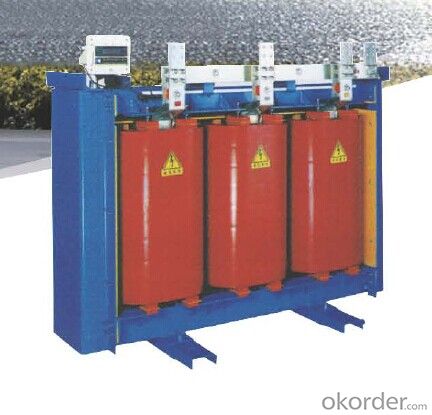
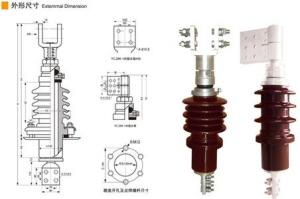
SC(B)H15 Type Amorphous Metal Dry-type Transformer
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 unit
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 unit/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like


- Q: How much capacity the transformer has
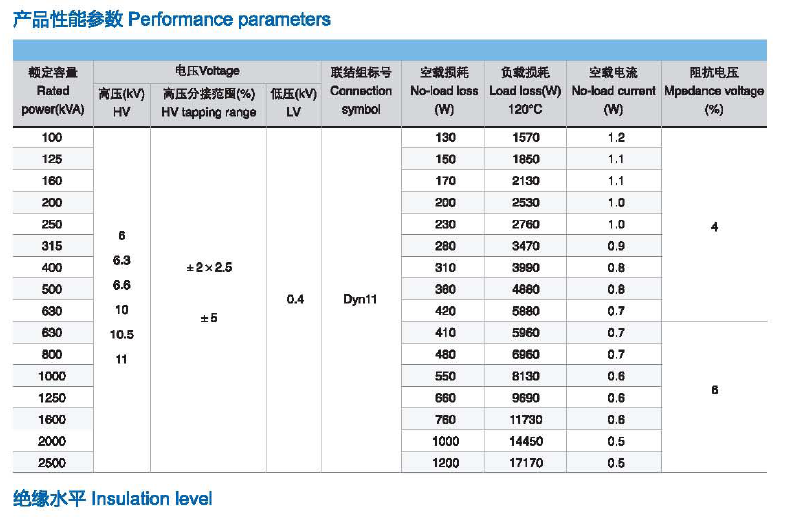
- For power transformers, there are 10 20 30 40 50 63 80 100 125 160 200 250 315 400 500 630 800 1000 1250 1600 2000 2500 3150 4000 5000 6300, etc. kVA.
- Q: As a small project I wish to wire a microwave transformer to create arcs in air via use of a wand (and yes I will be taking the necessary precautions but that's step 2) first I need to know a couple things: 1 on the high voltage secondary is it really as simple as take the two leads and put them anywhere near eachother? Would that not create a MASSIVE short circuit? Most of the tutorials I've seen use in series so perhaps that negates it in some way? Or am I reading it wrong? Is there some sort of safe load used? Or does it really arc to itself? And 2 what is a good way of preventing it from overheating (if that is a problem). This will probably be used as a Jacob's ladder or old motherboard destroyer. Thanks so much for the help!
- Don't.
- Q: Transformer Lightning
- Dry coil internal coil will burst open, so that the transformer outside the four sides of the shell will be bulging. Cylinders on the porcelain will burn black, porcelain will be black and cracked. The line breaker is tripped.
- Q: The core part of the transformer is composed of sub-and sub-components, which are generally divided into two transformers. Urgent, quick answer What is the core part of the "what" and "what" sub-composition ah? The "What" son, this "what" is to fill you ah.
- The core part of the transformer is the transformer is the exchange of AC voltage, current and impedance of the device, when the primary coil with AC current, the core (or core) will produce AC flux, the secondary coil induced voltage ( Or current). Sort by cooling: dry (self-cooling) transformers, oil immersion (self-cooling) transformers, fluoride (evaporative cooling) transformers. According to moisture-proof classification: open-type transformers, potting transformers, sealed transformers. According to the core or coil structure classification: core transformer (insert core, C core, ferrite core), shell transformer (insert core, C core, ferrite core), Ring transformers, metal foil transformers. According to the number of power supply categories: single-phase transformers, three-phase transformers, multi-phase transformers. By use classification: power transformers, voltage transformers, audio transformers, IF transformers, high-frequency transformers, pulse transformers.
- Q: 50KVA transformer each phase current maximum band
- Transformer output power is apparent power, and active power (KW) relationship: apparent power = active power × power factor. With an average power factor of 0.8, the 50 KVA transformer can be the load power (50 KVA × 0.8) 40KW of active power. Transformer (Transformer) is the use of electromagnetic induction principle to change the AC voltage of the device, the main components are primary coil, secondary coil and core (core). The main functions are: voltage conversion, current conversion, impedance conversion, isolation, voltage regulator (magnetic saturation transformer) and so on. According to the purpose can be divided into: power transformers and special transformers (electric furnace change, rectifier, frequency test transformer, voltage regulator, mine transformer, audio transformers, IF transformers, high-frequency transformers, impact transformers, instrument transformers, electronic transformers , Reactors, transformers, etc.). Circuit symbols commonly used as the beginning of the number. Example: T01, T201 and so on.
- Q: how to ground transformers at substations??
- The steel body of the transformer and the neutral (wye point) should be bonded to a suitably installed and tested rod or mat by a cable capable of carrying the fault current that could occur. The wye point, in some cases, may be connected through a fault limiting resistor but this involves extra protection equipment and proper coordination. The actual type of ground depends on local conditions. A simple rod may be used in conditions where the ground has low resistance, a mat or multiple rods may be used in others. The resistance of the ground should be tested to meet local codes (usually 5 or 10 Ω). Since the design involves engineering and knowledge of national and local codes, it is best to have this done by a reputable engineering company.
- Q: How does the core material affect a transformer? Such as if you use steel vs. air. Or wood vs. magnet.
- In 50 or 60 Hz transformers putting in a laminated magnetic iron core greatly increases the amount of magnetic flux which is generated by the primary current with the secondary on open circuit (the so called magnetising current). This enables the windings to generate a relatively high voltage with relatively small magnetising current. If you tried to make a 50/60 Hz transformer without a magnetic core (with say air or any other non-magnetic insulating material) it virtually wouldn't work because the magnetising current would be so high (the primary winding practically a short circuit). If you used a non-magnetic conducting material you'd be even worse off because eddy currrents generated in the material would prevent any flux being established and you'd have plenty of core heating but no coupling between primary and secondary. For this reason even the iron core must be laminated (unless it's non-conducting ferrite). The story is quite different for high frequencies where the inductive impedances of coils are enhanced by the frequency. There you can make quite effective air cored transformers; small ones at least - but you'd still better avoid conducting material in the core - that's what food is in a microwave oven; conducting material in the core of a high fequency transformer.
- Q: i study transformer and found calculation for pf for open/short circuit test. but the value is bit confusing.pf at open test: 0.182pf at short tets: 0.135what the value means??why we need that??
- Power Factor is very important , u know (apparent power)^2(active power)^2+(reactive power)^2 and also Iactive powerIIapparent powerI*cos(phi) phi is the angle between the voltage and current in transformer , and power factor is cos(phi) active power can transfer through the transformer(and also can transfer to mechanical power and torque in motors) but the transformer get the reactive power and send it back to the input power line,reactive power get back to heat of wires and voltage drop in power lines. so we like that reactive power be minimum (reactive powerapparent power*sin(phi)) or pho----0 then the cos(phi)----1 most of motors have power factor about 0.8-0.95 that is very good the value pf0.182 means the angle between the voltage and current vector is acos(0.182)79.5 at open test u have a very bad transformer it just transfer %18.2 of the apparent power
- Q: I purchased a doorbell in Europe, it has a transformer that goes from 220V to 14.8V, will the transformer work on 110, or do I have to replace the transformer?
- If the mains side (primary) has a switch or 4 connections then it can probably be configured to work, as some transformers have dual 110v windings and are connected in series for 220v and parallel for 110v. Otherwise its not up to it.
- Q: Transformer insulation level L175 AC35 / 5 What does it mean
- 2, the insulation level of the transformer is according to the high pressure, medium voltage, low voltage winding sequence listed in the tolerance voltage value (the impact level in the former), during which separated by a slash. The neutral insulation level of the graded insulation is followed by a horizontal line at its wire end insulation level. Such as: LI850AC360-LI400AC200 / LI480AC200-LI250AC95 / LI75AC35. Meaning: 220KV three-side insulation of the main transformer, high-voltage side of the lead-side lightning impulse withstand voltage is 850kV, power frequency withstand voltage is 360kV, high-voltage side of the neutral point of the terminal lightning impulse withstand voltage is 400kV, power frequency resistance The voltage is 200kV;
Send your message to us
SC(B)H15 Type Amorphous Metal Dry-type Transformer
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 unit
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 unit/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches