Z26 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Z26 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
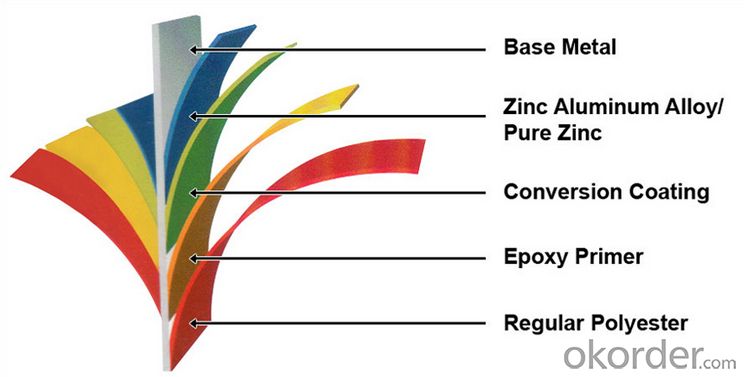
Description of Z26 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
PPGI is made by cold rolled steel sheet and galvanized steel sheets as baseplate, through the surface pretreatment (degreasing, cleaning, chemical conversion processing), coated by the method of continuous coatings (roller coating method),
and after roasting and cooling. Zinc coating: Z60, Z80, Z100, Z120, Z180, Z275, G30, G60, G90
Alu-zinc coating: AZ60, AZ80, AZ100, AZ120, AZ180, G30, G60, G90
Main Feature of Z26 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.Standard seaworthy export packing: 3 layers of packing, inside is kraft paper, water plastic film is in the middle and outside GI steel sheet to be covered by steel strips with lock, with inner coil sleeve.
Applications of Z26 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1. Construction and building: roofing; ventilating duct; handrail; partition panel;etc.
2. Electric appliance: refrigerator; washing machine; refrigerator; DVD;etc.
3.Transportation: oil tank; road sign; etc.
4.Agriculture:barn; etc.
5.Others:vending machine; game machine; etc. 
Specifications of Z26 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
| Classified symbol | Yield Point Minimum N/mm2 | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | ||||
| N/mm2 | Nominal Thickness mm (t) | |||||||
| JIS | Yogic | 0.25-0.4 | 0.4-0.6 | 0.6-1.0 | 1.0-1.6 | |||
| G3312 | specification | |||||||
| CGCC | CGCC | -205 | -270 | -20 | -21 | -24 | -24 | Commercial |
| CGCD | CGCD | --- | 270 | --- | 27 | 31 | 32 | Drawing |
| --- | CG340 | 245 | 340 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | Structural |
| CGC400 | CG400 | 295 | 400 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC440 | CG440 | 335 | 440 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC490 | CG490 | 365 | 490 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 16 | Structural |
| CGC570 | CG570 | 560 | 570 | --- | --- | --- | --- | Structural |
| ASTM Designation | Yield Point Minimum | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | Q/BQB 445-2004(China standard) | ASM A653/A653M | JISG 3312 | |
| ksi(MPa) | ksi(MPa) | TDC51D+Z | (CS TYPE A+Z) | CGCC | ||||
| A653(M)-99 CS TYPE A,B,C | --- | --- | --- | Commercial | TDC52D+Z | CGCD | ||
| A653(M)-99 FS | --- | --- | --- | Lock Forming | TS250GD+Z | (G250+Z) | - | |
| A653(M)-99 DS | --- | --- | --- | Drawing | TS300GS+Z | (G300+Z) | CGC 400 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade33(230) | 33(230) | 45(310) | 20 | Structural | TS350GD+Z | (G350+Z) | CGC490 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade37(255) | 37(255) | 52(360) | 18 | Structural | TS550GD+Z | (G550+Z) | CGC570 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade40(275) | 40(275) | 55(380) | 16 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade50(345) | 50(345) | 65(450) | 12 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade80(550) | 80(550) | 82(570) | --- | Structural | ||||
FAQ of Z26 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
1, ISO, BV, CE, SGS approved.
2, Competitive price and quality.
3, Efficient service team online for 24 hours.
4, Smooth production ability(50000tons/month) .
5, quick delivery and standard exporting package.
6, Flexible payment with T/T, L/C, Paypal, Kunlun bank, etc .
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the thermal conductivity of steel billets?
- The thermal conductivity of steel billets is influenced primarily by several factors. Firstly, the chemical composition of the steel plays a crucial role in determining its thermal conductivity. Elements like carbon, manganese, and silicon can impact the crystal structure and atom arrangement within the steel, thereby affecting its ability to conduct heat. Generally, steels with higher carbon content have lower thermal conductivity due to increased impurities and non-conductive carbide formation. Secondly, the microstructure of the steel also affects its thermal conductivity. Heat conduction in steel happens through lattice vibrations called phonons. Grain boundaries, dislocations, and other defects within the microstructure can hinder phonon movement, resulting in reduced thermal conductivity. Conversely, a more uniform and fine-grained microstructure enhances thermal conductivity. Furthermore, the temperature of the steel billet significantly impacts its thermal conductivity. As the temperature rises, the thermal conductivity of steel generally decreases due to increased scattering of phonons by lattice vibrations and higher thermal resistance. Another factor influencing the thermal conductivity of steel billets is their physical dimensions, specifically cross-sectional area and length. A larger cross-sectional area leads to higher thermal conductivity as there is more space for heat transfer. Similarly, longer billets tend to have lower thermal conductivity due to increased distance for heat conduction. Lastly, the presence of impurities and alloying elements in the steel can also affect its thermal conductivity. For instance, alloying elements like nickel, chromium, and copper can alter the crystal structure and lattice vibrations, thereby influencing the thermal conductivity of the steel billet. In conclusion, the thermal conductivity of steel billets is influenced by factors such as chemical composition, microstructure, temperature, physical dimensions, and the presence of impurities and alloying elements. Understanding these factors is crucial in various industrial applications where heat transfer and thermal management are critical.
- Q: What is the role of steel billets in the manufacturing of pressure vessels?
- Steel billets play a crucial role in the manufacturing of pressure vessels. Pressure vessels are designed to hold and contain fluids or gases at a higher pressure than the atmospheric pressure. These vessels are used in various industries such as oil and gas, chemical, pharmaceutical, and many more. The role of steel billets in the manufacturing process is to serve as the raw material for constructing the pressure vessel. Steel billets are semi-finished products that are obtained through the continuous casting or hot rolling of steel ingots. They have a rectangular or square cross-section and are typically made from carbon steel or alloy steel. Steel billets possess several key properties that make them ideal for pressure vessel manufacturing. Firstly, they have excellent strength and toughness, which is crucial for withstanding the high internal pressure exerted by the fluids or gases inside the vessel. This ensures the structural integrity and safety of the vessel. Secondly, steel billets have good weldability, which is essential for fabricating the pressure vessel. Welding is a common joining technique used in pressure vessel manufacturing, and the weld joints must have comparable strength to the base material. Steel billets allow for strong and reliable welds to be made during the fabrication process. Moreover, steel billets can be easily formed and shaped into the desired size and dimensions required for the pressure vessel. They can be forged, rolled, or extruded to create the necessary components of the vessel, such as the cylindrical body, heads, nozzles, and flanges. This versatility in shaping allows for customization based on the specific requirements of the pressure vessel. Furthermore, steel billets are known for their corrosion resistance, which is important for pressure vessels that come into contact with corrosive fluids or gases. The selection of the appropriate steel grade for the billets ensures that the pressure vessel can withstand the corrosive environment and maintain its integrity over time. In conclusion, steel billets are essential in the manufacturing of pressure vessels as they provide the raw material with the necessary properties to withstand high-pressure conditions. Their strength, weldability, formability, and corrosion resistance make them an ideal choice for constructing reliable and durable pressure vessels used in various industries.
- Q: Can steel billets be used in the production of agricultural equipment?
- Yes, steel billets can be used in the production of agricultural equipment. Steel billets are versatile and strong, making them suitable for manufacturing various components of agricultural machinery such as plows, harvesters, and tractors. The use of steel billets ensures durability, reliability, and resistance to corrosion, making them a preferred material choice in the agricultural industry.
- Q: What is the role of steel billets in the construction of power plants?
- Steel billets play a crucial role in the construction of power plants. These billets are semi-finished steel products that are used as raw material in various processes, including the fabrication of structural components and equipment for power plants. One of the primary applications of steel billets in power plant construction is in the production of structural steel. Structural steel is used to build the framework of power plant structures, such as the main building, turbine halls, reactor buildings, and cooling towers. Steel billets are melted, refined, and cast into various shapes and sizes to create the necessary structural components, including beams, columns, and trusses. These components provide the necessary support and stability to the power plant infrastructure. Additionally, steel billets are also used in the manufacturing of equipment and machinery required for power generation. For instance, they are used to produce turbine rotors, generator frames, and condensers. These components are essential for the operation of power plants and contribute to the efficient conversion of energy. Moreover, steel billets are utilized in the construction of storage tanks, pipelines, and ducts within power plants. These structures are necessary for the storage and transportation of various fluids, such as water, steam, and fuel. Steel billets are transformed into sheets, plates, and tubes to fabricate these components, which are designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures. Furthermore, steel billets are highly durable and possess excellent mechanical properties, such as strength and toughness. These properties make them suitable for withstanding the harsh operating conditions and loads experienced in power plants. They can withstand high temperatures, corrosion, and stresses, ensuring the structural integrity and longevity of power plant infrastructure. In summary, steel billets are essential in the construction of power plants as they are used to produce structural components, equipment, and machinery. Their durability, strength, and versatility make them a preferred material in this industry. The use of steel billets ensures the reliability and safety of power plants, contributing to the generation of electricity for various industries and communities.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the overall weight reduction of a structure?
- There are several ways in which steel billets contribute to reducing the overall weight of a structure. Firstly, through a process called continuous casting, steel billets can be precisely shaped and sized, resulting in lighter and more compact billets. This, in turn, decreases the weight of the structure. Secondly, advanced alloys and compositions can be used to make steel billets with high strength-to-weight ratios. These alloys are specifically designed to provide the same level of strength and durability as traditional steel, but with a lower weight. By incorporating these lightweight steel billets into the construction of a structure, the overall weight can be significantly reduced without sacrificing strength and performance. In addition, steel billets can be employed in the manufacturing of complex shapes and structures using techniques such as extrusion and forging. These methods allow for the creation of intricate designs and structures, eliminating the need for additional components and reducing the overall weight of the structure. Furthermore, steel billets can be used in the construction of lightweight structural elements such as beams, columns, and trusses. These elements can be designed to have hollow sections or thinner profiles, which reduces the amount of steel needed while still maintaining structural integrity. This results in a substantial decrease in the overall weight of the structure. In conclusion, steel billets contribute to weight reduction in structures by enabling the production of lighter and more compact components, utilizing advanced alloys with high strength-to-weight ratios, allowing for the creation of complex shapes and structures, and facilitating the construction of lightweight structural elements.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of chemical processing equipment?
- Steel billets are an essential component in the manufacturing of chemical processing equipment. These billets serve as the raw material that undergoes various processes to transform into the final products required in chemical processing plants. Firstly, steel billets are used to produce high-quality steel plates that form the structural framework of chemical processing equipment. These plates are cut, shaped, and welded together to create vessels, reactors, and storage tanks. The strength and durability of steel make it an ideal choice for containing corrosive chemicals and withstanding high pressures and temperatures. Additionally, steel billets are also utilized in the production of pipes and fittings used in chemical processing plants. These billets are heated and passed through a series of rollers to form seamless or welded pipes. The resulting pipes are then further processed and fabricated to meet specific requirements such as corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and pressure ratings. Furthermore, steel billets are used to manufacture various components of chemical processing equipment, including valves, flanges, and other fittings. These components play a crucial role in controlling the flow of chemicals, regulating pressure, and connecting different parts of the processing system. Steel billets are machined, forged, or cast to create these components, ensuring their strength, reliability, and resistance to chemical corrosion. Overall, steel billets are an integral part of the manufacturing process for chemical processing equipment. Their versatility, strength, and resistance to corrosion make them the preferred choice for constructing the structural framework, pipes, and fittings required in chemical processing plants. By utilizing steel billets, manufacturers can ensure the reliability, safety, and longevity of the equipment used in the chemical industry.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the manufacturing of industrial equipment?
- The production of industrial equipment heavily relies on steel billets, which are essential for the manufacturing process. These semi-finished steel products are created through casting and act as the raw material for a wide range of industrial equipment. A key aspect of steel billets is their versatility, which greatly contributes to the manufacturing of industrial equipment. They possess both malleability and strength, allowing them to be easily shaped and molded into various forms, such as bars, rods, or sheets. This adaptability enables manufacturers to produce durable and reliable components and structures capable of withstanding heavy loads and extreme conditions. Furthermore, steel billets offer an impressive strength-to-weight ratio, making them particularly suitable for applications where reducing weight is crucial without compromising structural integrity. This quality proves beneficial for industrial equipment that requires frequent transportation or movement, as the use of lightweight steel billets optimizes efficiency and minimizes energy consumption. Additionally, steel billets play a significant role in protecting industrial equipment against corrosion and wear. Many industrial environments expose equipment to harsh conditions, including moisture, chemicals, and abrasion. The utilization of steel billets ensures that the equipment remains resistant to these challenges, reducing maintenance and replacement costs while maintaining performance over time. Moreover, steel billets facilitate efficient heat treatment processes during the manufacturing of industrial equipment. Through controlled heating and cooling procedures, manufacturers can enhance the mechanical properties of the steel, such as hardness, toughness, and ductility. This enables the production of equipment capable of withstanding high temperatures, extreme pressures, and dynamic loading conditions, ensuring safety and reliability across various industrial applications. In conclusion, the role of steel billets in the manufacturing of industrial equipment is indispensable. Their versatility, strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and facilitation of heat treatment processes contribute to the creation of durable, reliable, and high-performance equipment capable of meeting the demands of diverse industries.
- Q: What are the potential applications of steel billets in the mining industry?
- Steel billets have a wide range of potential applications in the mining industry. Firstly, steel billets can be used in the construction of mining equipment and machinery. These billets can be shaped and welded to form various components such as frames, supports, and chassis for heavy mining machinery. The strength and durability of steel make it an ideal material for withstanding the harsh conditions and heavy loads encountered in mining operations. Secondly, steel billets can be utilized in the fabrication of conveyor belts, which are essential for the transportation of bulk materials in mines. The high tensile strength of steel ensures that the conveyor belts can withstand the weight of the material being transported, as well as the continuous movement and impact from the mining process. Additionally, steel billets can be employed in the construction of underground support systems, such as mine shafts and tunnels. These structures require strong and reliable materials to ensure the safety of workers and the integrity of the mining operation. Steel billets can be used to manufacture support beams, rods, and plates, providing the necessary stability and reinforcement. Moreover, steel billets can be used in the production of wear-resistant components, such as grinding balls and liners, which are crucial in mineral processing. These components are used in grinding mills to crush and grind the ore, and the abrasion-resistant properties of steel make it a suitable material for this application. By using steel billets, mining companies can enhance the efficiency and longevity of their mineral processing operations. Overall, the potential applications of steel billets in the mining industry are extensive. From equipment manufacturing and conveyor belt fabrication to underground support systems and wear-resistant components, steel billets play a vital role in improving the productivity, safety, and efficiency of mining operations.
- Q: Difference between billet, slab and billet
- Steel billet is a product made by steel-making furnace by casting. The billet can be divided into two kinds from the manufacturing process, mould blank and continuous casting billet. At present, the casting process has been basically eliminated. The classification is mainly divided into two kinds: slab: large cross section, high ratio, mainly used for rolling plate. Billet: cross section width, height equal, or difference is not big, mainly used for rolling steel, wire. Use billet is steel, through processing can be used as mechanical parts, forgings, processing all kinds of steel, steel, Q345B, channel steel, wire is the role of billet. Billet is used for the production of semi-finished steel products, generally can not be used directly for society. Billet and steel are strictly divided into standard, and can not be determined by the final product of the enterprise, but should be carried out according to the uniform standard of the whole society. Usually, billet and steel is relatively easy to distinguish, but for some billets, with the same specification and the same purpose (such as rolling and steel tube), whether for other industries by use, whether through steel processing process, whether after finishing mill processing to distinguish. Continuous cast steel square and rectangular billets are mainly made of plain carbon steel, low carbon and low silicon cold rolled material, high quality carbon structural steel, low alloy high strength steel, special steel and so on.
- Q: What is the cost of producing steel billets?
- The cost of producing steel billets can vary depending on various factors such as the quality of raw materials, energy costs, labor expenses, equipment maintenance, and market demand. It is difficult to provide a specific cost without considering these variables, but it generally involves substantial investment in machinery, infrastructure, and operational expenses.
Send your message to us
Z26 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords































