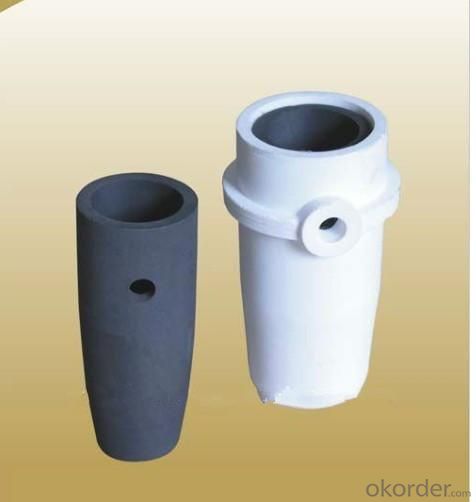
Clay Graphite Foundry Crucible - Jewellery Induction Casting Crucible Galloni CG40(500), Graphite Melting Crucible
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 5 Pieces pc
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 Pieces per Month pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
Detailed Product Description
Jewellery Casting crucible CG-40 induction casting machine. Crucible capacity 500 G
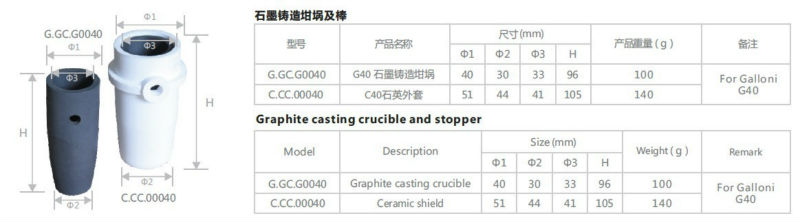
- Q: What are the different methods of preventing graphite crucible deformation?
- There are several methods that can be employed to prevent graphite crucible deformation. These methods are aimed at maintaining the structural integrity of the crucible and ensuring its longevity. 1. Proper Handling and Usage: The first and foremost method is to handle the graphite crucible with care and avoid subjecting it to unnecessary mechanical stress. This includes avoiding sudden temperature changes, impact or dropping the crucible, and using appropriate tools for handling. 2. Preheating: Before subjecting the crucible to extreme temperatures, it is advisable to preheat it gradually and evenly. This helps in reducing thermal shock and prevents deformation caused by rapid expansion or contraction. 3. Material Selection: Choosing the right type of graphite material for the crucible is crucial. High-quality graphite with appropriate thermal and mechanical properties should be selected, considering the specific application requirements. This ensures that the crucible can withstand the intended operating conditions without deforming. 4. Reinforcement: In certain cases, reinforcing the crucible can be beneficial. This can be achieved by using a protective coating or lining on the inner surface of the crucible, which provides additional strength and resistance to deformation. 5. Cooling Techniques: Implementing proper cooling techniques post-use can also aid in preventing crucible deformation. Gradually cooling the crucible in a controlled manner can help alleviate stress and minimize the risk of deformation. 6. Regular Maintenance: Crucibles should be inspected regularly for any signs of wear or damage. Any cracks, chips, or deformations should be addressed promptly to prevent further deterioration. Regular cleaning and proper storage also contribute to maintaining the crucible's structural integrity. By implementing these methods, the risk of graphite crucible deformation can be minimized, leading to improved performance, longer lifespan, and reduced costs associated with replacement or repairs.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for melting plutonium?
- Using a graphite crucible to melt plutonium is not possible. Plutonium, being a highly reactive and toxic element, demands specialized materials for safe containment. While graphite is commonly employed for melting metals due to its high melting point, it is unsuitable for handling plutonium due to the risk of reaction and contamination. When working with plutonium, it is crucial to utilize a crucible made from materials explicitly designed to endure its corrosive properties and prevent any chemical reactions that might jeopardize safety.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used with induction melting furnaces?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used with induction melting furnaces. Graphite crucibles have excellent thermal conductivity and high melting points, making them suitable for use in induction melting furnaces. The high conductivity allows for efficient heat transfer, ensuring uniform heating of the metal being melted. Additionally, graphite crucibles have good resistance to thermal shock, which is important in the intense heat environment of an induction melting furnace. However, it is essential to ensure that the graphite crucible is compatible with the specific metal being melted to avoid any chemical reactions or contamination.
- Q: How does a graphite crucible handle abrasion resistance?
- A graphite crucible has excellent abrasion resistance due to the unique properties of graphite.
- Q: Are there different sizes available for graphite crucibles?
- Yes, there are different sizes available for graphite crucibles. Graphite crucibles come in a variety of sizes to accommodate different needs and applications. They can range from small crucibles used in jewelry making or small-scale laboratory experiments to larger crucibles used in industrial applications like metal casting or melting. The size of the crucible needed depends on the amount of material to be melted or processed and the specific requirements of the application. Thus, various sizes are available to cater to different needs and ensure efficient and effective use of graphite crucibles.
- Q: How do you prevent graphite crucibles from thermal expansion-related issues?
- To prevent graphite crucibles from thermal expansion-related issues, several measures can be taken: 1. Preheating: Before using a graphite crucible, it is essential to preheat it gradually. This process helps to eliminate any residual moisture and volatile substances within the crucible. Gradual preheating also allows the crucible to expand uniformly, reducing the risk of thermal shock. 2. Controlled cooling: After use, it is crucial to cool down the graphite crucible carefully. Sudden temperature changes can cause thermal stress and lead to cracking or fracturing. By allowing the crucible to cool gradually, the thermal expansion will be more controlled and minimize the risk of damage. 3. Avoiding extreme temperatures: Graphite crucibles have a certain temperature range within which they can safely operate. Exposing the crucible to temperatures beyond its capacity can result in thermal expansion-related issues. It is essential to adhere to the manufacturer's guidelines and avoid subjecting the crucible to extreme temperatures. 4. Proper handling and storage: Graphite crucibles are relatively fragile and can be susceptible to damage if mishandled or stored improperly. Avoid dropping or impacting the crucible, as this can weaken its structure and make it more prone to thermal expansion issues. Additionally, store the crucibles in a cool and dry environment to prevent moisture absorption, which can impact their thermal stability. 5. Regular inspection: Regularly inspect the graphite crucibles for any signs of wear, cracks, or other damage. It is important to replace any crucibles that show signs of degradation to prevent potential thermal expansion-related issues during use. By following these preventive measures, the risk of thermal expansion-related issues in graphite crucibles can be significantly reduced, ensuring their longevity and optimal performance.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for melting nickel?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for melting nickel. Graphite crucibles are commonly used in high-temperature applications, including the melting of various metals and alloys. Graphite has excellent thermal conductivity and can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for melting nickel, which has a melting point of around 1,455 degrees Celsius (2,651 degrees Fahrenheit). Additionally, graphite crucibles have good chemical resistance and do not react with nickel, allowing for a clean and efficient melting process.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for melting non-metallic materials?
- Certainly! A graphite crucible possesses the ability to melt non-metallic materials. The versatility of graphite, an incredibly resilient material, enables it to withstand exceedingly high temperatures and thus renders it appropriate for melting a diverse array of substances, non-metallic materials included. Industries like glass manufacturing, ceramics, and precious stone melting commonly employ graphite crucibles. By virtue of its exceptional heat resistance, graphite adequately endures the intense temperatures necessary for melting non-metallic materials, thereby serving as a dependable and efficient choice for these specific purposes.
- Q: How is a graphite crucible used in the production of graphite electrodes?
- A graphite crucible is used in the production of graphite electrodes as it provides a container for melting and shaping the graphite material. The crucible is made of graphite, which has a high melting point and excellent thermal conductivity. It is heated to a high temperature, typically in an electric arc furnace, and the raw graphite material is placed inside. As the graphite melts, it can be poured or cast into molds to form the desired shape of the graphite electrodes. The crucible's ability to withstand high temperatures and its non-reactive nature make it an ideal tool for the production of graphite electrodes.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for metal powder atomization?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for metal powder atomization. Graphite crucibles are often preferred for their high melting point, excellent thermal conductivity, and chemical resistance. These properties make them suitable for the high-temperature process of metal powder atomization, where fine metal powders are produced by rapidly cooling molten metal. Additionally, graphite crucibles provide good control over the atomization process, making them a popular choice in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and additive manufacturing.
We are always keeping enlarging production scale, perfecting management system, and improving office facilities to expand our markets both at home and abroad.We sincerely welcome clients at home and abroad to come for negotiations.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Guangdong,China (Mainland) |
| Year Established | 2010 |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | North America South America Eastern Europe Southeast Asia Africa Oceania Mid East Eastern Asia Western Europe |
| Company Certifications |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | 61% - 70% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | 1,000-3,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | Above 10 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Clay Graphite Foundry Crucible - Jewellery Induction Casting Crucible Galloni CG40(500), Graphite Melting Crucible
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 5 Pieces pc
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 Pieces per Month pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






















