highly intense. Secondly, these refractories exhibit high refractoriness, meaning they can withstand extremely high temperatures without losing their strength or shape. This is essential in environments where temperatures can reach well above 1000 degrees Celsius. Additionally, monolithic refractories used in the iron and steel industry are known for their excellent corrosion resistance. They can resist the corrosive effects of molten metals, slags, and gases that are commonly encountered in these industrial processes. Furthermore, these refractories have good mechanical strength and abrasion resistance, allowing them to withstand the physical stresses and wear caused by handling and mechanical operations. Another important property of monolithic refractories is their ability to form strong bonds with the existing refractory lining. This ensures a secure and long-lasting installation, reducing the risk of failure and minimizing downtime for maintenance or repairs. Lastly, these refractories often have low porosity, which prevents the infiltration of molten metal or slag into the lining. This helps to maintain the integrity of the refractory structure and prolong its service life. Overall, the typical properties of monolithic refractories used in the iron and steel industry include thermal shock resistance, high refractoriness, corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, strong bonding, and low porosity. These properties collectively contribute to the efficient and reliable operation of iron and steel manufacturing processes.
- Q:How are monolithic refractories used in the repair and maintenance of ladle and tundish linings?
- Monolithic refractories are a type of refractory material that is commonly used in the repair and maintenance of ladle and tundish linings in the steel industry. These linings are crucial components of ladles and tundishes, which are used for the transportation and treatment of molten metal during the steelmaking process. When ladle and tundish linings are subjected to high temperatures and corrosive environments, they can deteriorate over time. This deterioration can lead to various issues such as heat loss, contamination of molten metal, and reduced refractory lining lifespan. To address these problems, monolithic refractories are used as repair and maintenance materials. Monolithic refractories are typically made from a combination of different refractory aggregates, binders, and additives. They are available in various forms, such as castables, gunning mixes, and ramming mixes. These materials are designed to be easily applied and shaped to conform to the specific geometry and dimensions of the ladle or tundish lining. During the repair process, the damaged areas of the lining are removed, and the monolithic refractories are then applied to these areas. Castables can be poured and vibrated into place, while gunning mixes can be sprayed using a high-pressure gunning machine. Ramming mixes, on the other hand, are manually compacted into the lining using a ramming tool. Monolithic refractories offer several advantages in the repair and maintenance of ladle and tundish linings. Firstly, their flexibility allows for easy installation and shaping, ensuring a snug fit to the lining. This helps to maximize the effectiveness of the refractory lining in preventing heat loss and maintaining the integrity of the ladle or tundish. Secondly, monolithic refractories have excellent thermal shock resistance and resistance to chemical attack. This makes them highly durable and capable of withstanding the harsh conditions encountered in ladles and tundishes. They can withstand repeated heating and cooling cycles without cracking or spalling, providing long-lasting protection to the lining. Lastly, monolithic refractories can be easily repaired and replaced when necessary. Their application and removal processes are relatively straightforward, allowing for efficient maintenance of ladle and tundish linings. This helps to minimize downtime and maintain the overall productivity of the steelmaking process. In conclusion, monolithic refractories play a crucial role in the repair and maintenance of ladle and tundish linings. Their ease of application, excellent thermal shock resistance, and resistance to chemical attack make them ideal materials for extending the lifespan and optimizing the performance of these linings in the steel industry.
- Q:What are some common maintenance practices for monolithic refractories in iron and steel furnaces?
- Some common maintenance practices for monolithic refractories in iron and steel furnaces include: 1. Regular inspections: Conducting routine inspections is essential to identify any potential issues with the monolithic refractories. Inspections should be carried out by trained professionals who can assess the condition of the refractories and detect any signs of wear, erosion, or damage. 2. Repair and patching: Promptly repairing any damaged or eroded areas is crucial to prevent further deterioration and maintain the integrity of the refractories. Patching materials, such as refractory mortars or castable refractories, can be used to fill in gaps or repair small cracks. 3. Cleaning: Regularly cleaning the refractory lining helps to remove any build-up of slag, scale, or other impurities that can negatively impact the performance of the refractories. Cleaning can be done mechanically, using brushes or scrapers, or through chemical methods such as acid cleaning. 4. Thermal cycling: Controlled thermal cycling is often performed to condition and strengthen the monolithic refractories. This involves gradually increasing and decreasing the temperature of the furnace to improve the refractory's resistance to thermal shock. 5. Coating and sealing: Applying protective coatings or sealants to the refractory lining can help enhance its resistance to chemical attack, erosion, and thermal cycling. These coatings act as a barrier, preventing the penetration of molten metals or slags into the refractory material. 6. Monitoring and control: Continuous monitoring of operating conditions such as temperature, pressure, and atmosphere inside the furnace is important to prevent any sudden changes that may negatively affect the refractories. Maintaining proper control over these parameters helps to extend the life of the monolithic refractories. 7. Training and education: Providing regular training and education to furnace operators and maintenance personnel is crucial for them to understand the importance of proper refractory maintenance practices. This ensures that the refractories are handled and operated correctly, reducing the risk of premature failure. Overall, implementing these maintenance practices can significantly prolong the lifespan of monolithic refractories in iron and steel furnaces and maximize their performance, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness in the production process.
- Q:What are the main challenges in designing the lining system with monolithic refractories?
- One of the main challenges in designing the lining system with monolithic refractories is achieving proper installation. Monolithic refractories are typically installed by casting, gunning, or shotcreting, which requires skilled labor and precise application techniques. Any errors or inconsistencies during installation can compromise the performance and longevity of the lining system. Another challenge is ensuring adequate bonding between the monolithic refractories and the existing structure. Proper adhesion is crucial to prevent refractory material from delaminating or separating from the underlying surface. Factors such as surface preparation, temperature differentials, and mechanical stress can affect the bond strength, requiring careful consideration during the design phase. The compatibility of monolithic refractories with various operating conditions is another challenge. Refractory materials are exposed to extreme temperatures, chemical reactions, and thermal cycling, which can lead to degradation and failure. Designing a lining system that can withstand these conditions requires a thorough understanding of the refractory properties and the specific requirements of the application. Furthermore, selecting the right monolithic refractory material for a given lining system is a significant challenge. There are various types of monolithic refractories available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Factors such as temperature range, chemical composition, thermal conductivity, abrasion resistance, and thermal shock resistance need to be considered when choosing the most suitable material for the application. Lastly, maintaining the integrity of the monolithic refractory lining system over its lifetime is a challenge. Regular inspections, repairs, and maintenance are necessary to address any issues such as cracks, erosion, or spalling. Developing a comprehensive maintenance plan and ensuring access to skilled personnel for repairs are essential aspects of designing a successful lining system with monolithic refractories.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | Henan, China |
| Year Established | 2007 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 60 Million |
| Main Markets | Mid East; Eastern Europe; North America |
| Company Certifications | ISO 9001:2008 |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Tianjin |
| Export Percentage | 31% - 50% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 21-50 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 36,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | Above 5 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | Average |
Send your message to us
Alumina Magnesium Castable for Ladle and Tundish
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords



























