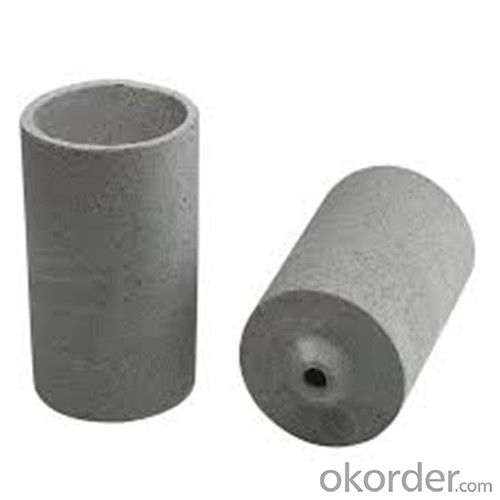
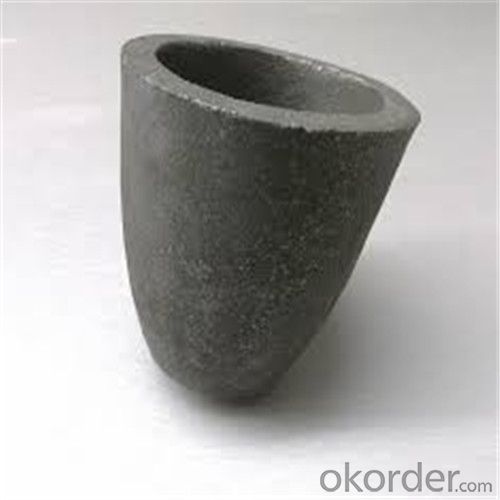
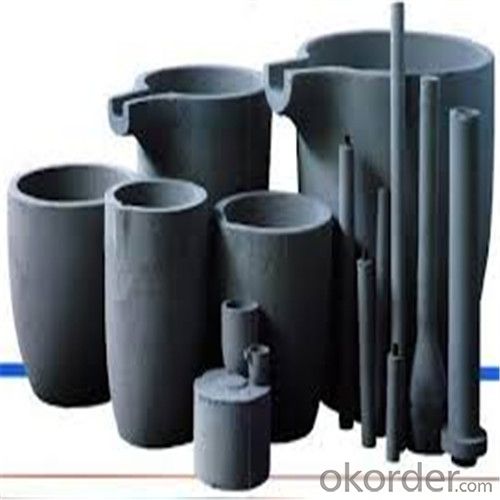
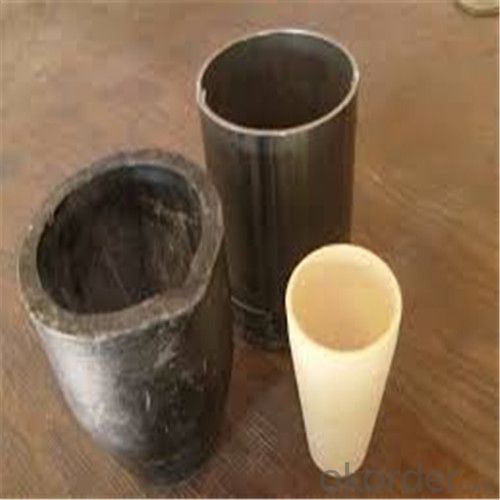
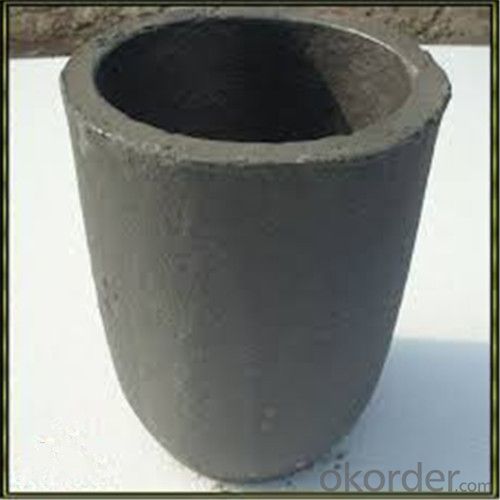
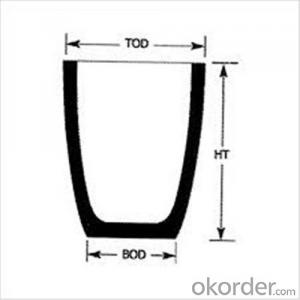
Carbon Graphite Crucible for Refractory SIC Crucible Melting Copper/Brass
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
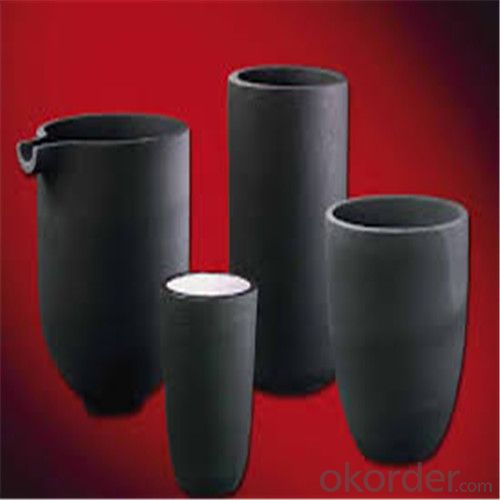
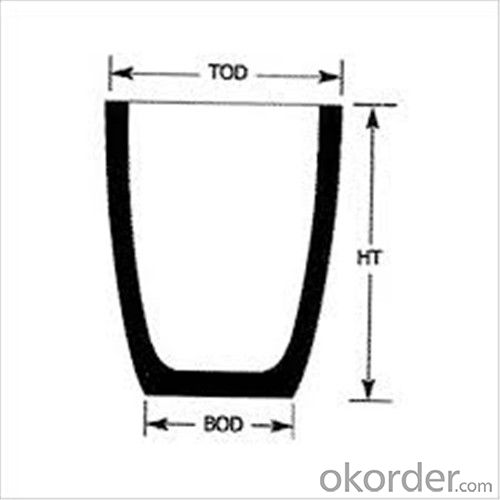

Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
Physicochemical Properties
Type of Crucible | Type S | Type D |
Carbon Content/% | ≥38 | ≥45 |
Bulk Density/(g/cm3) | ≥1.70 | ≥1.85 |
Apparent Porosity/% | ≤29 | ≤21 |
Compression Strength/MPa | ≥20 | ≥25 |
Refractoriness/°C | ≥1400 | ≥1400 |
Type S: Clay graphite crucible
Type D: Isostatic pressing graphite crucible
Cited from CNS China National Standard of Graphite Crucible, which is solely drifted by TIANFU company.
Content Composition
C% | Sic% | AL2O3% | SIO2% |
45%-50% | 20%-30% | 10%-12% | 15-25% |
FAQ
1.What's your MOQ?
We will indicate the MOQ for each item in the quotation list. We accept the sample and trail order.
2.Can I negotiate the Prices?
Sure, we may consider discounts for bulk order of products.
3.How long will it take to complete my order?
For the stock items, we can arrange the shippment within 2~3days after received your payment. For the customized items, we will indicate the delivery time in the quotation list.
4.Can you give warranty of your products?
Yes, we extend a 100% satifisfaction guarantee on all items. Please feel free to provide timely feedback if you're not satisfied with N&D's Quality and Service. For the overseas orders, if there is a quality problem, please kindly to provide the picturers to show the problem by e-mail. We will provide the replacements to you at our cost according to actual conditions.
5.Can I visit you?
Sure. If you're a volume buyer and would like to visit our in-house products and production line, please contact us to make an appointment.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for metal powder atomization?
- Metal powder atomization can utilize graphite crucibles. These crucibles are widely employed in metallurgical procedures because of their impressive thermal conductivity, chemical inertness, and resistance to extreme temperatures. During metal powder atomization, the crucible is subjected to high temperatures, causing the metal feedstock to melt and subsequently be atomized into fine powder particles through the use of a gas or water jet. The graphite crucible is instrumental in maintaining a stable temperature throughout the atomization process, as well as facilitating efficient heat transfer, leading to the production of consistent and high-quality metal powder. Moreover, graphite crucibles possess the ability to withstand the corrosive properties of molten metals, thereby making them suitable for a wide range of metal powder atomization applications.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for melting iron?
- Melting iron cannot be done using graphite crucibles. Although graphite crucibles are commonly utilized for melting metals like gold, silver, and copper due to their ability to conduct heat well and endure high temperatures, they are not appropriate for iron melting. The reason is that iron has a significantly higher melting point compared to other metals, reaching approximately 1,535 degrees Celsius (2,795 degrees Fahrenheit). Graphite crucibles have a temperature limit, typically around 1,200 degrees Celsius (2,192 degrees Fahrenheit) or lower. Consequently, if exposed to the extreme heat required for iron melting, graphite crucibles would risk breaking down, losing their structural integrity, and contaminating the molten iron. For melting iron, it is preferable to use materials with higher melting points and better resistance to high temperatures, such as clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucibles. These crucibles can withstand the intense heat necessary for iron melting while maintaining their shape and integrity. Choosing the appropriate crucible material based on the specific metal being melted is crucial to ensure safety, efficiency, and quality in the melting process.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for semiconductor doping?
- Semiconductor doping requires the use of graphite crucibles. The semiconductor industry frequently relies on graphite crucibles because of their unique characteristics. These crucibles possess high thermal conductivity, chemical inertness, and the ability to endure high temperatures, which makes them ideal for various semiconductor manufacturing processes, including doping. Throughout the doping procedure, the crucibles serve as containers for both the dopant material and the semiconductor wafer. Their purpose is to create a stable and controlled environment for the diffusion of dopant atoms into the semiconductor material. Moreover, graphite crucibles offer excellent thermal stability, which is crucial during the doping process since it involves subjecting the wafer to elevated temperatures. The crucibles help maintain a consistent temperature, ensuring uniform doping across the semiconductor wafer. Additionally, graphite crucibles exhibit chemical inertness, meaning they do not react with either the dopant material or the semiconductor material. This is essential in preventing any contamination or undesired reactions that may affect the doping process or the quality of the semiconductor material. In summary, graphite crucibles are extensively used in semiconductor doping due to their high thermal conductivity, chemical inertness, and ability to withstand high temperatures. They create a stable and controlled environment for the doping process, guaranteeing uniform doping across the semiconductor wafer.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for melting reactive metals?
- Indeed, graphite crucibles are capable of melting reactive metals. Graphite exhibits exceptional resistance to heat and possesses superb thermal conductivity, rendering it an optimal substance for high-temperature purposes such as the melting of reactive metals. Moreover, graphite is chemically inert and does not undergo reactions with majority of metals, including numerous reactive variants. Nevertheless, it is crucial to acknowledge that specific reactive metals, for instance alkali metals or certain rare earth metals, may react with graphite when exposed to elevated temperatures. In such scenarios, alternative crucible materials such as refractory metals or ceramics might be deemed more appropriate.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for carbonization processes?
- Carbonization processes can make use of graphite crucibles. Graphite is highly suitable for applications that involve high temperatures because of its exceptional thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock. Graphite crucibles are frequently employed in carbonization processes, where carbon-rich materials are heated to high temperatures without the presence of oxygen. These crucibles effectively contain and heat the materials. Graphite's high thermal conductivity ensures efficient transfer of heat, resulting in uniform heating and minimal heat loss. Furthermore, graphite's resistance to thermal shock enables it to withstand sudden temperature changes that occur during the carbonization process. In conclusion, graphite crucibles are a dependable and appropriate choice for carbonization processes.
- Q: How do you determine the appropriate crucible capacity for a specific application?
- To determine the appropriate crucible capacity for a specific application, there are several factors that need to be considered. Firstly, you need to consider the quantity of material that needs to be melted or heated in the crucible. This can be determined by the volume or weight of the material. It is important to choose a crucible size that can accommodate the material without overflowing or being too empty, as both scenarios can affect the heating efficiency and the quality of the final product. Secondly, you need to consider the melting or heating temperature required for the specific application. Different materials have different melting points, and some may require higher temperatures than others. The crucible should have the capacity to withstand and maintain the desired temperature without cracking or deforming. Additionally, the duration of the application should be taken into account. If the application requires a prolonged period of melting or heating, it is important to choose a crucible size that can hold the material for the required duration without the need for frequent refilling or emptying. This ensures a continuous and efficient operation. Furthermore, the type of crucible material is also important in determining the appropriate capacity. Different materials have different thermal conductivity and compatibility with certain materials. It is crucial to choose a crucible material that is suitable for the specific application to prevent contamination or reaction between the crucible and the material being heated. Lastly, it is recommended to consult the manufacturer or supplier of the crucible for their recommendations. They have the expertise and knowledge to guide you in selecting the appropriate crucible capacity based on your specific application requirements. By considering these factors and seeking expert advice, you can determine the appropriate crucible capacity for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance and desired results.
- Q: What is graphite?
- Of the six Fang system with a complete lamellar cleavage. The cleavage surface is mainly based on molecular bonds, and has weaker molecular attraction, so its natural floatability is very good.
- Q: How does the thermal shock resistance of graphite affect the performance of a crucible?
- The performance of a crucible is greatly influenced by the thermal shock resistance of graphite. Graphite is well-known for its exceptional thermal conductivity and high melting point, making it an ideal material for crucibles used in high-temperature applications. However, compared to other materials, the thermal shock resistance of graphite is relatively low. Thermal shock resistance refers to a material's capacity to endure sudden and extreme temperature changes without cracking or breaking. In the case of a crucible, it undergoes rapid heating and cooling cycles during various processes like melting, casting, or chemical reactions. These temperature fluctuations can impose stress on the material, potentially leading to thermal shock failure if the crucible lacks sufficient resistance. A crucible with low thermal shock resistance is more susceptible to cracking or fracturing when subjected to rapid temperature changes. This can result in the leakage of molten materials, loss of containment, or contamination of the process. Additionally, the overall structural integrity of the crucible may be compromised, negatively impacting its performance and longevity. On the contrary, a crucible with high thermal shock resistance can withstand rapid temperature changes without significant damage. It can maintain its structural integrity, ensuring the effective containment of molten materials throughout the process. This enhances the reliability and efficiency of the crucible, facilitating consistent and uninterrupted operations. Thus, it is evident that the thermal shock resistance of graphite plays a pivotal role in determining the performance of a crucible. Crucibles with superior thermal shock resistance offer increased reliability, durability, and efficiency, guaranteeing the successful execution of high-temperature processes without the risk of premature failure or contamination.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for ceramic molding?
- No, a graphite crucible cannot be used for ceramic molding. Graphite crucibles are primarily used for melting and holding metals and alloys at high temperatures. They are not suitable for ceramic molding as they do not possess the necessary properties to withstand the high temperatures required for ceramic firing and molding processes. Ceramic molding typically involves firing the ceramic material at temperatures ranging from 1000 to 1600 degrees Celsius, which can cause graphite crucibles to degrade, crack, or even melt. For ceramic molding, it is recommended to use crucibles made from materials such as alumina, zirconia, or other refractory materials that can withstand the extreme temperatures involved in the ceramic firing process.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for jewelry making?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for jewelry making. Graphite crucibles are known for their high melting point, making them ideal for melting and casting precious metals such as gold, silver, and platinum. They are also highly resistant to thermal shock and have good thermal conductivity, allowing for efficient and uniform heat distribution. Additionally, graphite crucibles are chemically inert, meaning they do not react with the molten metals and therefore do not contaminate the jewelry being made. This makes them a popular choice for jewelers and craftsmen who require a reliable and durable crucible for their jewelry making processes.
Send your message to us
Carbon Graphite Crucible for Refractory SIC Crucible Melting Copper/Brass
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords