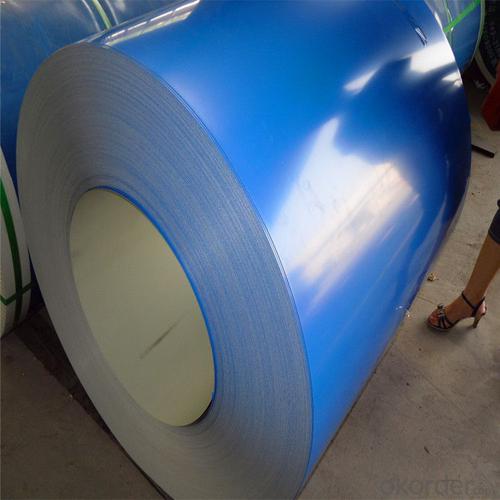
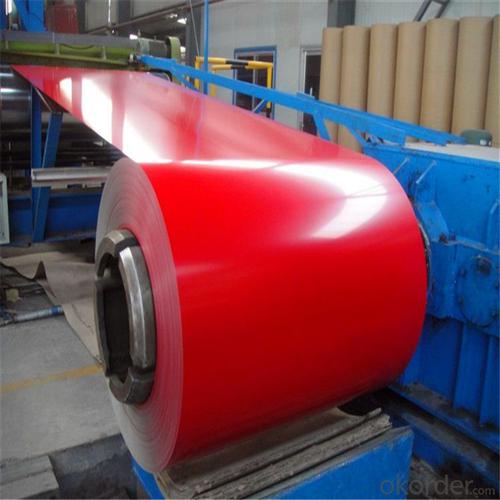
Secondary PPGI Steel Coils from Shangdong
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Item specifice
Secondary PPGI Steel Coils
Description of Secondary PPGI Steel Coils
Product | PPGI/PPGL |
Capacity | 5,000 tons/month |
Base material | Hot dipped galvanized steel |
Thickness | 0.2-2.0mm |
Width | 600-1250mm(according to your need) |
Coil Weight | 3-6tons |
Quality | SGCC, DX51D |
Color | RAL No. or customers samples’ color |
Zinc-coating | 30g/m2-180g/m2 |
Coil ID | 508mm/610mm |
Technique | Cold rolled—hot dipped galvanized—color coated |
Painting | Top painting:15~25μm |
Back painting: 6~10μm | |
Tolerance | Thickness: +/-0.02mm |
Width:+/-2mm | |
Shipment time | within 15-45 workdays |
Payment | T/T, L/C at sight |
Packing | Standard export packing |
The special order can be negotiated. | |
Application of Secondary PPGI Steel Coils
APPLICATION OF OUR PREPAINTED STEEL | ||||||||||
Construction | Outside | Workshop,agricultural warehouse,residential precast unit | ||||||||
corrugated roof,roller shutter door,rainwater drainage pipe,retailer booth | ||||||||||
Inside | Door,doorcase,light steel roof stucture,folding screen,elevator,stairway,ven gutter,Construction Wall | |||||||||
Electrical applicance | Refrigerator,washer,switch cabnet,instrument cabinet,air conditioning,micro-wave owen,bread maker | |||||||||
Fuiniture | Central heating slice,lampshade,chifforobe,desk,bed,locker,bookself | |||||||||
Carrying trade | Exterior decoration of auto and train,clapboard,container,isolation lairage,isolation board | |||||||||
Qthers | Writing panel,garbagecan,billboard,timekeeper,typewriter,instrument panel,weight sensor,photographic equipment | |||||||||
Products Show of Secondary PPGI Steel Coils

Product Advantages
1.With nearly 20 years experience in prepainted steel, accommodate different marketdemands. | ||||||||||||||
2.'Quality first, service first' is our business aim; 'The good faith get respect,cast quality market' is our Business philosophy . | ||||||||||||||
3.Having two series producttion line,with the abbual production capacity of 240000 tons. | ||||||||||||||
4.Exceed International ISO9001:2008&ISO14001:2004 quality and environmental standards | ||||||||||||||
5.Meet with ROHS standard |
Company Information
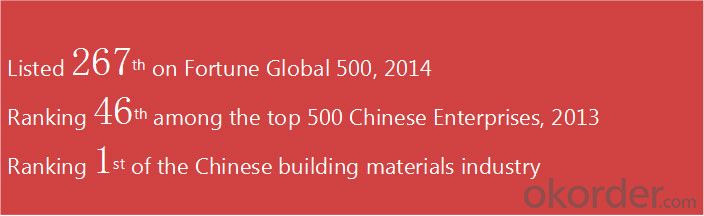
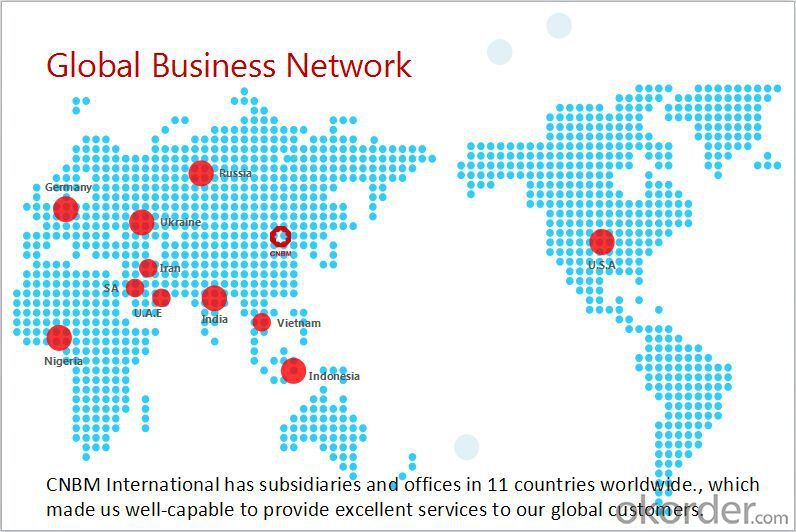
CNBM International Corporation is the most important trading platform of CNBM group.
Whith its advantages, CNBM International are mainly concentrate on Cement, Glass, Iron and Steel, Ceramics industries and devotes herself for supplying high qulity series of refractories as well as technical consultancies and logistics solutions.
F A Q
1, Your advantages?
professional products inquiry, products knowledge train (for agents), smooth goods delivery, excellent customer solution proposale
2, Test & Certificate?
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem
3, Factory or Trading Company?
CNBM is a trading company but we have so many protocol factories and CNBM works as a trading department of these factories. Also CNBM is the holding company of many factories.
4, Payment Terms?
30% TT as deposit and 70% before delivery.
Irrevocable L/C at sight.
5, Trading Terms?
EXW, FOB, CIF, FFR, CNF
6, After-sale Service?
CNBM provides the services and support you need for every step of our cooperation. We're the business partner you can trust.
For any problem, please kindly contact us at any your convenient time.
We'll reply you in our first priority within 24 hours.
- Q:What are the factors that can affect the machinability of special steel?
- There are several factors that can affect the machinability of special steel. One of the main factors is the composition of the steel. The presence of certain elements such as carbon, chromium, and nickel can greatly influence the machinability. For example, high carbon content can result in increased hardness and brittleness, making the steel more difficult to machine. On the other hand, the addition of elements like sulfur and lead can improve machinability by enhancing chip formation and reducing friction. The heat treatment of the steel also plays a significant role in machinability. Different heat treatments, such as annealing or quenching, can alter the microstructure of the steel, affecting its hardness and toughness. Heat-treated steels may be more difficult to machine due to their increased hardness or the presence of residual stresses. The mechanical properties of special steel, such as hardness and tensile strength, can also impact machinability. Harder steels require more cutting force and may result in increased tool wear or vibration during machining. Similarly, steels with high tensile strength may pose challenges in terms of chip formation and tool life. The cutting conditions and machining parameters used also affect machinability. Factors such as cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut can significantly impact the process. High cutting speeds can result in increased temperatures and tool wear, while low cutting speeds may lead to poor surface finish. Additionally, the choice of cutting tools, their geometry, and their coatings can also influence the machinability of special steel. Finally, the presence of impurities or contaminants in the steel, such as non-metallic inclusions or surface defects, can negatively affect machinability. These impurities can cause tool wear, poor surface finish, or even tool breakage. Therefore, the quality and cleanliness of the steel are crucial for achieving good machinability. In summary, the factors that can affect the machinability of special steel include its composition, heat treatment, mechanical properties, cutting conditions, and the presence of impurities. Understanding and optimizing these factors can help improve the machinability and overall performance of special steel during machining operations.
- Q:What are the different mechanical defects in special steel?
- There are several mechanical defects that can occur in special steel, which can compromise its overall strength and performance. Some of the most common defects include: 1. Inclusions: Inclusions are foreign particles or impurities that are present in the steel. These can include oxides, sulfides, or other non-metallic materials. Inclusions can weaken the steel and reduce its ductility, making it more prone to cracking or failure. 2. Segregation: Segregation refers to the uneven distribution of alloying elements within the steel. This can lead to variations in hardness, strength, and other mechanical properties across the material. Segregation can create localized areas of weakness, increasing the likelihood of failure under stress. 3. Cracks: Cracks can occur in special steel due to a variety of factors, such as improper cooling, excessive heat, or high levels of stress. Cracks can significantly reduce the structural integrity of the steel and may propagate over time, leading to catastrophic failure. 4. Laminations: Laminations are thin layers or sheets of material that are formed during the manufacturing process. They can occur due to improper rolling or forging, or the presence of inclusions. Laminations can weaken the steel and lead to premature failure under load. 5. Decarburization: Decarburization is the loss of carbon from the surface of the steel, typically due to exposure to high temperatures or oxidation. This can result in a layer of softer, lower carbon steel on the surface, reducing the overall hardness and strength of the material. 6. Grain growth: Grain growth occurs when the individual crystals within the steel (grains) grow larger over time. This can happen due to high temperatures, prolonged exposure to stress, or improper heat treatment. Grain growth can reduce the strength and toughness of the steel, making it more prone to deformation or fracture. It is important to note that these mechanical defects can vary in severity and are often influenced by factors such as the manufacturing process, quality control measures, and the specific composition of the special steel. Regular inspection, testing, and adherence to proper handling and processing techniques are essential to minimize these defects and ensure the desired mechanical properties in special steel.
- Q:What are the properties of die steel?
- Die steel is a type of tool steel known for its high hardness, wear resistance, and toughness. It possesses excellent dimensional stability, allowing it to maintain its shape and size even under extreme temperature variations. Die steel also has good machinability and can be easily shaped and formed into intricate designs. Additionally, it offers high thermal conductivity, enabling efficient heat transfer during the die-casting process.
- Q:What are the different surface treatment methods for special steel?
- Some of the different surface treatment methods for special steel include heat treatment, coating or plating, polishing, shot blasting, and passivation. Heat treatment involves subjecting the steel to specific temperatures and cooling processes to alter its properties. Coating or plating involves applying a layer of another material, such as zinc or chrome, to protect the steel from corrosion. Polishing is done to create a smooth and glossy surface finish. Shot blasting is a process that involves using abrasive materials to remove impurities and create a textured surface. Passivation is a chemical treatment used to remove iron contaminants and improve corrosion resistance. These methods can be utilized individually or in combination to enhance the surface characteristics of special steel.
- Q:What are the benefits of using special steel in the energy sector?
- Using special steel in the energy sector comes with various advantages. To begin with, special steel provides exceptional strength and durability, making it the ideal material for constructing different energy infrastructure components like pipelines, pressure vessels, and turbines. Its high tensile strength and resistance to corrosion ensure that these structures can withstand the harsh conditions and pressures encountered in the energy sector, thereby reducing the risk of failures and increasing their lifespan. Additionally, special steel exhibits excellent heat resistance properties, which is crucial in the energy sector where high temperatures are generated. This makes it suitable for applications such as power generation, where it can be used in the construction of boilers, heat exchangers, and nuclear reactors. The ability of special steel to withstand extreme heat without deforming or losing its mechanical properties is vital for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of energy facilities. Furthermore, special steel offers superior weldability and formability, allowing for easier fabrication and assembly of complex energy infrastructure components. This makes it easier and more cost-effective to manufacture and install equipment in the energy sector, reducing both production costs and construction time. Another advantage of using special steel in the energy sector is its resistance to fatigue and cracking. Energy infrastructure components are subjected to cyclic loading and stress, which can lead to fatigue failure over time. The ability of special steel to resist fatigue and crack propagation ensures the long-term reliability and safety of energy infrastructure. Moreover, special steel offers excellent magnetic properties, making it suitable for use in power transmission and electrical equipment. Its magnetic permeability and low electrical resistance allow for efficient transmission and distribution of electricity, reducing energy losses and improving overall system performance. In conclusion, the use of special steel in the energy sector provides enhanced strength, durability, heat resistance, weldability, and fatigue resistance. These properties contribute to the reliability, safety, and efficiency of energy infrastructure, making special steel an invaluable material for the energy sector.
- Q:How is case-hardening steel used in the production of gears and shafts?
- Case-hardening steel is used in the production of gears and shafts to provide them with a hard outer layer, while maintaining a tough and durable core. The steel is heated and then subjected to a process known as carburizing, where it comes into contact with carbon-rich materials to absorb carbon into its surface. This process creates a high carbon concentration at the outer layer, resulting in increased hardness and wear resistance. The case-hardened gears and shafts offer superior durability, allowing them to withstand heavy loads and friction in various applications.
- Q:What are the different types of special steel?
- There are several types of special steel, including stainless steel, tool steel, alloy steel, and high-speed steel. Each type has unique properties and characteristics that make them suitable for specific applications. Stainless steel is corrosion-resistant and commonly used in kitchen utensils and construction materials. Tool steel is known for its hardness and used in cutting tools and dies. Alloy steel contains additional elements to enhance strength, toughness, and wear resistance, often used in automotive and construction industries. High-speed steel is designed to withstand high temperatures and used in cutting tools and drill bits.
- Q:How is special steel used in toolmaking?
- Due to its exceptional properties, special steel is widely utilized in toolmaking to create durable and high-performance tools. Various tools, including drills, saws, cutting tools, dies, and molds, are manufactured in toolmaking. The purpose of incorporating special steel in toolmaking is to guarantee that these tools possess the necessary strength, hardness, toughness, and wear resistance needed for their intended applications. The primary advantage of special steel in toolmaking is its high strength. This is achieved by alloying special steel with elements such as chromium, molybdenum, vanadium, and tungsten, which enhance its strength and hardness. Consequently, the tools can endure heavy loads, resist deformation, and maintain their structural integrity even under extreme working conditions. In addition to strength, special steel also exhibits excellent hardness. Heat treatment processes like quenching and tempering are applied to tools made from special steel to achieve the desired hardness level. This hardness is crucial in toolmaking as it allows the tools to efficiently cut, drill, or shape various materials without succumbing to damage or wear easily. Furthermore, special steel possesses exceptional toughness. Toughness refers to a material's ability to absorb energy and resist cracking or fracturing. Tools made from special steel can withstand impact and heavy loads, ensuring that they remain intact and do not chip easily during use. This is of utmost importance in toolmaking as tools often encounter high-stress situations where toughness is essential to prevent premature failure. Another significant advantage of special steel in toolmaking is its excellent wear resistance. Constant friction, abrasion, and contact with hard materials subject tools to wear and tear. Special steel is designed specifically to resist wear, allowing the tools to maintain their cutting or shaping abilities over prolonged periods. Consequently, the tool's lifespan is extended, ensuring consistent performance and high-quality output. Special steel is also renowned for its corrosion resistance, which is advantageous in toolmaking, especially when working with corrosive materials or in harsh environments. The inclusion of certain elements like chromium in special steel enhances its resistance to corrosion, preventing rust and deterioration of the tools. In conclusion, special steel is an indispensable material in toolmaking as it provides the necessary strength, hardness, toughness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. These properties enable tools to perform effectively and efficiently, ensuring durability and longevity. Whether it is for cutting, drilling, shaping, or molding, special steel is essential in producing high-quality tools that meet the demands of various industries.
- Q:How is special steel used in the production of consumer goods?
- Special steel is used in the production of consumer goods due to its exceptional strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. It is commonly employed in the manufacturing of kitchen appliances, cutlery, automotive parts, and electronics, ensuring high-quality and long-lasting products for consumers.
- Q:What is the role of boron in special steel alloys?
- Boron plays a crucial role in special steel alloys, particularly in enhancing their mechanical properties and overall performance. One of the primary functions of boron is as a hardenability agent, meaning it improves the hardness and strength of the steel. This is achieved through the formation of boride particles, which act as strengthening agents within the microstructure. Additionally, boron aids in the refinement of the grain structure of steel, resulting in improved toughness and resistance to cracking. It promotes the formation of fine-grained microstructures, which in turn increase the steel's ability to withstand high temperatures, pressure, and wear. Moreover, boron assists in the solidification process of steel, reducing the risk of hot cracking during casting or welding. It lowers the melting point of steel, allowing for better fluidity and improved flowability during manufacturing processes. Furthermore, boron can also enhance the machinability of steel alloys, making them easier to work with and reducing tool wear. Overall, the addition of boron to special steel alloys significantly contributes to their strength, hardness, toughness, and resistance to various forms of degradation. Its role is vital in optimizing the performance and durability of these alloys in demanding applications such as automotive components, aerospace structures, and industrial machinery.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Secondary PPGI Steel Coils from Shangdong
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords