Miniature Ball Bearings Steel
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50MT m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000TONS/YEAR m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications of Miniature Ball Bearings Steel
1. Dimensional sizes: Thickness: 14~100mm.Length:3000~5800mm,Diameter :14-500mm
2.Chemical composition: C=0.96~1.05,Si=0.15~0.35,Mn=0.25~0.45,Cr=1.4~1.65,
P≤0.025,S≤0.025,Ni≤0.22,Cu≤0.20,Mo≤0.08
3. Grade: SAE51200/ GCr15 / 100cr6
4. Heat Treatment:
Soft annealing: heat to 680-720°C, cool slowly.
Hardness after annealing: Max. 241 HB
Hardening: 820 - 850 °C
Normalizing temperature: 840-880°C
Tempering: 540-680°C
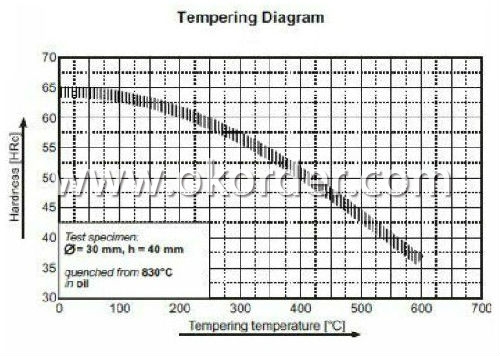
5. Surface requirements: Black, grinding, bright, polish
6. Payment terms: 20% deposit, balance against L/C at sight or T/T.
Usage & Applications of Miniature Ball Bearings Steel
Miniature ball bearings are machinery components, which comprise an outer ring, inner ring, balls, retainers, shields and snap rings. High quality through hardened bearing steel improves reliability. High grade balls have improved roundness and finish to reduce vibration and noise. Super finished raceways to reduce friction, vibration and noise resulting in increased bearing life and reduced maintenance cost. Proven seal solutions effectively retain lubricant and exclude contamination from moisture, dust, and dirt which extends bearing life and reduces maintenance cost. Premium grease reduces noise, vibration and meets high temperature application requirements which extend bearing life. Bearings available 100% noise tested on state-of the art equipment to meet Electric Motor OEM low noise expectations. Product tolerances exceed bearing industry standards to allow for global interchangeability.
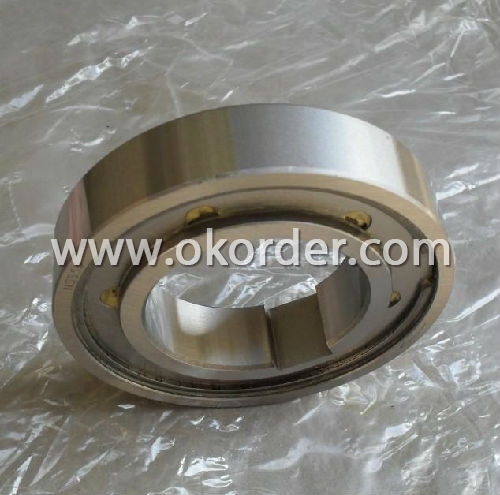


Packaging & Delivery of Miniature Ball Bearings Steel
10 pieces in one plastic tube, 10 tubes in one paper box or as customer required
Delivery time: 20 days after order confirmed.
Samples Policy: please arrange the sample cost and freight or freight collected. We will reduce this part expense from the total value of our first order.
Note:
1. According to national standard (GB) for our products, if not, supply according to national standards (GB) or agreement.
2. We can not only provide electric furnace +LF+VD and electro-slag re-melting (ESR)steel forging materials, but also forging products of piece, bar, etc.
3. Our company is equipped with roll equipment and can provide our customers with roll billets or finished.
4. Please send us your detailed specifications when inquire. We will reply to you ASAP.
- Q: What are the international standards for special steel?
- The international standards for special steel are a set of guidelines and specifications established by organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). These standards outline the requirements for various properties of special steel, including its chemical composition, mechanical properties, and manufacturing processes. They ensure that special steel products meet the necessary quality and performance criteria for use in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction worldwide.
- Q: What are the different stamping grades of special steel?
- The different stamping grades of special steel include stainless steel, high-strength steel, tool steel, and alloy steel. Each grade has unique properties and characteristics that make them suitable for various stamping applications.
- Q: What are the safety measures taken during the production of special steel?
- To ensure the safety and wellbeing of workers and reduce potential hazards, various safety measures are taken during the production of special steel. These measures encompass the following: 1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): All workers involved in special steel production must wear appropriate PPE, including safety helmets, goggles, gloves, and protective clothing. This safeguards them from injuries, burns, and exposure to hazardous substances. 2. Training and Education: Workers undergo comprehensive training and education on safe work practices and procedures. They gain knowledge about the potential hazards associated with special steel production and receive training on the proper handling of equipment and materials. 3. Risk Assessments: Regular risk assessments are conducted to identify potential hazards and evaluate the level of risk associated with each task. This facilitates the implementation of control measures to mitigate risks and prevent accidents. 4. Machinery and Equipment Safety: All machinery and equipment used in the production process are meticulously maintained and regularly inspected to ensure optimal working conditions. Safety features, such as emergency stop buttons and guards, are installed to prevent accidents and injuries. 5. Ventilation and Exhaust Systems: Given the high temperatures and use of chemicals in special steel production, ventilation and exhaust systems are installed to eliminate harmful fumes and gases from the work environment. This ensures a safe and healthy atmosphere for workers. 6. Fire Prevention: To minimize the risk of fire accidents, fire prevention measures are implemented, including the installation of fire alarms, extinguishers, and sprinkler systems. Workers are also trained on fire safety protocols and evacuation procedures. 7. Emergency Response Plans: Comprehensive emergency response plans are developed and communicated to all workers. These plans outline the steps to be taken in the event of accidents, fires, or other emergencies, ensuring a swift and organized response. 8. Regular Safety Inspections: Safety professionals conduct regular inspections to identify any potential safety hazards or non-compliance with safety protocols. Any issues or deficiencies are promptly addressed to maintain a safe working environment. By implementing these safety measures, special steel production can be carried out in a controlled and safe manner, safeguarding workers and minimizing the risk of accidents or injuries.
- Q: How does special steel perform in impact loading conditions?
- Known for its exceptional performance in impact loading conditions, special steel possesses remarkable strength, toughness, and resistance to deformation, thanks to its unique composition and manufacturing process. By effectively absorbing and dissipating energy, special steel minimizes the risk of catastrophic failure or damage when subjected to impact loading. The high strength of special steel enables it to withstand high impact forces without experiencing significant deformation or fracture, making it particularly suitable for applications where impact loading is prevalent, such as in the construction of heavy machinery, automotive components, and structural elements. In addition to its strength, special steel's toughness plays a crucial role in its performance during impact loading conditions. With excellent fracture toughness, special steel can resist crack propagation and absorb impact energy without fracturing, ensuring that it can withstand sudden and severe impacts without compromising its structural integrity. Furthermore, special steel is often subjected to treatments that enhance its resistance to impact loading conditions. Processes like heat treatment, forging, and quenching and tempering can increase the material's hardness and strength, further improving its ability to withstand impact forces. To summarize, special steel excels in impact loading conditions due to its high strength, toughness, and resistance to deformation. Its efficient energy absorption and dissipation, coupled with its resistance to fracture, make it an ideal choice for applications where impact loading is a concern.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the production of bearings?
- Yes, special steel can be used in the production of bearings. Special steel alloys such as stainless steel or high-carbon chromium steel are often used to manufacture bearings due to their superior strength, durability, and corrosion resistance properties. These specialized steels ensure that bearings can withstand heavy loads, high temperatures, and harsh operating conditions, making them suitable for various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
- Q: Classification of special steel products
- Carbon structural steels are normally used directly under heat supply without heat treatment. The mass fraction of Q195, Q215, Q235 are usually of low carbon steel, good welding performance, good plasticity and toughness, a certain strength, often rolled into a sheet, steel, welded steel pipe, used for bridges, buildings and general manufacturing rivet, screw and nut parts etc.. Q255 and Q275 mass fraction of carbon steel is slightly high, high strength, good plasticity and toughness, can be welded steel, steel rolling, usually forming and plate structure and simple manufacturing machinery, connecting rod, gear coupling, pins and other parts. Plain carbon steel high carbon steel is basically contains alloy elements, the carbon content in the range of 0.65% ~ 1.35%, the production of low cost, easy to obtain raw materials, good machinability, after treatment can obtain high hardness and high wear resistance, so the steel is widely used to manufacture various. Cutting tool, mold, measuring tools.But the red hardness difference of this kind of steel, that is, when the working temperature is greater than 250 degrees, the hardness and wear resistance of steel will decline rapidly, and lose their ability to work. In addition, if carbon tools steel is made into larger parts, it is difficult to harden, and deformation and crack are easy to occur. This kind of steel must ensure both chemical composition and mechanical properties. The number is two digits by the average mass fraction of carbon steel in the 000 fraction (W C * 10000). For example, steel 45 shows the average mass fraction of carbon in steel is 0.45%; 08 steel indicates the average mass fraction of carbon in steel is 0.08%.
- Q: What are the different methods of measuring the hardness of special steel?
- There are several methods available for measuring the hardness of special steel. These methods can be categorized into two main categories: destructive and non-destructive testing. 1. Rockwell Hardness Test: This is a widely used destructive testing method that measures the depth of penetration of an indenter into the steel surface. The Rockwell hardness test provides a hardness value based on the resistance of the steel to indentation. It is a simple and quick method that requires minimal sample preparation. 2. Brinell Hardness Test: Another destructive testing method, the Brinell hardness test, involves applying a known load to a hardened steel ball and measuring the diameter of the indentation left on the steel surface. The hardness value is determined based on the ratio of the applied load to the surface area of the indentation. 3. Vickers Hardness Test: This is a micro-indentation test that utilizes a diamond pyramid-shaped indenter. The Vickers hardness test measures the diagonal length of the indentation left on the steel surface and calculates the hardness value based on the applied load. 4. Knoop Hardness Test: Similar to the Vickers test, the Knoop hardness test is a micro-indentation method that uses a diamond pyramid-shaped indenter. However, instead of measuring the diagonal length of the indentation, it measures the length of the long axis. This test is particularly useful for measuring the hardness of thin steel samples or steel coatings. 5. Ultrasonic Hardness Test: This non-destructive testing method measures the hardness of steel by analyzing the propagation of ultrasonic waves through the material. The hardness value is determined based on the correlation between the velocity of the waves and the hardness of the steel. 6. Magnetic Hardness Test: This non-destructive testing method utilizes magnetic properties to measure the hardness of steel. It involves applying a magnetic field to the steel and measuring the magnetic response. The hardness value is determined based on the correlation between the magnetic response and the hardness of the steel. It is important to note that each method has its advantages and limitations, and the choice of method depends on factors such as the type of steel, the required accuracy, the sample size, and the available equipment and expertise.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the semiconductor manufacturing industry?
- Yes, special steel can be used in the semiconductor manufacturing industry. Special steel, such as stainless steel or tool steel, is commonly employed in various applications within the semiconductor industry. It is used for making equipment and components that require high levels of cleanliness, corrosion resistance, and precision. Special steel alloys are often utilized in the fabrication of semiconductor processing tools, vacuum chambers, wafer carriers, and other critical parts to ensure optimal performance and reliability in the manufacturing process.
- Q: What are the requirements for special steel used in corrosive environments?
- The requirements for special steel used in corrosive environments include high resistance to corrosion, especially against specific corrosive agents such as acids, alkalis, or saline solutions. The steel should possess a strong passive film formation ability, preventing further corrosion. It should also have good mechanical properties, including high strength and toughness, to withstand the harsh conditions. Additionally, the steel must possess good welding and fabrication characteristics, as well as be cost-effective and readily available.
- Q: How is alloy steel different from carbon steel?
- Alloy steel is different from carbon steel because it is made by adding other elements to carbon steel, such as chromium, nickel, or manganese, to enhance its properties. This makes alloy steel stronger, more resistant to corrosion, and better suited for specific applications compared to carbon steel, which is primarily composed of iron and carbon.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Jiangsu, China |
| Year Established | 1990 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 20 Million |
| Main Markets | Mid East; Eastern Europe; North America |
| Company Certifications |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Shanghai |
| Export Percentage | 20% - 30% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 21-50 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 100,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | 1 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered; |
| Product Price Range | High; Average |
Send your message to us
Miniature Ball Bearings Steel
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50MT m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000TONS/YEAR m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























