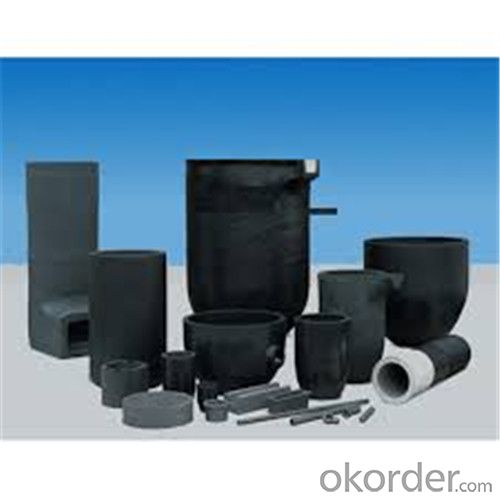
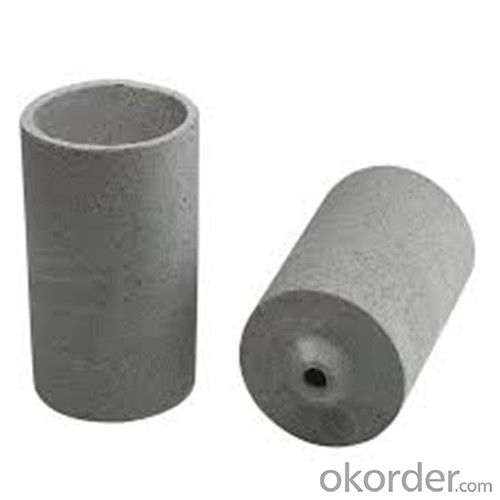
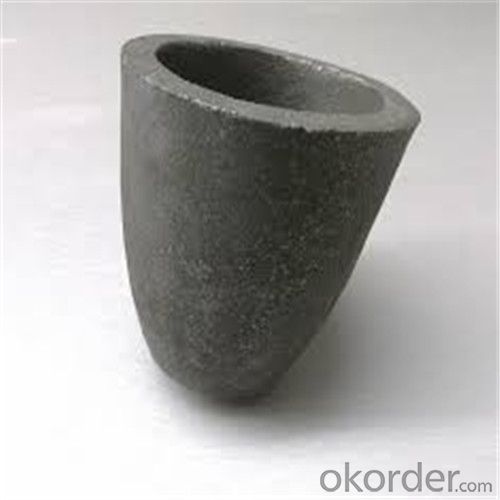
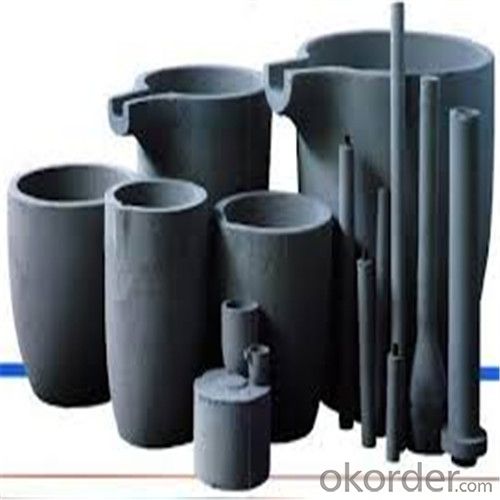
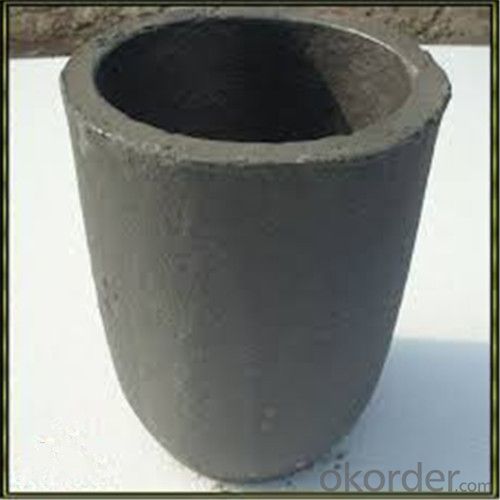
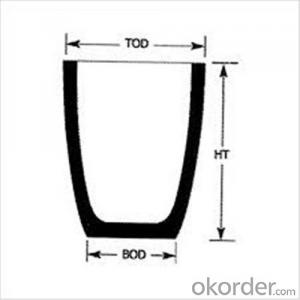
Graphite Crucible Small - Refractory SIC Crucible for Brass/Aluminum
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
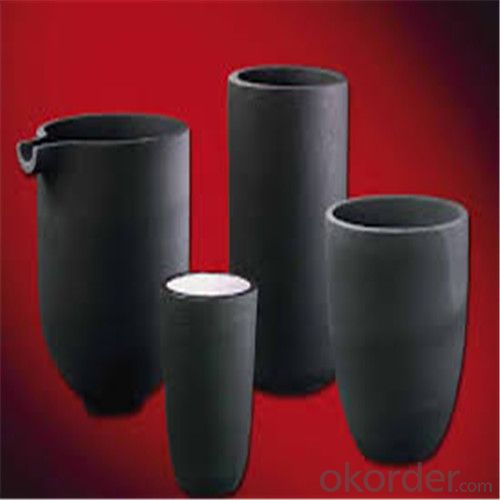
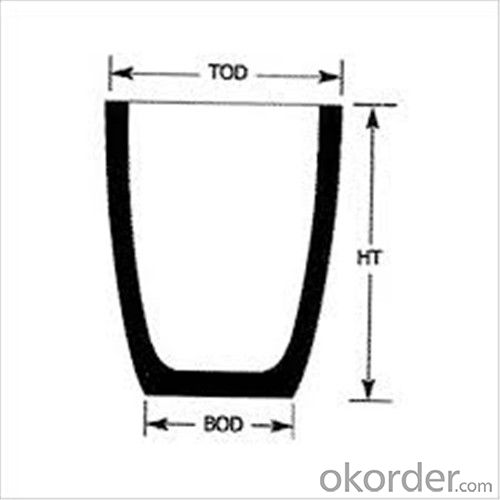

Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
Physicochemical Properties
Type of Crucible | Type S | Type D |
Carbon Content/% | ≥38 | ≥45 |
Bulk Density/(g/cm3) | ≥1.70 | ≥1.85 |
Apparent Porosity/% | ≤29 | ≤21 |
Compression Strength/MPa | ≥20 | ≥25 |
Refractoriness/°C | ≥1400 | ≥1400 |
Type S: Clay graphite crucible
Type D: Isostatic pressing graphite crucible
Cited from CNS China National Standard of Graphite Crucible, which is solely drifted by TIANFU company.
Content Composition
C% | Sic% | AL2O3% | SIO2% |
45%-50% | 20%-30% | 10%-12% | 15-25% |
Packaging & Shipping
Package: Wooden case and wooden pallet or pack as customer's requirement of graphite crucible.
Delivery time: depend on distance, usually 20 days to 50days after deposit of graphite crucible.
We can supply the products according to customer's drawings, samples and performance requirement.
Other Products


FAQ
1.What's your MOQ?
We will indicate the MOQ for each item in the quotation list. We accept the sample and trail order.
2.Can I negotiate the Prices?
Sure, we may consider discounts for bulk order of products.
3.How long will it take to complete my order?
For the stock items, we can arrange the shippment within 2~3days after received your payment. For the customized items, we will indicate the delivery time in the quotation list.
4.Can you give warranty of your products?
Yes, we extend a 100% satifisfaction guarantee on all items. Please feel free to provide timely feedback if you're not satisfied with N&D's Quality and Service. For the overseas orders, if there is a quality problem, please kindly to provide the picturers to show the problem by e-mail. We will provide the replacements to you at our cost according to actual conditions.
Welcome to visit our factory.
- Q: Why does China choose quartz crucible directly in the aspect of Czochralski silicon?
- Because (1) the melting point of silicon is at 1450 degrees, the container for molten silica must be sufficiently high. (2) Czochralski silicon is the rearrangement of the atomic structure. High purity is essential and insoluble impurities. Quartz crucible material is SiO2, high temperature and stability, will not bring other impurities. That is, the O atoms of the quartz crucible also affect the quality of monocrystalline silicon. (3) when foreign countries engage in these scientific studies, China is still living long with the emperor, so these technologies were introduced into China in the last century of 50s, and the current development is still 50 years from home!
- Q: Is the silicon carbide crucible good for use? What's the difference between an ordinary graphite crucible and a graphite crucible?
- Easy to use and convenient.The ordinary graphite crucible can not guarantee the safety in the high temperature environment, moreover, the conduction speed is slow in the test, which is not good for the experiment.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for melting refractory metals?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for melting refractory metals. Graphite has excellent thermal conductivity and high melting point, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. Refractory metals, such as tungsten, molybdenum, and niobium, have extremely high melting points and can easily withstand the temperatures reached in a graphite crucible. Additionally, graphite has low reactivity with most metals, making it a suitable material for containing and melting refractory metals without contamination. However, it is important to choose a high-quality graphite crucible that is specifically designed for melting refractory metals to ensure optimal performance and durability.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for powder injection molding?
- Yes, a graphite crucible can be used for powder injection molding. Graphite is a popular choice for crucibles in various high-temperature applications due to its excellent thermal conductivity, high melting point, and low chemical reactivity. In powder injection molding, a graphite crucible can withstand the high temperatures required for the process, typically ranging from 1300 to 1600 degrees Celsius. Additionally, graphite crucibles provide good resistance to thermal shock and can effectively contain the molten feedstock during the injection molding process. Overall, using a graphite crucible in powder injection molding is a suitable option due to its favorable characteristics and compatibility with the required operating conditions.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for semiconductor doping?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for semiconductor doping. Graphite crucibles are commonly used in the semiconductor industry due to their unique properties. They have high thermal conductivity, chemical inertness, and can withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for various semiconductor manufacturing processes, including doping. During the doping process, impurity atoms are introduced into the semiconductor material to modify its electrical properties. Graphite crucibles can be used to hold the dopant material and the semiconductor wafer during the doping process. The crucible provides a stable and controlled environment for the diffusion of dopant atoms into the semiconductor material. Graphite crucibles also offer good thermal stability, which is crucial during the doping process as it involves heating the wafer to high temperatures. The crucible helps in maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the process, ensuring uniform doping across the semiconductor wafer. Furthermore, graphite crucibles are chemically inert, meaning they do not react with the dopant material or the semiconductor material. This is important to prevent any contamination or unwanted reactions that could affect the doping process or the quality of the semiconductor material. In conclusion, graphite crucibles are commonly used for semiconductor doping due to their high thermal conductivity, chemical inertness, and ability to withstand high temperatures. They provide a stable and controlled environment for the doping process, ensuring uniform doping across the semiconductor wafer.
- Q: What are the different methods of monitoring the melting process in a graphite crucible?
- There are various techniques available to monitor the melting process in a graphite crucible, which can offer valuable insights into the temperature, consistency, and progress of the process. 1. Visual Inspection: An uncomplicated method involves visually examining the melting process. This entails observing the color, consistency, and movement of the materials as they melt. For instance, if the materials transform into a liquid state and flow smoothly, it indicates that the melting process is proceeding as anticipated. 2. Thermocouples: Widely utilized for temperature measurement in industrial processes, thermocouples are employed for melting in graphite crucibles. These devices consist of two dissimilar metals joined together at one end. By measuring the voltage difference between the two ends, the temperature can be determined. Accurate temperature monitoring can be achieved by inserting thermocouples into or near the crucible. 3. Infrared Pyrometers: Non-contact temperature measurement devices known as infrared pyrometers utilize infrared radiation to determine an object's temperature. They can be utilized to monitor the temperature of the graphite crucible during the melting process without physical contact. Infrared pyrometers offer swift and precise temperature readings. 4. Optical Emission Spectroscopy (OES): OES is a technique that analyzes the light emitted by the melting materials to ascertain their composition and temperature. By analyzing the spectral lines and intensities of the emitted light, OES can provide valuable information about the melting process, including temperature and the presence of impurities or alloying elements. 5. Pressure Measurement: Monitoring the pressure within the graphite crucible can serve as an indicator of the melting process. As the materials melt and vaporize, the pressure inside the crucible may increase. Pressure sensors can be utilized to measure pressure changes during the melting process, offering insight into the progress of the melting and the behavior of the materials. These techniques can be employed individually or in combination to monitor the melting process in a graphite crucible. By utilizing one or more of these methods, operators can ensure that the melting process is proceeding as intended and make any necessary adjustments or interventions to maintain optimal conditions.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for melting food-grade substances?
- No, a graphite crucible should not be used for melting food-grade substances as graphite can react with the food and contaminate it. It is important to use food-grade materials specifically designed for heating and melting food substances.
- Q: What are the considerations for selecting a crucible stand for graphite crucibles?
- There are several key considerations when selecting a crucible stand for graphite crucibles. Firstly, the material of the stand should be compatible with graphite, as some materials can react with graphite and cause contamination or degradation. Additionally, the stand should have sufficient stability and strength to support the weight of the crucible and withstand high temperatures without warping or deforming. It is also important to consider the design and shape of the stand, ensuring that it securely holds the crucible and minimizes the risk of tipping or spilling. Finally, factors such as cost, availability, and ease of use should also be taken into account when selecting a crucible stand for graphite crucibles.
- Q: What are the different methods of sealing a graphite crucible?
- Several methods exist for sealing a graphite crucible, each with its own advantages and considerations. One commonly used method involves the application of a graphite cement or adhesive to the joints or seams of the crucible, which is then allowed to dry or cure. This method ensures a strong and durable seal that remains intact even during high-temperature applications. However, it can be time-consuming and may require periodic reapplication. Another approach is to employ a graphite crucible cover or lid, placed on top of the crucible to create a seal. This method is relatively quick and easy to implement. However, it may not provide as tight of a seal as other methods, necessitating proper alignment and fitting of the lid or cover. In some cases, a combination of mechanical fasteners like bolts or clamps, along with a high-temperature gasket material, can be used to seal the crucible. This involves securing the crucible joints with the fasteners and applying gasket material for a tight seal. This method ensures a reliable and secure seal, even under high-temperature conditions. However, it may demand additional time and effort for installation and removal of the fasteners and gasket material. It is crucial to consider the specific application and requirements when selecting the appropriate sealing method for a graphite crucible. Factors such as operating temperature, duration, and the type of material being processed should be taken into account. Consulting the manufacturer's guidelines and instructions for the specific crucible being used is recommended to ensure proper sealing techniques are followed.
- Q: Can sintering rare earth fluorides be made of corundum crucibles?
- Graphite crucibleIs the crucible, crystalline form of natural graphite as the main raw material, plastic refractory clay as binder, refractory graphite crucible with different types of clinker with which is mainly used in smelting special alloy steel, nonferrous metals and alloy melting. Graphite crucibles are an integral part of refractories in terms of their properties and uses.
Send your message to us
Graphite Crucible Small - Refractory SIC Crucible for Brass/Aluminum
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords