parallel flange channel steel in U shaped
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
Products Information:
| 1.Products size | Size : 5#--40# | ||||
| 2.Products length | Lengths : 6m--12m | ||||
| 3.Product standard | Standard : GB, ASTM, JIS, DIN | ||||
| 4.Product Grade | Grades : Q235B, Q345B, SS400 | ||||
| 5.Application | Used or building structures, vehicle | ||||
| manufacturing and other industrial structures | |||||
| 6.Customized requirement | Can produce special specification products | ||||
| as per our customers' requirement | |||||
| 7.Delivery Time | 15-30 days after recieve the LC or pre-paid | ||||
| 8.Detail Package | Bundles, seaworthy wooden cases with or without | ||||
| edge protector, steel hoop and seals, or as per | |||||
| customers' requirements | |||||
Drawings and Datas (for know more about the structure and size)
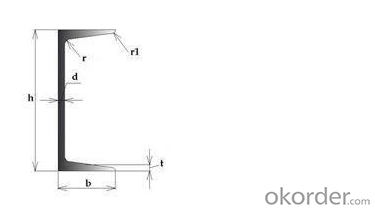
Specification | h | b | d | t | Cm2 | (kg/m) |
5 | 50 | 37 | 4.5 | 7 | 6.93 | 5.44 |
6.3 | 63 | 40 | 4.8 | 7.5 | 8.45 | 6.63 |
8 | 80 | 43 | 5 | 8 | 10.24 | 8.04 |
10 | 100 | 48 | 5.3 | 8.5 | 12.74 | 10 |
12.6 | 126 | 53 | 5.5 | 9 | 15.69 | 12.37 |
14a | 140 | 58 | 6 | 9.5 | 18.51 | 14.53 |
14b | 140 | 60 | 8 | 9.5 | 21.31 | 16.73 |
16a | 160 | 63 | 6.5 | 10 | 21.95 | 17.23 |
16 | 160 | 65 | 8.5 | 10 | 25.15 | 19.74 |
18a | 180 | 68 | 7 | 10.5 | 25.69 | 20.17 |
18 | 180 | 70 | 9 | 10.5 | 29.29 | 22.99 |
- Q: Can stainless steel angles be used for lighting fixtures?
- Certainly! Lighting fixtures can utilize stainless steel angles. With its durability and resistance to corrosion, stainless steel proves itself suitable for a wide range of applications, including lighting fixtures. Not only do stainless steel angles provide structural support and stability to these fixtures, but they also enhance their appearance with a sleek and contemporary aesthetic. Moreover, stainless steel's easy-to-clean and low-maintenance nature renders it a practical option for lighting fixtures that may encounter environmental elements or necessitate regular upkeep.
- Q: What is the difference between 304H and 316H stainless steel angles?
- The main difference between 304H and 316H stainless steel angles lies in their chemical composition and performance characteristics. 304H stainless steel angles are composed of 18% chromium and 8% nickel, which gives them good corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength. They are commonly used in applications where corrosion resistance is required, such as in the food processing industry, chemical plants, and architectural applications. Additionally, 304H stainless steel angles have excellent weldability and formability. On the other hand, 316H stainless steel angles contain 16% chromium, 10% nickel, and 2% molybdenum. The addition of molybdenum enhances their corrosion resistance, especially against chlorides and other aggressive chemicals. This makes 316H stainless steel angles suitable for use in marine environments, coastal areas, and applications involving exposure to harsh chemicals. They also exhibit excellent heat resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. In summary, while both 304H and 316H stainless steel angles offer good corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength, 316H stainless steel angles provide superior resistance against corrosive chemicals and are well-suited for marine and chemical industry applications. However, it is important to consider the specific requirements of the intended application before deciding which stainless steel angle to use.
- Q: How do you calculate the shear stress for torsion of a stainless steel angle?
- To determine the shear stress in torsion for a stainless steel angle, one must take into account the angle's geometry and the applied torque. The formula for calculating shear stress is as follows: Shear Stress = (Torque * Distance from center of angle) / (Polar Moment of Inertia) The torque refers to the twisting force exerted on the angle and is typically measured in Newton-meters (Nm) or foot-pounds (ft-lb). The distance from the center of the angle is the perpendicular distance from the center to the location where shear stress is being calculated, usually measured in meters (m) or feet (ft). The polar moment of inertia is a characteristic of the angle section that indicates its resistance to torsional deformation. It can be computed using the following equation: Polar Moment of Inertia = (Width * Height^3) / 12 Here, the width represents the distance between the two legs of the angle, while the height denotes the length of one leg of the angle. After obtaining the values for torque, distance, and polar moment of inertia, one can substitute them into the shear stress formula to calculate the shear stress. The resulting shear stress will be expressed in pressure units, typically measured in Pascals (Pa) or pounds per square inch (psi). It is crucial to note that the material properties of the stainless steel angle, such as its yield strength and ultimate strength, must also be taken into consideration to ensure that the calculated shear stress falls within the acceptable limits for the material.
- Q: Are stainless steel angles lightweight?
- No, stainless steel angles are not considered lightweight. Stainless steel is a dense and heavy material, which means that stainless steel angles also have a significant weight to them. However, the weight of stainless steel angles can vary depending on their size and thickness.
- Q: What are the UV resistance properties of stainless steel angle?
- Due to its composition and surface finish, stainless steel angle exhibits exceptional resistance to UV rays. The presence of chromium in stainless steel leads to the formation of a protective oxide layer when exposed to oxygen. This oxide layer acts as a shield against UV radiation, preventing the steel from corroding or deteriorating when subjected to prolonged sunlight exposure. Moreover, stainless steel angle often features a polished or brushed surface finish, which further enhances its ability to resist UV rays. The smooth surface reduces the likelihood of dirt, dust, or other particles accumulating on the steel, thus minimizing any potential impact on its UV resistance. The UV resistance of stainless steel angle is particularly significant in outdoor applications or environments with high levels of sunlight exposure. This property ensures that the material remains durable, long-lasting, and visually appealing over time, as it is able to withstand the damaging effects of UV radiation.
- Q: What is the minimum surface finish requirement for stainless steel angles?
- The required surface finish for stainless steel angles varies depending on the specific application and industry standards. Generally, stainless steel angles should have a smooth and even surface finish to ensure optimal performance and aesthetics. This typically involves eliminating any surface imperfections, such as burrs or roughness, and achieving a consistent finish across the entire angle surface. Mill finish is the natural surface finish produced during manufacturing, while brushed or polished finishes are used to enhance the visual appeal. To determine the specific minimum surface finish requirement for stainless steel angles in a particular application, it is important to refer to industry specifications or customer requirements.
- Q: Can stainless steel angles be used in the construction of support structures?
- Yes, stainless steel angles can be used in the construction of support structures. Stainless steel is known for its strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, making it an ideal material for support structures that need to withstand heavy loads. Stainless steel angles are particularly useful in providing structural support and stability as they have a right angle shape that can be easily bolted or welded to other components. They can be used in various applications such as building frames, bridges, platforms, and equipment supports. Additionally, stainless steel angles have a sleek and modern appearance, making them suitable for architectural and aesthetic purposes as well. Overall, stainless steel angles are a reliable choice for constructing support structures due to their strength, longevity, and versatility.
- Q: Can stainless steel angles be submerged in water?
- Yes, stainless steel angles can be submerged in water without any issues. Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and rust, making it a suitable material for applications involving water exposure. The chromium content in stainless steel forms a protective layer on the surface, preventing the metal from reacting with water and other corrosive elements. Submerging stainless steel angles in water will not cause any degradation or damage to the material, ensuring its durability and longevity even in wet environments.
- Q: What are the dimensions of a standard stainless steel angle?
- The dimensions of a standard stainless steel angle can vary depending on the specific requirements and standards set by manufacturers. However, in general, stainless steel angles typically have equal legs, meaning that the length and width of the two sides are the same. The most common sizes of stainless steel angles range from 20mm x 20mm to 200mm x 200mm, with thicknesses varying from 3mm to 20mm. These angles often have a standard length of 6 meters, but they can also be customized to different lengths based on specific project needs. Overall, the dimensions of a standard stainless steel angle will ultimately depend on the manufacturer and the intended application.
- Q: What are the different surface treatments for anti-fingerprint stainless steel angles?
- Anti-fingerprint stainless steel angles offer a variety of surface treatments to minimize the visibility of fingerprints and smudges. One option is the application of a fingerprint-resistant coating, which forms a thin layer on the stainless steel surface to prevent fingerprints from sticking and make cleaning easier. Another choice is a brushed finish, achieved by using a wire brush or abrasive pad to create a textured pattern that not only adds a decorative element but also conceals fingerprints. Passivation, a chemical treatment, removes iron or iron oxide from the surface, preventing rusting and corrosion while increasing resistance to fingerprints. Lastly, etching, done through chemicals or lasers, enhances the angle's aesthetic appeal and reduces the visibility of fingerprints. Ultimately, the surface treatment decision relies on personal preference, desired aesthetics, and specific application requirements.
Send your message to us
parallel flange channel steel in U shaped
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


























