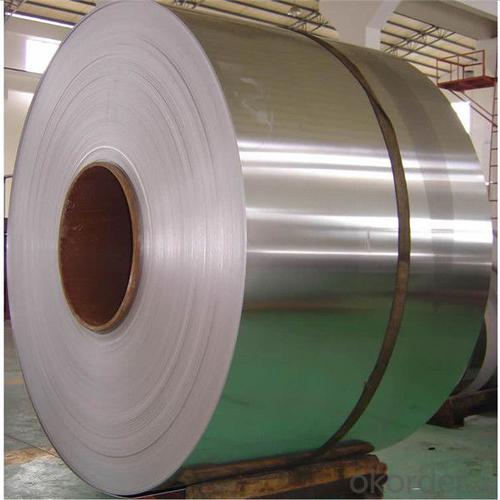
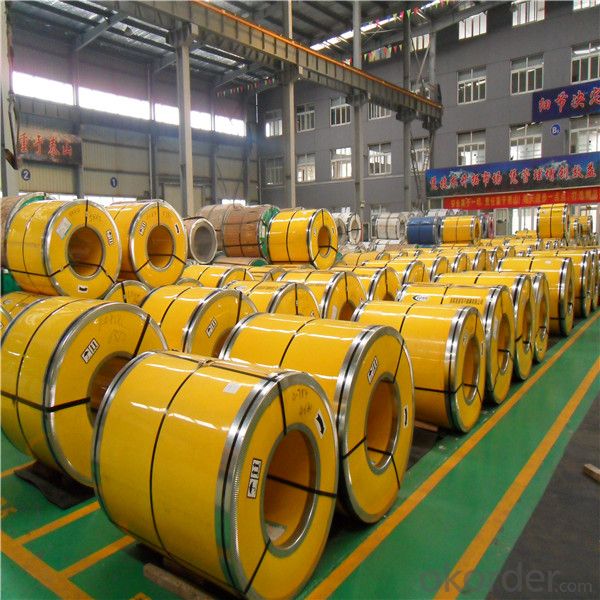
201 202 304 304L Stainless Steel Coil manufacturers
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 4 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
2MM thickness cold rolled baosteel aisi 201 202 304 304L stainless steel coil manufacturers
Stainless steel is a production which not easy rust,acid resistance and corrosion resistance,so it is widely used in light industry,heavy industry,daily necessities and the decoration industry.my company long-term supply stainless steel products including:stainless steel sheet,stainless steel coil and stainless steel tube.
Specification:
| Commodity | 2MM thickness cold rolled baosteel aisi 201 202 304 304L stainless steel coil manufacturers | |||||
| Width | 1000mm,1219mm,1240mm,1500mm,2000mm or as customer's demand | |||||
| Thickness | Cold Rolled:0.3-3.0mm Hot Rolled:3.0-150mm | |||||
| Length | 1000mm-6000mm or as customer's demand | |||||
| Surface | No.1,2B,8K,BA,2D,No.4,No.6,ect. | |||||
| Material | 201,202,301,302,303,304,304L,309S,316,316L,316N,410,420,ect. | |||||
| Grade | 200/300/400 series | |||||
| Certification | SGS ISO | |||||
| Application | Construction,Industry,Kitchenware,Building,etc | |||||
| Packing | Kraft Paper and Seaworthy Wooden Pallet or according to client's request | |||||
| Place of Origin | Shanxi China (MAINLAND) | |||||
| Payment terms | L/C & T/T | |||||
| Delivery Time | Up To Order | |||||
Surface:
| Surface | Definition | Application | |||
| No.1 | The surface finiyshed by heat treatment and pickling or processcorresponding there to after hot rolling. | Chemical tank,pipe | |||
| 2B | Those finished,after cold rolling,by heattreatment,pickling or otherequivalent treatment and lastly bycold rolling to given appropriate luster. | Medical equipment,Food industry,Construction material | |||
| No.3 | Those finished by polishing with No.100 to No.120 abrasives specified in JIS R6001. | Kitchen utensils,Building | |||
| No.4 | Those finished by polishing with No.150 to No.180 abrasive specified in JIS R6001 | Medical equipment | |||
| BA | Those processed with bright heat treatment after cold rolling. | Electric equipment, Building | |||
| HL | Those finished polishing so as to give continuous polishing streaks by use=ing abrasive of suitable grain size. | Kitchen utensils,Building | |||
Chemical Composition(in percentage):
| Grade | C | Mn(Max) | P(Max) | S(Max) | Si(Max) | Cr(Max) | Ni(Max) | Mo(Max) |
| 201 | 0.15 | 5.5-7.5 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 1 | 16.0-18.0 | 3.5-5.5 | |
| 202 | 0.15 | 7.5-10.5 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 1 | 17.0-19.0 | 4.0-6.0 | |
| 304 | 0.08 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 1 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-10.5 | |
| 304L | 0.03 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 1 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-12.0 | |
| 310S | 0.08 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 1.5 | 24.0-26.0 | 19.0-22.0 | |
| 316 | 0.08 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 1 | 16.0-18.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 2.0-3.0 |
| 316L | 0.03 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 1 | 16.0-18.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 2.0-3.0 |
| 317 | 0.08 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 0.75 | 18.0-20.0 | 11.0-14.0 | 3.0-4.0 |
| 317L | 0.03 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 0.75 | 18.0-20.0 | 11.0-15.0 | 3.0-4.0 |
| 321 | 0.08 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 0.75 | 17.0-19.0 | 9.0-12.0 | |
| 409 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 1 | 10.5-11.75 | 0.5 | |
| 410S | 0.08 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 1 | 11.5-13.5 | 0.6 | |
| 410 | 0.15 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 1 | 11.5-13.5 | 0.75 | |
| 420 | 0.35 | 0.5 | 0.035 | 0.015 | 0.5 | 12.0-13.0 | 0.2-3.0 |
Application:

Packaging & Shipping
Packing :

Our Factory:

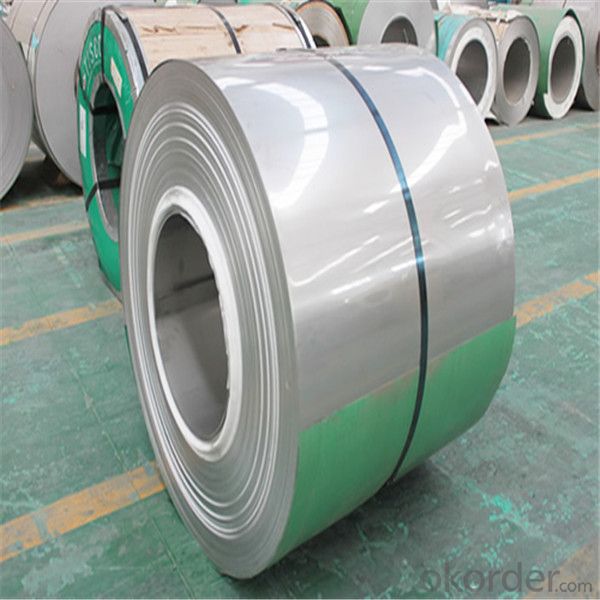
Process Flow:
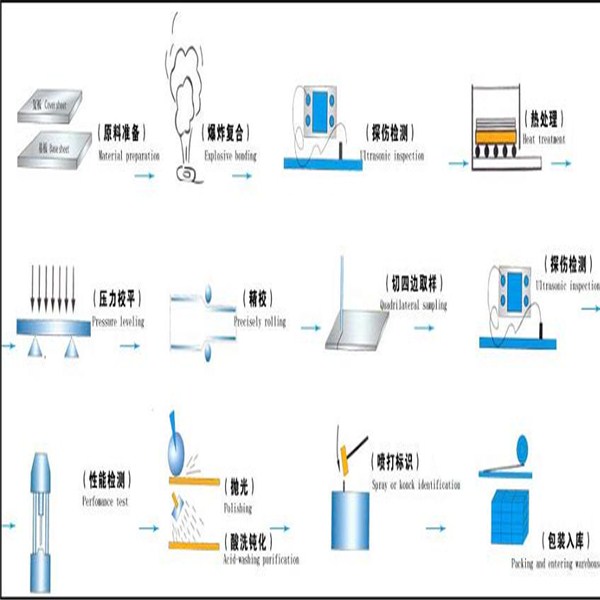


- Q: What are the different types of welding processes used for stainless steel strips?
- For stainless steel strips, there are various welding processes commonly utilized. These processes encompass: 1. TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) Welding: Renowned for its capability to create precise and high-quality welds, TIG welding is favored for stainless steel strips. It employs a non-consumable tungsten electrode to generate the arc and an inert gas, like argon, to safeguard the weld pool against impurities. 2. MIG (Metal Inert Gas) Welding: Another prevalent technique for stainless steel strips is MIG welding, which involves a continuous feed of consumable wire electrode through a welding gun. The electrode melts and unites the base metals while an inert gas shield prevents oxidation in the weld area. 3. Plasma Arc Welding: Plasma arc welding is highly versatile and suitable for stainless steel strips. It utilizes a concentrated and high-temperature plasma arc to fuse the metals together. This method provides excellent control and precision, making it well-suited for thin stainless steel strips. 4. Resistance Welding: Resistance welding relies on the heat generated from electrical resistance to join metals. This process can be applied to stainless steel strips using spot or seam welding techniques. It is commonly employed in high-speed production applications. 5. Laser Welding: Laser welding is a contactless process that employs a highly focused laser beam to join stainless steel strips. It offers exceptional precision and control, making it ideal for intricate or delicate welds. Industries that require a superior finish, both aesthetically and in terms of quality, often use laser welding. These represent only a fraction of the welding processes available for stainless steel strips. The selection of a particular process relies on factors such as strip thickness, desired weld quality, production requirements, and the intended application of the stainless steel strips.
- Q: What are the different types of surface finishes for stainless steel strips?
- There are several different types of surface finishes that are commonly used for stainless steel strips. These finishes are applied to the surface of the stainless steel in order to improve its appearance, increase its corrosion resistance, and enhance its durability. 1. Mill Finish: This is the most basic type of surface finish, which is achieved by leaving the stainless steel strip in its original, as-produced state. It has a dull, non-reflective appearance and may have visible imperfections or marks from the manufacturing process. 2. No. 1 Finish: Also known as hot-rolled annealed and pickled (HRAP), this finish is achieved by annealing the stainless steel strip and then pickling it in acid. It has a smooth, reflective surface with a slightly matte appearance. No. 1 finish is commonly used in industrial applications where surface appearance is not a primary concern. 3. No. 2B Finish: This finish is achieved by cold-rolling the stainless steel strip and then annealing and pickling it. It has a smooth, reflective surface with a bright, semi-reflective appearance. No. 2B finish is commonly used in applications that require a good balance between appearance and corrosion resistance, such as kitchen appliances and architectural elements. 4. No. 4 Finish: Also known as brushed or satin finish, this finish is achieved by mechanically polishing the stainless steel strip with abrasive materials. It has a smooth, matte appearance with fine parallel lines, giving it a brushed texture. No. 4 finish is commonly used in decorative applications, such as furniture, elevator panels, and decorative trims. 5. No. 8 Finish: Also known as mirror finish, this finish is achieved by polishing the stainless steel strip to a highly reflective surface. It has a mirror-like appearance with excellent reflectivity. No. 8 finish is commonly used in architectural and decorative applications that require a high-end, polished look, such as signage, jewelry, and automotive trims. In addition to these main surface finishes, there are also other specialized finishes available for specific applications, such as embossed finishes, patterned finishes, and colored finishes. These finishes further enhance the aesthetic appeal and functionality of stainless steel strips in various industries.
- Q: What are the common uses of stainless steel strips in the pharmaceutical packaging industry?
- The pharmaceutical packaging industry relies on stainless steel strips for various purposes. One primary use involves the manufacturing of packaging containers and components. Different types of containers, including vials, ampoules, and syringes, are made from stainless steel strips due to their ability to resist corrosion, withstand high temperatures, and maintain sterility. By choosing stainless steel, the industry ensures the safety and integrity of the packaged drugs. Moreover, stainless steel strips are also employed in the production of packaging components like lids, caps, and closures. These components are crucial in preserving the quality and freshness of pharmaceutical products. Stainless steel's resistance to rust and its ability to create an airtight seal are essential in guaranteeing the integrity of the packaged medications. Additionally, stainless steel strips find use in constructing pharmaceutical machinery and equipment. The manufacturing processes often involve heavy machinery that requires durable and corrosion-resistant materials. Stainless steel strips are frequently used to fabricate machine parts, conveyor systems, and packaging equipment, ensuring their longevity and reliability. Another common application of stainless steel strips in the pharmaceutical packaging industry is for labeling and identification purposes. Important information such as batch numbers, expiration dates, and drug identification codes can be engraved or etched onto stainless steel strips. This ensures accurate tracking, tracing, and identification of the pharmaceutical products throughout the packaging and distribution process. In summary, stainless steel strips offer numerous advantages in the pharmaceutical packaging industry. Their corrosion resistance, durability, and ability to maintain sterility make them essential for manufacturing containers, components, machinery, and labeling in the sector.
- Q: Can 111 stainless steel strips be polished to a mirror-like finish?
- It is indeed possible to achieve a mirror-like finish on 111 stainless steel strips. However, the key factors that determine this outcome are the quality of the stainless steel strips and the polishing method employed. Stainless steel possesses inherent qualities such as a smooth surface and resistance to corrosion, which enable it to be polished to a high shine. Nevertheless, attaining a mirror-like finish necessitates a meticulous polishing process that involves several stages of abrasive materials and polishing compounds. By employing the appropriate equipment and technique, it becomes feasible to polish 111 stainless steel strips to a mirror-like finish, resulting in an exceptionally reflective and aesthetically pleasing surface.
- Q: Can stainless steel strips be used in aerospace manufacturing?
- Indeed, aerospace manufacturing can make use of stainless steel strips. Renowned for its robustness and resistance to corrosion, stainless steel emerges as a prime option for diverse aerospace applications. It finds frequent utilization in the assembly of aircraft structures, including fuselage frames, wing components, engine mounts, and landing gear. Moreover, stainless steel strips boast an impressive strength-to-weight ratio, rendering them fitting for endeavors that demand substantial strength and rigidity while minimizing mass. Furthermore, stainless steel demonstrates exceptional endurance in the face of extreme temperatures, all the while exhibiting remarkable resistance to fatigue. These qualities combine to establish stainless steel as a dependable material for aerospace manufacturing.
- Q: How are stainless steel strips different from stainless steel sheets or plates?
- Stainless steel comes in various forms, including strips, sheets, and plates. However, these forms differ in terms of their dimensions and applications. For instance, stainless steel strips are slim and lengthy pieces with a thickness typically ranging from 0.2mm to 6mm. These strips find common use in industries such as automotive, construction, and manufacturing. Their thinness and flexibility make them ideal for precise shaping, bending, or forming. As a result, they are commonly employed in the production of components, springs, and electrical connectors. In contrast, stainless steel sheets and plates are larger and thicker. Sheets usually have a thickness of 0.4mm to 6mm, while plates are even thicker, ranging from 6mm to 80mm or more. These forms of stainless steel are utilized in various sectors, including architecture, kitchenware, and industrial equipment. Their larger size and thickness make them suitable for applications such as cladding, roofing, countertops, and heavy-duty machinery parts. Although both stainless steel strips and sheets/plates possess corrosion resistance and durability, their distinct dimensions and applications make them suitable for specific uses. The decision to choose between strips, sheets, or plates depends on the project's requirements, including the desired thickness, size, and intended application.
- Q: What are the factors affecting the weldability of 111 stainless steel strips?
- The weldability of 111 stainless steel strips can be influenced by various factors. 1. The composition of the stainless steel strips, including the levels of carbon, chromium, nickel, and other alloying elements, can have a significant impact on their weldability. Higher carbon content can make the strips more prone to cracking during welding, while the presence of certain alloying elements can enhance their weldability. 2. The weldability of stainless steel strips can be affected by the heat input during welding, which is determined by the combination of current, voltage, and travel speed. Excessive heat input can cause the material to overheat, resulting in distortion, loss of corrosion resistance, and even cracking. 3. Proper surface preparation, including thorough cleaning and removal of contaminants, is crucial to ensure good weldability. Additionally, post-weld treatments such as annealing or stress relieving may be necessary to minimize distortion and reduce residual stresses that could compromise the integrity of the weld. 4. The choice of welding process, such as gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) or gas metal arc welding (GMAW), can impact the weldability of stainless steel strips. Certain processes may require specific shielding gases or filler materials to achieve optimal weld quality. 5. The design of the joint, including its type and dimensions, can also influence the weldability of stainless steel strips. Proper joint design can ensure proper fit-up and decrease the likelihood of weld defects, such as lack of fusion or excessive porosity. 6. The skill and technique of the welder play a significant role in achieving good weldability of stainless steel strips. Correct welding techniques, such as maintaining the appropriate arc length, controlling the heat input, and ensuring consistent travel speed, are essential for producing sound and defect-free welds. By considering these factors and implementing suitable measures, the weldability of 111 stainless steel strips can be optimized, resulting in high-quality welds with excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
- Q: How do stainless steel strips handle exposure to acids?
- Stainless steel strips have excellent resistance to acids due to their high chromium content, which forms a protective oxide layer on the surface. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing the acid from corroding the steel.
- Q: Can stainless steel strips be used in medical applications?
- Yes, stainless steel strips can be used in medical applications. Stainless steel is known for its corrosion resistance, durability, and ease of sterilization, making it suitable for various medical devices and equipment such as surgical instruments, implants, and catheters.
- Q: Can 111 stainless steel strips be used in high-temperature applications?
- No, 111 stainless steel strips cannot be used in high-temperature applications as they lack the necessary heat resistance required for such conditions.
Send your message to us
201 202 304 304L Stainless Steel Coil manufacturers
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 4 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


























