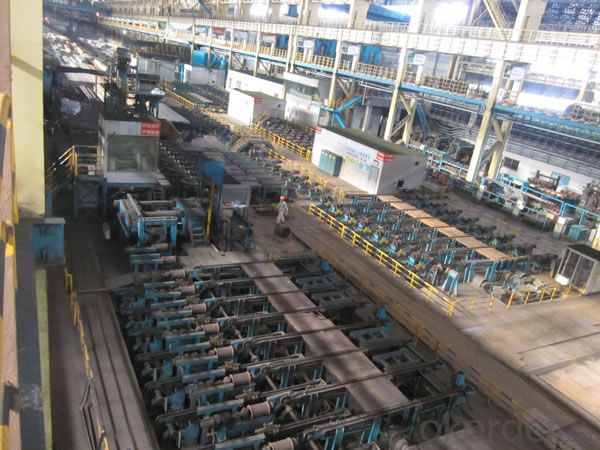
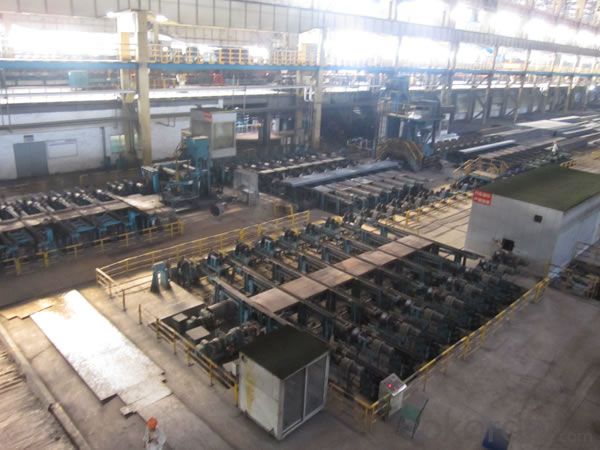
Z29 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Z29 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
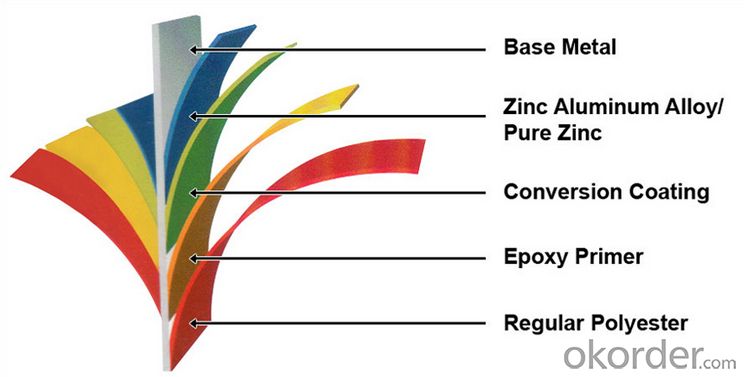
Description of Z29 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
PPGI is made by cold rolled steel sheet and galvanized steel sheets as baseplate, through the surface pretreatment (degreasing, cleaning, chemical conversion processing), coated by the method of continuous coatings (roller coating method),
and after roasting and cooling. Zinc coating: Z60, Z80, Z100, Z120, Z180, Z275, G30, G60, G90
Alu-zinc coating: AZ60, AZ80, AZ100, AZ120, AZ180, G30, G60, G90
Main Feature of Z29 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.Standard seaworthy export packing: 3 layers of packing, inside is kraft paper, water plastic film is in the middle and outside GI steel sheet to be covered by steel strips with lock, with inner coil sleeve.
Applications of Z29 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1. Construction and building: roofing; ventilating duct; handrail; partition panel;etc.
2. Electric appliance: refrigerator; washing machine; refrigerator; DVD;etc.
3.Transportation: oil tank; road sign; etc.
4.Agriculture:barn; etc.
5.Others:vending machine; game machine; etc. 
Specifications of Z29 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
| Classified symbol | Yield Point Minimum N/mm2 | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | ||||
| N/mm2 | Nominal Thickness mm (t) | |||||||
| JIS | Yogic | 0.25-0.4 | 0.4-0.6 | 0.6-1.0 | 1.0-1.6 | |||
| G3312 | specification | |||||||
| CGCC | CGCC | -205 | -270 | -20 | -21 | -24 | -24 | Commercial |
| CGCD | CGCD | --- | 270 | --- | 27 | 31 | 32 | Drawing |
| --- | CG340 | 245 | 340 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | Structural |
| CGC400 | CG400 | 295 | 400 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC440 | CG440 | 335 | 440 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC490 | CG490 | 365 | 490 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 16 | Structural |
| CGC570 | CG570 | 560 | 570 | --- | --- | --- | --- | Structural |
| ASTM Designation | Yield Point Minimum | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | Q/BQB 445-2004(China standard) | ASM A653/A653M | JISG 3312 | |
| ksi(MPa) | ksi(MPa) | TDC51D+Z | (CS TYPE A+Z) | CGCC | ||||
| A653(M)-99 CS TYPE A,B,C | --- | --- | --- | Commercial | TDC52D+Z | CGCD | ||
| A653(M)-99 FS | --- | --- | --- | Lock Forming | TS250GD+Z | (G250+Z) | - | |
| A653(M)-99 DS | --- | --- | --- | Drawing | TS300GS+Z | (G300+Z) | CGC 400 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade33(230) | 33(230) | 45(310) | 20 | Structural | TS350GD+Z | (G350+Z) | CGC490 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade37(255) | 37(255) | 52(360) | 18 | Structural | TS550GD+Z | (G550+Z) | CGC570 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade40(275) | 40(275) | 55(380) | 16 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade50(345) | 50(345) | 65(450) | 12 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade80(550) | 80(550) | 82(570) | --- | Structural | ||||
FAQ of Z29 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
1, ISO, BV, CE, SGS approved.
2, Competitive price and quality.
3, Efficient service team online for 24 hours.
4, Smooth production ability(50000tons/month) .
5, quick delivery and standard exporting package.
6, Flexible payment with T/T, L/C, Paypal, Kunlun bank, etc .
- Q: How are steel billets inspected for internal and surface defects?
- Steel billets are inspected for internal and surface defects through various methods, including visual inspection, ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, and eddy current testing. Visual inspection involves examining the billets for any visible defects such as cracks, holes, or surface irregularities. Ultrasonic testing utilizes high-frequency sound waves to detect internal defects by analyzing the reflected waves. Magnetic particle inspection uses magnetic fields and iron particles to identify surface cracks or defects that may not be visible to the naked eye. Eddy current testing involves passing an electrical current through the billets to identify surface defects or inconsistencies in conductivity. These inspection techniques ensure the quality and integrity of steel billets for further processing.
- Q: Can steel billets be used in the production of marine equipment?
- Marine equipment can indeed utilize steel billets. Steel possesses remarkable characteristics such as strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, rendering it a fitting choice for marine purposes. In the process of manufacturing steel, semi-finished products called steel billets can be further processed and transformed into diverse components for marine equipment, including ship hulls, propeller shafts, rudders, and offshore structures. The remarkable strength-to-weight ratio of steel makes it an ideal material to withstand the rigorous conditions encountered in marine environments, encompassing exposure to saltwater, extreme temperatures, and mechanical stresses. Moreover, steel allows for easy fabrication, welding, and machining, enabling the customization and production of intricate designs for marine equipment. Ultimately, steel billets represent a valuable raw material in the production of marine equipment due to their strength, durability, and suitability for marine applications.
- Q: What is the role of steel billets in the construction of power plants?
- The construction of power plants relies heavily on steel billets, which are semi-finished steel products utilized as raw materials in various processes involved in power plant production. A significant application of steel billets in this field is the creation of structural steel, which forms the framework of power plant structures like the main building, turbine halls, reactor buildings, and cooling towers. To produce the necessary structural components such as beams, columns, and trusses, steel billets are melted, refined, and cast into different shapes and sizes. These components provide essential support and stability to power plant infrastructure. Furthermore, steel billets are crucial in the manufacturing of equipment and machinery necessary for power generation. Turbine rotors, generator frames, and condensers are among the components produced using steel billets. These components play a vital role in the operation of power plants and contribute to efficient energy conversion. Moreover, steel billets are utilized in the construction of storage tanks, pipelines, and ducts within power plants. These structures are crucial for storing and transporting various fluids like water, steam, and fuel. Steel billets are transformed into sheets, plates, and tubes to fabricate these components, which are designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures. Steel billets are also highly durable and possess exceptional mechanical properties such as strength and toughness. These properties enable them to withstand the harsh operating conditions and loads experienced in power plants. They can endure high temperatures, corrosion, and stresses, ensuring the structural integrity and longevity of power plant infrastructure. In conclusion, steel billets are indispensable in power plant construction as they are employed in the production of structural components, equipment, and machinery. Their durability, strength, and versatility make them the preferred material in this industry. The use of steel billets guarantees the reliability and safety of power plants, ultimately contributing to the generation of electricity for various industries and communities.
- Q: What are the challenges in welding steel billets?
- Welding steel billets presents various obstacles that need to be addressed. One of the primary hurdles involves achieving proper heat distribution throughout the welding process. Given their considerable size and thickness, steel billets make it difficult to evenly distribute heat across the material. Consequently, this can lead to inconsistencies in the weld, resulting in weak areas or even joint failure. Another challenge revolves around the possibility of distortion and warping during the welding process. The application of heat to the steel causes the material to expand and contract, leading to undesired changes in shape and dimensions. This issue becomes particularly problematic when dealing with larger or more intricate structures, as maintaining the desired shape and dimensions becomes crucial. Furthermore, steel billets may contain impurities and contaminants that can impact the weld's quality. These impurities, such as sulfur, phosphorus, and other elements, can trigger the formation of brittle zones or other defects in the weld. To mitigate these challenges, it is necessary to adequately clean and prepare the billet surface, as well as employ appropriate welding techniques and filler materials. Moreover, the high carbon content commonly found in steel billets makes them susceptible to cracking during the welding process. Carbon acts as a hardening agent in steel and can increase its vulnerability to cracking, particularly if proper preheating and post-weld heat treatment procedures are not followed. Essential measures include controlling the cooling rate and implementing stress-relieving techniques to prevent cracking and ensure weld integrity. Lastly, the sheer size and weight of steel billets can pose logistical challenges during welding. The handling and positioning of these heavy objects necessitate specialized equipment and skilled operators to guarantee safety and accuracy. Additionally, achieving precise alignment and fit-up becomes more complex with larger billets, demanding careful planning and execution. To summarize, welding steel billets involves overcoming challenges such as heat distribution, distortion and warping, impurities and contaminants, carbon-induced cracking, and logistical issues. Successfully navigating these obstacles requires expertise, appropriate equipment, and adherence to proper welding techniques and procedures.
- Q: What are the safety precautions when working with steel billets?
- When working with steel billets, it is important to follow certain safety precautions to prevent any accidents or injuries. Some of the key precautions include: 1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate PPE such as safety goggles, gloves, steel-toe boots, and protective clothing to protect yourself from potential hazards. 2. Proper Handling Techniques: Use proper lifting techniques when moving or transporting steel billets to avoid strain or injuries. Use mechanical aids like cranes or forklifts if necessary. 3. Inspection and Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain equipment such as forklifts, cranes, and lifting slings to ensure they are in good working condition and can safely handle the weight and load of the steel billets. 4. Secure Storage: Store steel billets in a secure and designated area to prevent them from falling or rolling over, which can cause serious injuries. 5. Fire Safety: Be aware of fire hazards and ensure that fire extinguishers are readily available in case of emergencies. Proper storage and handling of flammable substances should also be followed. 6. Communication and Signage: Properly communicate and provide clear signage to indicate potential hazards, restricted areas, and safety procedures. 7. Training and Awareness: Provide appropriate training to workers about the potential hazards associated with working with steel billets, as well as the necessary safety procedures to follow. Regularly reinforce safety protocols and encourage a safety-conscious work environment. By following these safety precautions, the risk of accidents or injuries when working with steel billets can be significantly reduced, ensuring a safer work environment for everyone involved.
- Q: Are steel billets affected by extreme temperatures?
- Yes, steel billets can be affected by extreme temperatures. High temperatures can cause the billets to soften and become more malleable, making them easier to shape or deform. On the other hand, extremely low temperatures can make the steel brittle and prone to cracking or fracturing. Therefore, it is important to carefully control and monitor the temperature conditions during the production and processing of steel billets.
- Q: I want to buy a fishing pole, I don't know how to distinguish it. Know what, please reply, thank you, [em10]!
- The tonality of a fishing rod is actually modulated by a different modulus of carbon cloth.Some fishing overall with the 30T following carbon cloth, just use a very small amount of 40T or 46T carbon cloth, called high carbon rod, is actually confuse the public practice of fishing by weighing, hand identification, high carbon rod with real light, hard, two rods in a play, a ratio is obvious.
- Q: What are the potential defects or flaws in steel billets?
- There are several potential defects or flaws that can occur in steel billets, which can affect the quality and performance of the final product. Some of these defects include: 1. Surface defects: Steel billets can develop surface cracks, scales, or scratches during the manufacturing process. These defects can weaken the material and reduce its structural integrity. 2. Internal defects: Inclusions, such as non-metallic impurities or gas bubbles, can be present within the steel billets. These internal defects can cause localized weaknesses and reduce the overall strength of the material. 3. Segregation: Uneven distribution of alloying elements or impurities can lead to segregation, where certain areas of the billet have different chemical compositions. Segregation can result in inconsistent mechanical properties across the material and decrease its uniformity. 4. Central segregation: This defect occurs when there is a concentration of impurities or alloying elements in the central region of the billet, leading to a weaker core. Central segregation can cause structural failures and reduce the overall reliability of the steel billet. 5. Shrinkage cavities: During the solidification process, shrinkage cavities can form in the steel billet due to the contraction of the molten metal. These cavities can weaken the material and compromise its structural integrity. 6. Surface decarburization: Exposure to high temperatures or improper heat treatment can cause the surface of the steel billet to lose carbon content, resulting in surface decarburization. This defect can reduce the hardness and strength of the material. 7. Laminations: Laminations are thin, elongated voids or layers that can form parallel to the surface of the billet. These defects can weaken the material and make it prone to cracking or failure under stress. 8. Internal cracks: Internal cracks can occur due to improper cooling or handling of the billet during the manufacturing process. These cracks can compromise the structural integrity of the steel billet and potentially lead to catastrophic failure. It is important to detect and address these defects early on to ensure the quality and reliability of the steel billets. Various non-destructive testing techniques, such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection, can be utilized to identify and mitigate these potential flaws.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the corrosion resistance of a product?
- The corrosion resistance of a product is not directly affected by steel billets. Instead, it is determined by the specific composition and treatment of the steel billets. Steel billets are essentially semi-finished steel products that act as raw materials for various downstream processes like forging, rolling, and extrusion, which ultimately produce the final product. To improve the corrosion resistance of a product, specific alloying elements and controlled processing techniques can be used during the manufacturing of steel billets. For example, stainless steel billets have a higher chromium content, which creates a protective oxide layer called chromium oxide on the steel's surface. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing direct contact between the steel and corrosive environments, thus enhancing the corrosion resistance of the final product. Additionally, steel billets can undergo further treatments like heat treatment, surface coatings, or galvanization to enhance their corrosion resistance. Heat treatment processes like annealing, quenching, or tempering can modify the microstructure of steel billets, resulting in improved corrosion resistance properties. Surface coatings like paint, powder coating, or electroplating can provide an additional layer of protection, preventing direct exposure to corrosive substances. Galvanization involves coating steel billets with a layer of zinc, which acts as a sacrificial anode, corroding instead of the underlying steel to protect it. In conclusion, while steel billets themselves do not directly contribute to the corrosion resistance of a product, the composition, alloying elements, and treatments applied during their manufacturing process play a crucial role in enhancing the corrosion resistance of the final product.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the circular economy?
- Steel billets contribute to the circular economy in several ways. Firstly, they are a key component in the recycling process of steel. Steel is one of the most recycled materials in the world, and the use of steel billets enables the recycling of scrap steel into new products. By using steel billets, the steel industry can reduce the demand for virgin iron ore and the energy-intensive processes associated with its extraction and production. Moreover, steel billets can be produced from various sources, including industrial waste, automotive scrap, and construction waste. This allows for the repurposing of materials that would otherwise end up in landfills, reducing waste and conserving resources. By utilizing steel billets made from recycled materials, the industry can promote a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to steel production. Furthermore, steel billets are highly versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications. This versatility extends the lifespan of steel products and reduces the need for replacement. In the circular economy, the aim is to maximize the use of resources, and steel billets contribute to this goal by enabling the production of durable and long-lasting steel products. Lastly, the circular economy emphasizes the importance of closing the loop and ensuring that materials are reused or recycled at the end of their life cycle. Steel billets facilitate this process by being a readily available feedstock for the production of new steel products. This not only reduces the reliance on virgin materials but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with extracting and processing raw materials. In conclusion, steel billets play a crucial role in the circular economy by enabling the recycling of steel, repurposing of waste materials, promoting durability, and closing the loop in the steel production process. Their use contributes to the conservation of resources, reduction of waste, and overall sustainability of the steel industry.
Send your message to us
Z29 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords































