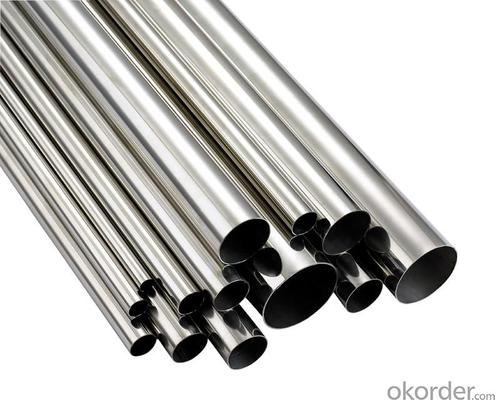
Stainless steel pipes 316 pipe
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
In metallurgy, stainless steel, also known as inox steel or inox from French "inoxydable", is a steelalloy with a minimum of 10.5%[1]chromium content by mass.
Stainless steel does not readily corrode, rust or stain with water as ordinary steel does. However, it is not fully stain-proof in low-oxygen, high-salinity, or poor air-circulation environments.[2] There are different grades and surface finishes of stainless steel to suit the environment the alloy must endure. Stainless steel is used where both the properties of steel and corrosion resistance are required.
Stainless steel differs from carbon steel by the amount of chromium present. Unprotected carbon steel rusts readily when exposed to air and moisture. This iron oxide film (the rust) is active and accelerates corrosion by forming more iron oxide; and, because of the greater volume of the iron oxide, this tends to flake and fall away. Stainless steels contain sufficient chromium to form a passive film of chromium oxide, which prevents further surface corrosion by blocking oxygen diffusion to the steel surface and blocks corrosion from spreading into the metal's internal structure, and, due to the similar size of the steel and oxide ions, they bond very strongly and remain attached to the surface.[3]
Passivation occurs only if the proportion of chromium is high enough and oxygen is present.
Oxidation[edit]
High oxidation resistance in air at ambient temperature is normally achieved with additions of a minimum of 13% (by weight) chromium, and up to 26% is used for harsh environments.[14] The chromium forms a passivation layer of chromium(III) oxide (Cr2O3) when exposed to oxygen. The layer is too thin to be visible, and the metal remains lustrous and smooth. The layer is impervious to water and air, protecting the metal beneath, and this layer quickly reforms when the surface is scratched. This phenomenon is called passivation and is seen in other metals, such as aluminium and titanium. Corrosion resistance can be adversely affected if the component is used in a non-oxygenated environment, a typical example being underwater keel bolts buried in timber.
When stainless steel parts such as nuts and bolts are forced together, the oxide layer can be scraped off, allowing the parts to weld together. When forcibly disassembled, the welded material may be torn and pitted, an effect known as galling. This destructive galling can be avoided by the use of dissimilar materials for the parts forced together, for example bronze and stainless steel, or even different types of stainless steels (martensitic against austenitic). However, two different alloys electrically connected in a humid environment may act as Voltaic pile and corrode faster. Nitronic alloys made by selective alloying with manganese and nitrogen may have a reduced tendency to gall. Additionally, threaded joints may be lubricated to prevent galling.
Acids[edit]
Stainless steel is generally highly resistant to attack from acids, but this quality depends on the kind and concentration of the acid, the surrounding temperature, and the type of steel. Type 904 is resistant to sulfuric acid at room temperature, even in high concentrations, type 316 and 317 are resistant below 10% and 304 should not be used at any concentration. All types of stainless steel resist attack from phosphoric acid, 316 and 317 more so than 304; and Types 304L and 430 have been successfully used with nitric acid. Hydrochloric acid will damage any kind of stainless steel, and should be avoided.[15]
Bases[edit]
The 300 series of stainless steel grades is unaffected by any of the weak bases such as ammonium hydroxide, even in high concentrations and at high temperatures. The same grades of stainless exposed to stronger bases such as sodium hydroxide at high concentrations and high temperatures will likely experience some etching and cracking, especially with solutions containing chlorides.[15]
Organics[edit]
Types 316 and 317 are both useful for storing and handling acetic acid, especially in solutions where it is combined with formic acid and when aeration is not present (oxygen helps protect stainless steel under such conditions), though 317 provides the greatest level of resistance to corrosion. Type 304 is also commonly used with formic acid though it will tend to discolor the solution. All grades resist damage from aldehydes and amines, though in the latter case grade 316 is preferable to 304; cellulose acetate will damage 304 unless the temperature is kept low. Fats and fatty acids only affect grade 304 at temperatures above 150 °C (302 °F), and grade 316 above 260 °C (500 °F), while 317 is unaffected at all temperatures. Type 316L is required for processing of urea.[15]
Electricity and magnetism[edit]
Similarly to steel, stainless steel is a relatively poor conductor of electricity, with a lower electrical conductivity than that of copper.
Ferritic and martensitic stainless steels are magnetic. Austenitic stainless steels are non-magnetic.
- Q: Are stainless steel pipes suitable for oil and gas applications?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes are suitable for oil and gas applications. They have excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and can withstand high temperatures and pressures commonly found in oil and gas operations. Additionally, stainless steel pipes are easily maintainable and have a long lifespan, making them a reliable choice for such applications.
- Q: What is the maximum length of a stainless steel pipe?
- The maximum length of a stainless steel pipe can vary depending on various factors such as the manufacturing process, the specific grade of stainless steel used, and the intended application. In general, stainless steel pipes can be manufactured in lengths ranging from a few feet to several hundred feet. However, it is important to consider practical limitations such as transportation and installation requirements, as longer lengths may pose logistical challenges. Additionally, longer pipes may be prone to increased structural stress and potential for bending or sagging. Therefore, it is advisable to consult with a manufacturer or supplier to determine the maximum length of a stainless steel pipe suitable for a specific application.
- Q: Mirror stainless steel tube 60*60 how much is one meter?
- Examples are stainless steel 63 round tubes, solid thickness 0.82 stainless steel tubes, single support 6 meters long, weight (63-0.82) *0.82*0.02491*6=7.62kg, a six meter long 63 round tube, thickness 0.82, theoretical weight is 7.62kg;
- Q: What are the specifications of stainless steel decorative pipes?
- The steel pipe seamless steel pipe and welded steel pipe (seamed pipe) two categories. It can be divided into round tube and special-shaped tube according to the sectional shape. The round steel tube is widely used, but there are some special-shaped steel tubes such as square, rectangle, semicircle, hexagon, equilateral triangle and octagon.
- Q: How do you determine the size of a stainless steel pipe?
- The size of a stainless steel pipe is determined by measuring its outer diameter using a caliper or a tape measure.
- Q: What is the maximum operating temperature for stainless steel pipes?
- The specific grade of stainless steel used can cause the maximum operating temperature for stainless steel pipes to vary. Nevertheless, stainless steel pipes, on the whole, can endure high temperatures. Typically, austenitic stainless steel grades like 304 and 316 are capable of handling temperatures up to 870°C (1600°F). Conversely, ferritic stainless steel grades like 430 have a lower maximum operating temperature of approximately 760°C (1400°F). To determine the precise maximum operating temperature for a specific stainless steel grade and pipe, it is crucial to refer to the manufacturer's specifications and guidelines.
- Q: What are the factors to consider when selecting stainless steel pipes for a specific application?
- When selecting stainless steel pipes for a specific application, several factors need to be considered to ensure the right choice is made. 1. Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel is known for its exceptional resistance to corrosion, but different grades offer varying levels of protection against specific corrosive environments. The type of corrosive agents present in the application, such as chemicals, moisture, or high temperatures, should be carefully evaluated to select a stainless steel grade that can withstand them effectively. 2. Temperature and Pressure: Stainless steel pipes are used in a wide range of temperature and pressure conditions. The selected grade must have the necessary strength and resistance to handle the specific temperature and pressure levels required by the application. Higher temperatures may require grades with increased heat resistance, while high-pressure environments may benefit from pipes with higher tensile strength. 3. Material Compatibility: In some applications, stainless steel pipes may come into contact with other materials or substances, such as liquids or gases. It is crucial to consider the compatibility of the stainless steel with these materials to avoid any potential chemical reactions, contamination, or degradation. Compatibility testing or consulting with experts can help determine the best choice of material. 4. Size and Dimensions: The size and dimensions of the stainless steel pipes should match the requirements of the application. This includes considering the diameter, thickness, and length of the pipes. Proper sizing ensures optimal flow rates, structural integrity, and ease of installation. 5. Cost: Cost is always a factor to consider in any decision-making process. Different stainless steel grades vary in price, and it is essential to balance the desired properties with the available budget. While cost should not be the sole determining factor, it is important to find a stainless steel pipe that meets the required specifications without exceeding the allotted budget. 6. Standards and Certifications: Depending on the application, certain standards and certifications may be required, such as ASTM, ASME, or ISO. These standards ensure that the stainless steel pipes meet specific quality and performance criteria. It is crucial to select pipes that comply with the necessary standards and have appropriate certifications to ensure reliability and safety. 7. Maintenance and Durability: Consider the maintenance requirements and expected lifespan of the stainless steel pipes. Some applications may require regular cleaning, inspection, or maintenance, while others may need pipes with long-term durability and resistance to wear and tear. By carefully evaluating these factors, one can make an informed decision when selecting stainless steel pipes for a specific application, ensuring they meet the necessary performance, quality, and safety requirements.
- Q: Are stainless steel pipes suitable for drinking water applications?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes are suitable for drinking water applications. Stainless steel is a highly durable and corrosion-resistant material, making it an excellent choice for transporting drinking water. It does not leach harmful substances into the water and is resistant to rust and scaling, ensuring the water remains clean and safe for consumption. Additionally, stainless steel pipes are easy to clean and maintain, which further promotes the hygiene of the water supply. The long lifespan and reliability of stainless steel pipes also make them a cost-effective solution for drinking water applications.
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be used for rainwater harvesting systems?
- Stainless steel pipes are indeed suitable for rainwater harvesting systems. This material possesses durability and resistance to corrosion, making it an ideal selection for the collection and storage of rainwater. Moreover, stainless steel pipes are effortless to maintain and boast a prolonged lifespan, guaranteeing the system's effectiveness and longevity. Furthermore, due to their hygienic nature, stainless steel pipes do not taint the collected rainwater, ensuring its safety for multiple applications, including irrigation, cleaning, and even drinking in certain instances.
- Q: What is the difference between nominal diameter and actual diameter in stainless steel pipes?
- The difference between nominal diameter and actual diameter in stainless steel pipes lies in their respective definitions and practical applications. Nominal diameter, also known as nominal size, refers to the designation given to a pipe based on its approximate internal diameter. It is a standardized measurement used in industry to facilitate communication and categorization of pipes. The nominal diameter is typically expressed in inches or millimeters, and it is often rounded to the nearest whole number. For example, a pipe with a nominal diameter of 2 inches would typically have an internal diameter close to, but not exactly, 2 inches. On the other hand, actual diameter refers to the precise measurement of the internal diameter of a stainless steel pipe. It is determined by physically measuring the inside diameter using tools such as calipers or a micrometer. The actual diameter provides an accurate measurement of the pipe's internal size, allowing for precise calculations and fitting purposes. The difference between nominal diameter and actual diameter can vary depending on the manufacturing process and the specific tolerances of the stainless steel pipes. In general, the actual diameter is slightly smaller than the nominal diameter due to factors such as the thickness of the pipe's walls and the manufacturing tolerances. The difference between the two measurements is known as the nominal wall thickness. Understanding the difference between nominal diameter and actual diameter is crucial in various industries, especially in plumbing, construction, and engineering. It helps ensure that pipes are correctly selected, installed, and connected, avoiding any potential issues related to misalignment, leakage, or improper fittings. Therefore, it is important to consider both the nominal diameter and actual diameter when working with stainless steel pipes to ensure the proper functioning and structural integrity of the system.
Send your message to us
Stainless steel pipes 316 pipe
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords