Z35 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Z35 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
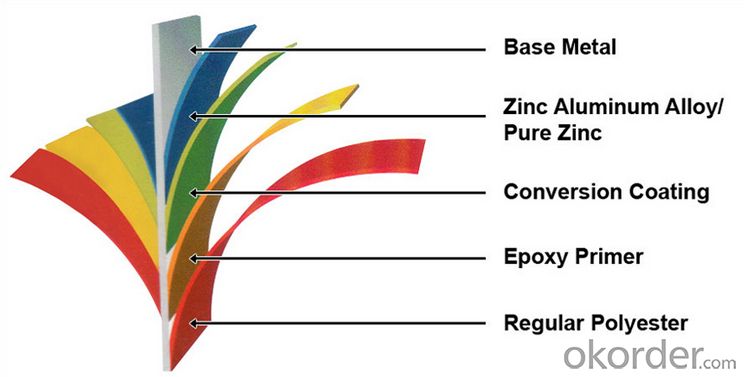
Description of Z35 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
PPGI is made by cold rolled steel sheet and galvanized steel sheets as baseplate, through the surface pretreatment (degreasing, cleaning, chemical conversion processing), coated by the method of continuous coatings (roller coating method),
and after roasting and cooling. Zinc coating: Z60, Z80, Z100, Z120, Z180, Z275, G30, G60, G90
Alu-zinc coating: AZ60, AZ80, AZ100, AZ120, AZ180, G30, G60, G90
Main Feature of Z35 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.Standard seaworthy export packing: 3 layers of packing, inside is kraft paper, water plastic film is in the middle and outside GI steel sheet to be covered by steel strips with lock, with inner coil sleeve.
Applications of Z35 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1. Construction and building: roofing; ventilating duct; handrail; partition panel;etc.
2. Electric appliance: refrigerator; washing machine; refrigerator; DVD;etc.
3.Transportation: oil tank; road sign; etc.
4.Agriculture:barn; etc.
5.Others:vending machine; game machine; etc. 
Specifications of Z35 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
| Classified symbol | Yield Point Minimum N/mm2 | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | ||||
| N/mm2 | Nominal Thickness mm (t) | |||||||
| JIS | Yogic | 0.25-0.4 | 0.4-0.6 | 0.6-1.0 | 1.0-1.6 | |||
| G3312 | specification | |||||||
| CGCC | CGCC | -205 | -270 | -20 | -21 | -24 | -24 | Commercial |
| CGCD | CGCD | --- | 270 | --- | 27 | 31 | 32 | Drawing |
| --- | CG340 | 245 | 340 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | Structural |
| CGC400 | CG400 | 295 | 400 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC440 | CG440 | 335 | 440 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC490 | CG490 | 365 | 490 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 16 | Structural |
| CGC570 | CG570 | 560 | 570 | --- | --- | --- | --- | Structural |
| ASTM Designation | Yield Point Minimum | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | Q/BQB 445-2004(China standard) | ASM A653/A653M | JISG 3312 | |
| ksi(MPa) | ksi(MPa) | TDC51D+Z | (CS TYPE A+Z) | CGCC | ||||
| A653(M)-99 CS TYPE A,B,C | --- | --- | --- | Commercial | TDC52D+Z | CGCD | ||
| A653(M)-99 FS | --- | --- | --- | Lock Forming | TS250GD+Z | (G250+Z) | - | |
| A653(M)-99 DS | --- | --- | --- | Drawing | TS300GS+Z | (G300+Z) | CGC 400 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade33(230) | 33(230) | 45(310) | 20 | Structural | TS350GD+Z | (G350+Z) | CGC490 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade37(255) | 37(255) | 52(360) | 18 | Structural | TS550GD+Z | (G550+Z) | CGC570 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade40(275) | 40(275) | 55(380) | 16 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade50(345) | 50(345) | 65(450) | 12 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade80(550) | 80(550) | 82(570) | --- | Structural | ||||
FAQ of Z35 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
1, ISO, BV, CE, SGS approved.
2, Competitive price and quality.
3, Efficient service team online for 24 hours.
4, Smooth production ability(50000tons/month) .
5, quick delivery and standard exporting package.
6, Flexible payment with T/T, L/C, Paypal, Kunlun bank, etc .
- Q: What is the impact of impurities on the quality of steel billets?
- Impurities play a significant role in determining the quality of steel billets. Steel billets are semi-finished products that are used as raw material for further processing into various steel products. The presence of impurities in steel billets can have several negative impacts on their quality. Firstly, impurities can weaken the mechanical properties of steel billets. For instance, the presence of sulfur can lead to the formation of sulfide inclusions, which can reduce the strength and toughness of the steel. Similarly, phosphorus can form phosphide inclusions that negatively affect the ductility and impact resistance of the billets. These impurities can also promote the formation of cracks and other defects, further compromising the quality of the steel. Secondly, impurities can adversely affect the machinability of steel billets. High levels of impurities can increase the hardness and reduce the machinability of the steel, making it more difficult to shape into the desired end products. This can result in increased processing time and cost, as well as reduced productivity. Moreover, impurities can impact the surface finish of steel billets. Oxide inclusions, which are commonly formed due to the presence of impurities, can lead to surface defects and roughness. This can affect the appearance and aesthetics of the final steel products, making them less desirable in the market. Furthermore, impurities can influence the corrosion resistance of steel billets. Certain impurities, such as chromium and nickel, can enhance the corrosion resistance of steel. However, other impurities like sulfur and phosphorus can promote corrosion, reducing the lifespan and reliability of the steel products made from these billets. Overall, the impact of impurities on the quality of steel billets is significant and can result in weakened mechanical properties, reduced machinability, compromised surface finish, and decreased corrosion resistance. Therefore, it is crucial for steel manufacturers to carefully control and minimize the presence of impurities during the production process to ensure the production of high-quality steel billets.
- Q: How are steel billets marked for identification and traceability?
- Various methods are utilized to mark steel billets for identification and traceability. One prevalent approach involves the utilization of unique identification numbers or codes. These numbers or codes can be engraved or stamped onto the billet's surface, enabling easy identification. Laser engraving machines or steel stamping tools are frequently employed for this purpose. Aside from identification numbers, other significant details, such as the grade, heat number, and production date, can also be marked on the billet. These details play a crucial role in traceability, allowing for the tracking of the steel's origin and quality. Moreover, some manufacturers may choose to employ additional marking techniques, such as paint or ink marking. This may entail the use of specific colors or symbols to represent different characteristics or attributes of the billet. For example, a particular color might indicate the intended use of the steel, while a symbol may signify the manufacturer's logo or quality certification. Overall, the marking of steel billets for identification and traceability is indispensable in ensuring quality control, verifying compliance with industry standards, and facilitating efficient inventory management throughout the supply chain.
- Q: Can steel billets be coated for improved corrosion resistance?
- Yes, steel billets can be coated with various materials such as zinc, aluminum, or polymer coatings to enhance their corrosion resistance.
- Q: What is the role of steel billets in the manufacturing of pressure vessels?
- The manufacturing of pressure vessels heavily relies on steel billets, which have a crucial role to play. Pressure vessels, designed to contain fluids or gases at higher pressures than atmospheric pressure, find applications across industries like oil and gas, chemical, pharmaceutical, and more. Steel billets serve as the raw material for constructing pressure vessels, forming a significant part of the manufacturing process. These semi-finished products are obtained through continuous casting or hot rolling of steel ingots and have a rectangular or square cross-section. Typically, they are made from carbon steel or alloy steel. Steel billets possess key properties that make them ideal for pressure vessel manufacturing. Their excellent strength and toughness allow them to withstand the high internal pressure exerted by fluids or gases, ensuring the integrity and safety of the vessel. Another important property of steel billets is their good weldability. This is crucial for fabricating pressure vessels as welding is a common joining technique. The weld joints must have comparable strength to the base material, and steel billets allow for strong and reliable welds during the fabrication process. In addition, steel billets can be easily formed and shaped into the desired size and dimensions for pressure vessels. They can be forged, rolled, or extruded to create various components like cylindrical bodies, heads, nozzles, and flanges. This versatility allows for customization based on specific pressure vessel requirements. Moreover, steel billets are known for their corrosion resistance, which is vital for pressure vessels in contact with corrosive fluids or gases. The selection of the appropriate steel grade for the billets ensures the vessel can withstand the corrosive environment and maintain its integrity over time. In conclusion, steel billets are indispensable in pressure vessel manufacturing as they provide the necessary raw material with properties required to withstand high-pressure conditions. Their strength, weldability, formability, and corrosion resistance make them an excellent choice for constructing reliable and durable pressure vessels used across various industries.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the toughness of steel billets?
- There are several main factors that can affect the toughness of steel billets. 1. Composition: The chemical composition of the steel, including the presence of certain elements such as carbon, manganese, and silicon, can significantly impact its toughness. For example, higher carbon content tends to increase hardness but decrease toughness, while the addition of alloying elements like nickel or chromium can improve both strength and toughness. 2. Heat treatment: The heat treatment process, including the rate of cooling and the temperature at which it is performed, can have a significant effect on the toughness of steel. Quenching and tempering are common heat treatment techniques used to enhance the toughness of steel by controlling the microstructure and reducing the presence of brittle phases. 3. Microstructure: The microstructure of steel, which is determined by factors such as cooling rate, grain size, and phase distribution, can greatly influence its toughness. Fine-grained structures tend to exhibit better toughness compared to coarse-grained ones, as smaller grains can inhibit crack propagation. 4. Impurities and inclusions: The presence of impurities and inclusions in steel can negatively impact its toughness. These impurities can act as stress concentrators, leading to localized failure and reduced overall toughness. Therefore, the steelmaking process needs to ensure proper purification and removal of impurities. 5. Manufacturing processes: Various manufacturing processes, such as rolling or forging, can influence the toughness of steel billets. These processes can induce residual stresses and introduce defects that can affect the material's overall toughness. Proper control and optimization of these processes can help enhance the toughness of steel billets. 6. Service conditions: The specific application and service conditions of the steel billets also play a role in determining its toughness requirements. Factors such as temperature, stress levels, and exposure to corrosive environments can impact the material's toughness performance. Understanding and accounting for these conditions is crucial in selecting the appropriate steel grade and ensuring long-term durability. In summary, the main factors affecting the toughness of steel billets include composition, heat treatment, microstructure, impurities, manufacturing processes, and service conditions. By carefully considering and optimizing these factors, manufacturers can produce steel billets with the desired toughness properties for various applications.
- Q: Are steel billets affected by extreme temperatures?
- Yes, steel billets can be affected by extreme temperatures. High temperatures can cause the billets to soften and become more malleable, making them easier to shape or deform. On the other hand, extremely low temperatures can make the steel brittle and prone to cracking or fracturing. Therefore, it is important to carefully control and monitor the temperature conditions during the production and processing of steel billets.
- Q: What are the different methods of steel billet surface cleaning?
- There are several methods of steel billet surface cleaning, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the common methods include: 1. Shot Blasting: This method involves shooting small metallic or non-metallic particles at high velocity onto the surface of the billet. The impact of these particles removes any rust, scale, or surface contaminants. Shot blasting is an effective method for cleaning large surfaces quickly, but it can cause surface roughness and may not be suitable for all types of steel. 2. Acid Pickling: Acid pickling involves immersing the steel billet in an acid solution, typically hydrochloric or sulfuric acid, to remove scale and rust. The acid reacts with the surface contaminants, dissolving them and leaving a clean surface. Acid pickling is effective in removing stubborn scale and rust, but it requires careful handling of the corrosive acids and proper disposal of the waste. 3. Mechanical Cleaning: Mechanical cleaning methods involve using abrasive tools or brushes to physically scrub the surface of the billet. This can be done manually or using machinery. Mechanical cleaning is effective in removing loose contaminants and scale, but it may not be suitable for heavily rusted or stubbornly adhered contaminants. 4. High-Pressure Water Jetting: This method uses high-pressure water jets to clean the surface of the billet. The force of the water removes scale, rust, and other contaminants. High-pressure water jetting is environmentally friendly as it does not involve the use of chemicals, but it may not be as effective in removing heavy scale or rust. 5. Ultrasonic Cleaning: Ultrasonic cleaning involves immersing the steel billet in a tank filled with a cleaning solution and subjecting it to high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations. The vibrations create tiny bubbles in the cleaning solution, which implode on the surface of the billet, effectively removing contaminants. Ultrasonic cleaning is effective in removing even microscopic particles and can reach complex geometries, but it may not be suitable for large-scale cleaning operations. Each of these methods has its own strengths and limitations, and the choice of method depends on factors such as the type and condition of the surface contaminants, the time and cost constraints, and the desired surface finish.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of consumer goods?
- Steel billets are a crucial raw material used in the manufacturing of consumer goods. These billets are primarily utilized as feedstock in various metalworking processes such as hot rolling, forging, and extrusion. By shaping and forming the steel billets into desired shapes, manufacturers are able to produce a wide range of consumer goods like automobiles, appliances, construction materials, and machinery components. The high strength and durability of steel make it an ideal choice for consumer goods, ensuring reliability and longevity in the final products.
- Q: What are the different types of steel billet reheating furnaces?
- There are several types of steel billet reheating furnaces, including walking beam furnaces, pusher furnaces, rotary hearth furnaces, and roller hearth furnaces. Each type has its own advantages and uses, depending on the specific requirements of the steel production process.
- Q: How is a steel billet made?
- A steel billet is made through a process called continuous casting. It involves pouring molten steel into a water-cooled mold, which solidifies the steel into a rectangular shape. The solidified steel is then cut to the desired length to form a steel billet.
Send your message to us
Z35 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






























