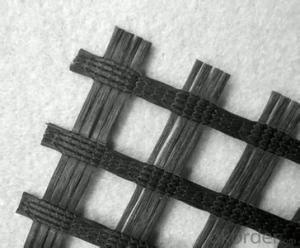
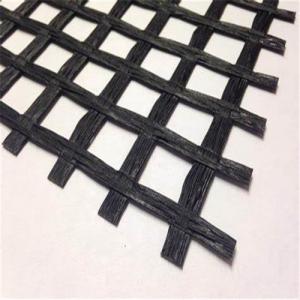
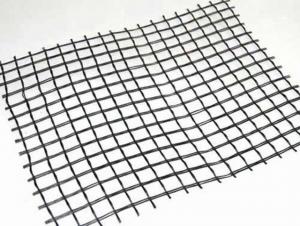
Tx170 Geogrid
Tx170 Geogrid Related Searches
Tensar Triax Tx170 Geogrid Tx150 Geogrid Geogrid Tx160 Geogrid Tx150 Geogrid Tx140 Tx 130 Geogrid Tx 140 Geogrid Tensar Tx160 Geogrid Tx160 Triaxial Geogrid Tx7 Geogrid Triax Tx160 Geogrid Tx190l Geogrid Tx160 Geogrid Price Tensar Tx140 Geogrid Tensar Triax Tx160 Geogrid Tx-5 Geogrid Triax Geogrid Tx160 Tensar Tx 130 Geogrid Tensar Geogrid Tx140 Tensar Tx7 Geogrid Tensar Tx160 Geogrid Price Tensar Triax Geogrid Tx160 Tensar Triax Tx140 Geogrid Tensar Tx5 Geogrid Tensar Tx-5 Geogrid Tensar Triax Tx130s Geogrid Tensar Triax Tx 140 Geogrid Triax Tx Geogrid Tensar Triax Tx7 Geogrid Tensar Triax Tx5 GeogridTx170 Geogrid Supplier & Manufacturer from China
Tx170 Geogrid is a high-performance geosynthetic product designed to enhance the stability and load-bearing capacity of various civil engineering projects. This innovative material is engineered to provide optimal performance in applications such as road construction, soil reinforcement, and slope stabilization. Tx170 Geogrid's unique properties allow it to distribute loads evenly, reducing the risk of soil deformation and failure.In various construction and infrastructure projects, Tx170 Geogrid plays a crucial role in enhancing the overall structural integrity. It is widely used in applications such as reinforcing soil layers, providing support for retaining walls, and improving the performance of paved surfaces. By incorporating Tx170 Geogrid into these projects, engineers can achieve greater stability, increased load-bearing capacity, and extended service life for the infrastructure.
Okorder.com is a leading wholesale supplier of Tx170 Geogrid, offering a vast inventory to cater to the diverse needs of various industries. With a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, Okorder.com ensures that each Tx170 Geogrid product is manufactured to the highest standards and is readily available for shipment. This makes Okorder.com the go-to source for contractors, engineers, and project managers seeking a reliable and efficient solution for their geosynthetic needs.
Hot Products