Glass Fiber Textile Epoxy Glass Cloth Products
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 800 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
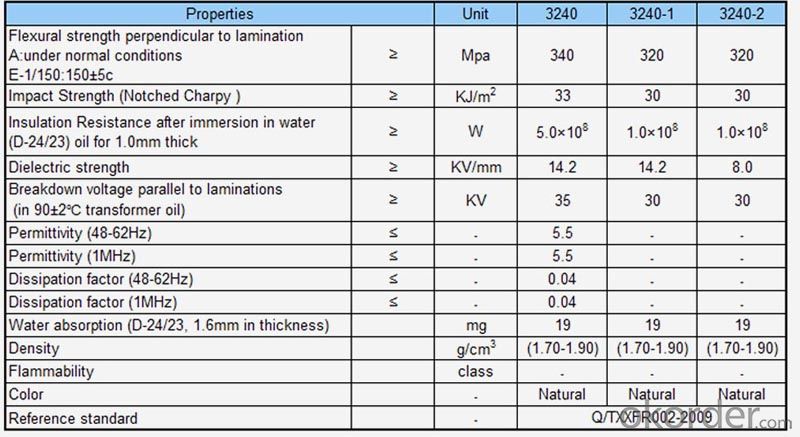
Laminate Type ◆ 3240 G10 G11 FR-4 FR-5 ◆ Thickness:0.5mm-90mm ◆ Size:1000×1200mm 1000×2000mm 1000×2400mm Rod/Tube Type ◆ 3721 3722 3723 3724 3725 3840 3841 3520 3526 3640 ◆ Diameter:6mm 8mm 10mm-200mm ◆ Length:1000mm | |
| 3240 * Temperature grade: B glass (130℃) * Color: nature, red, green, black * Thickness: 0.5-80mm * Size: 1020x2040mm | 3240-1 & 3240-2 * Temperature grade: B glass (130℃) * Color: nature,yellow * Thickness: 0.5-80mm * Size: 1020x2040mm |
 | |
| F880A F881A * Temperature grade: B glass (130℃) * Color: nature, green * Thickness: 0.5-80mm * Size(mm): 1020x1220 1020x2040 1220x2470 | F882A F883A * Temperature grade: F glass (155℃) * Color: nature, green * Thickness: 0.5-80mm * Size(mm): 1020x1220 1020x2040 1220x2470 |
- Q: Can glass fiber textiles be used in the automotive industry?
- Yes, glass fiber textiles can be used in the automotive industry. Glass fiber textiles, commonly known as fiberglass, have several properties that make them suitable for automotive applications. Firstly, fiberglass is lightweight yet strong, which makes it ideal for components that need to be both durable and lightweight, such as car body panels and interior trim. Additionally, fiberglass has excellent thermal insulation properties, making it useful for parts that require heat resistance, like engine covers and exhaust components. Furthermore, fiberglass is resistant to corrosion, chemicals, and UV radiation, ensuring its longevity and durability in harsh automotive environments. Lastly, fiberglass can be easily molded into complex shapes, allowing for the production of intricate automotive parts. Overall, glass fiber textiles offer many advantages that make them a valuable material for use in the automotive industry.
- Q: Are glass fiber textiles resistant to solvents?
- Yes, glass fiber textiles are generally resistant to solvents.
- Q: Can glass fiber textile be used in architectural applications?
- Glass fiber textile, commonly referred to as fiberglass, holds potential for use in architectural applications. This material possesses numerous advantages that cater to the field of architecture. It is lightweight, sturdy, long-lasting, and exhibits exceptional thermal and acoustic insulation properties. Due to these qualities, it can be employed in a variety of architectural functions, including cladding, roofing, partition walls, and facades. Architects can utilize glass fiber textile as a reinforcing agent in composite panels, providing structural reinforcement and augmenting the overall strength of a building. Furthermore, it can be shaped and molded into diverse forms, enabling the creation of inventive and original architectural designs. Moreover, the resistance of glass fiber textile to corrosion, moisture, and ultraviolet radiation renders it an optimal choice for exterior applications. It can endure severe weather conditions and necessitates minimal maintenance, offering a significant advantage for long-term architectural projects. Additionally, the implementation of glass fiber textile can enhance energy efficiency within buildings. Its exceptional insulation properties effectively reduce heat transfer, ultimately resulting in diminished energy consumption for heating and cooling purposes. This, in turn, contributes to sustainability endeavors while simultaneously lowering overall energy expenses. To summarize, glass fiber textile stands as a fitting material for architectural applications due to its lightweight nature, robustness, durability, insulation properties, and corrosion resistance. Its versatility and ability to enhance energy efficiency render it a popular selection for a wide range of architectural projects.
- Q: What are the different surface finishes available for glass fiber textile?
- Glass fiber textiles offer a variety of surface finishes, each with its own purpose and unique properties. Some common finishes include the following: 1. Sizing: Glass fiber textiles can be treated with sizing to improve their handling during processing. This lubricating finish prevents fiber clumping, making the material easier to work with during weaving and manufacturing. 2. Silane: Silane coatings enhance the adhesion of glass fiber textiles to different matrix materials, like resins or polymers. By creating a chemical bond between the fibers and the matrix, silane finishes improve the strength and durability of the final composite product. 3. Epoxy: Epoxy finishes are commonly used to protect glass fiber textiles from chemical degradation and environmental factors. By offering enhanced chemical resistance, this finish extends the lifespan of the material by shielding it from exposure to chemicals, moisture, and UV radiation. 4. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA): PVA coatings improve the wetting and dispersion properties of glass fiber textiles. By ensuring even distribution of liquid materials throughout the fibers, PVA finishes enhance impregnation and adhesion between the fibers and the matrix material. 5. Fire retardant: Fire retardant finishes increase the heat and flame resistance of glass fiber textiles. These specialized coatings hinder fire spread and decrease the release of toxic gases, making them ideal for applications prioritizing fire safety. 6. Anti-static: Anti-static finishes are used to minimize or eliminate static electricity buildup on glass fiber textiles. These coatings dissipate static charges, preventing potential damage to sensitive electronic equipment and reducing the risk of electrostatic discharge in specific environments. These examples showcase the range of surface finishes available for glass fiber textiles, each chosen based on specific application requirements, including adhesion, chemical resistance, fire safety, or conductivity.
- Q: What are the disadvantages of using glass fiber textile?
- There are several disadvantages of using glass fiber textile in various applications. Firstly, glass fiber textiles are relatively brittle and can break easily when subjected to high levels of stress or impact. This makes them unsuitable for applications where flexibility or resistance to breakage is critical. Secondly, glass fiber textiles have poor resistance to UV radiation. Over time, exposure to sunlight can cause the fibers to degrade and weaken, reducing their overall strength and durability. This limits their use in outdoor applications, especially those requiring long-term exposure to sunlight. Another drawback of glass fiber textiles is their relatively high cost compared to other textile materials. The production process for glass fibers involves complex and energy-intensive manufacturing techniques, which contribute to the higher price. This can make glass fiber textiles less economically viable for certain applications, especially when there are alternative materials available at lower costs. Furthermore, glass fiber textiles can be challenging to work with due to their sharp edges and rough surface texture. This can pose safety risks during handling and installation, requiring the use of protective equipment and careful handling practices. Lastly, glass fibers are not biodegradable, meaning they do not break down naturally over time. This can lead to environmental concerns, as the disposal and waste management of glass fiber textiles can be challenging and potentially harmful to the environment. Overall, while glass fiber textiles have several advantageous properties like high strength and resistance to chemicals, they also come with significant disadvantages such as brittleness, UV degradation, high cost, difficult handling, and environmental concerns. These factors need to be carefully considered when choosing the appropriate material for a specific application.
- Q: How do glass fiber textiles contribute to noise reduction?
- Glass fiber textiles contribute to noise reduction through their unique properties and construction. Firstly, glass fiber textiles have excellent sound absorption properties. The fibers in the textile are woven or knitted in a specific pattern that creates a porous structure. This structure helps to trap and absorb sound waves, preventing them from bouncing off hard surfaces and causing echo or reverberation. The fibers also have a high surface area, which further enhances their sound absorbing capabilities. Additionally, glass fiber textiles often have a high density, which further aids in noise reduction. The dense structure of the textile helps to block and dampen sound waves, preventing them from passing through the material and into the surrounding environment. Furthermore, glass fiber textiles can be used as insulation materials in walls, ceilings, and floors. This insulation helps to reduce the transmission of sound from one area to another, effectively isolating and containing noise within a specific space. This is particularly useful in buildings with multiple occupants or in industrial settings where noise control is important. Moreover, glass fiber textiles are durable and long-lasting, which makes them an effective solution for noise reduction. They can withstand harsh environmental conditions and maintain their sound absorbing properties over time. This makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, including commercial buildings, residential spaces, automotive interiors, and industrial facilities. In summary, glass fiber textiles contribute to noise reduction by absorbing, blocking, and isolating sound waves. Their unique properties and construction make them an effective solution for controlling and minimizing noise in various settings.
- Q: What are the different thickness options for glass fiber textile?
- The thickness options for glass fiber textiles can vary, but commonly range from thin and lightweight options such as 0.1mm to thicker and more durable options like 0.5mm or even thicker. The specific thickness chosen depends on the intended use and application of the glass fiber textile.
- Q: If people inhale air with glass fiber for a long time, what will happen to people? What kind of symptoms will people appear?
- For a long time there will be pneumoconiosis, China due to labor protection is not comprehensive, and many miners are pneumoconiosis deaths, death is particularly miserable, the lungs can not breathe, alive suffocated!!! X light shows that the lungs are shadows and nothing is visible!
- Q: How do glass fiber textiles contribute to lightweight construction?
- Glass fiber textiles contribute to lightweight construction by providing strength and durability while being significantly lighter than traditional construction materials. The use of glass fiber textiles in building components such as walls, roofs, and facades reduces the overall weight of the structure, making it more efficient and cost-effective. Additionally, the flexibility and versatility of glass fiber textiles allow for design freedom and easy installation, further enhancing their contribution to lightweight construction.
- Q: How do glass fiber textiles perform in terms of impact resistance?
- Glass fiber textiles have excellent impact resistance properties. Due to the inherent strength and rigidity of glass fibers, textiles made from them are able to withstand high impact forces without breaking or deforming. This makes them highly suitable for applications where impact resistance is crucial, such as in automotive parts, protective gear, and construction materials.
Send your message to us
Glass Fiber Textile Epoxy Glass Cloth Products
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 800 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords