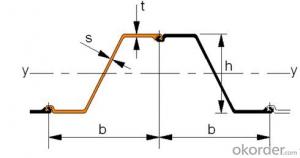
Bilstein Cold Rolled Steel
Bilstein Cold Rolled Steel Related Searches
Cold Rolled Steel Cold Rolled Steel Plate Hot Rolled Mild Steel Cold Rolled Steel Price Cold Rolled Steel Prices Hot Rolled Steel Cold Rolled Steel Grades Galvanized Steel Roll Hot Rolled Steel Plate Hot Rolled Steel Prices Weld Galvanized Steel Hot Rolled Steel Price Stainless Steel Blackstone Galvanized Corrugated Steel Stainless Steel Roller Rusting Galvanized Steel Steel Galvanized High Speed Steel Rusted Galvanized Steel Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Cold Forming Aluminum German Stainless Steel Corrugated Galvanized Steel Vollrath Stainless Steel Grinding Wheels For Steel Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Powder Coating Galvanized Steel Hot Rolled Steel Futures Colander Stainless Steel Galling Stainless SteelBilstein Cold Rolled Steel Supplier & Manufacturer from China
Bilstein Cold Rolled Steel is a high-quality steel product that is manufactured through a precise process of rolling steel at room temperature. This results in a smooth, uniform surface and tight tolerances, making it ideal for various applications that require precision and strength. The product is known for its excellent formability, weldability, and machinability, which makes it suitable for a wide range of industries such as automotive, construction, and manufacturing.Bilstein Cold Rolled Steel is widely used in the production of various components and structures due to its superior mechanical properties and durability. It is commonly employed in the manufacturing of automotive parts, such as chassis, suspension systems, and body panels, as well as in the construction of buildings and infrastructure, including beams, columns, and frames. The product's versatility and reliability make it a popular choice for engineers and designers who demand the highest standards of performance and safety.
Okorder.com is a leading wholesale supplier of Bilstein Cold Rolled Steel, offering a vast inventory of this premium product to cater to the needs of various industries. With a strong commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, Okorder.com ensures that each order is fulfilled with the utmost care and attention to detail. By maintaining a large inventory, they are able to provide prompt delivery and competitive pricing, making them a trusted choice for businesses seeking to source high-quality Bilstein Cold Rolled Steel for their projects.
Hot Products