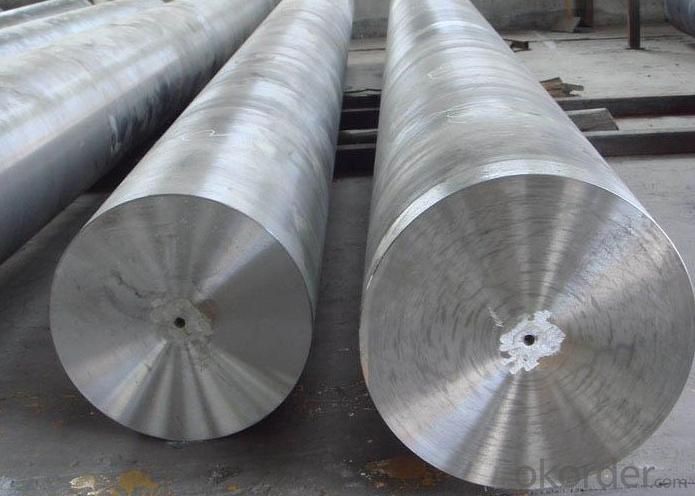
Japanese Standard Bearing Steel
- Loading Port:
- Guangzhou
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25MT m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 600000 Tons/Year m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications of Japanese Standard Bearing Steel
|
Material |
SUJ2 | ||
|
Chemical Composition |
Mechanical Properties(In Quenched & Tempered State) | ||
|
C |
0.95-1.05 |
Hardness |
HRC≈67 |
|
Si |
0.15-0.35 |
HRC61-66 | |
|
Mn |
0.25-0.45 |
HRC62-66 | |
|
Cr |
1.40-1.65 |
-- | |
|
Mo |
≤0.10 |
-- | |
|
P |
≤0.025 |
HB170-207 | |
|
S |
≤0.025 |
HB207-229 | |
|
Cu |
≤0.25 |
HB270-390 | |
|
Ni+Cu |
≤0.50 |
HB229-285 | |
Dimension: Thickness: 20mm-1000mm, Length: 500mm-6000mm
Technique: Hot rolled, cold drawn, forged
Surface treatment: Black, grinding, bright, polish
Type: Alloy Steel Bar
Documents required: Commercial invoice; Packing list; Bill of lading; Certificate of origin and others that the target market needs.
Usage and Applications of Japanese Standard Bearing Steel
High Quality Bearing steel is used for manufacturing ball, roller bearing steel and rings. Bearing in work is under great pressure and friction, so have high demands bearing steel and hardness and resistance, and high elastic limit.
Bearing steels are used for ball and roller bearing applications and are comprised of low carbon steels and high carbon through harden able steel.
For example, bearing ring, steel rolling mill, machinery, 100Cr6 bearing steel ball is widely used in high-speed and low-noise bearing, bicycle, motorcycle, automobile, bags electronically.
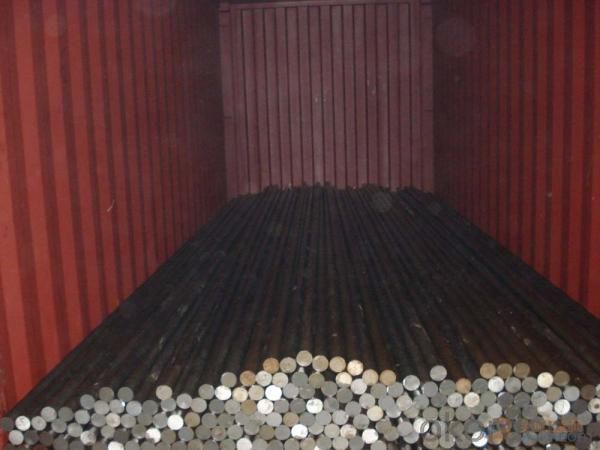
Packaging & Delivery of Japanese Standard Bearing Steel
Packaging Detail: Standard seaworthy packing or as customer required.
Delivery Detail: 45 days
Trade terms: FOB, CFR, CIF
MOQ: 25 tons or at customer's demands
Weight: Theprice invoicing on theoretical weight basis or actual weight basis depends on customer’s request.
Shipment: The shipment of bulk break or container is depends on customer’s request.
Other equivalent steel materials of Japanese Standard Bearing Steel
|
USA |
Japanese |
Germany |
British |
France |
|
ASTM&AISI&SAE |
JIS |
EN DIN |
EN BS |
EN NF |
|
52100 |
SUj2 |
100Cr6 |
100Cr6 |
100Cr6 |
|
1.2067 |
1.2067 |
1.2067 |
Characteristics of Japanese Standard Bearing Steel
1. The technical workers we employed are the ones with many years’ working experience, who know the technology procedures very well.
2. We will strictly inspect our production that we sold according to the customer’s request.
3. Our steel reaches international quality standards. Besides, our company is equipped with large-sized vertical saw machines, horizontal saw machines, milling machines, grinding machines and other advanced equipment. All our products are carried out hardness tests, such as the ultrasonic flaw detection before shipment. Therefore, there is no quality problem. With more competitive price than other suppliers, our steel has good sales in the markets of North America, South America, East Europe, Southeast Asia, Africa, Oceania, the Middle East, East Asia and West Europe.
4. We can accept L/C usance or L/C at sight.
5. Quality should be in conformity with the specification of the manufacturer. Quantity and packing conditions should be in conformity with the term in this contract.
- Q: What are the properties of leaded steel?
- Leaded steel is a type of steel alloy that contains a small percentage of lead. This addition of lead provides several properties to the steel, including improved machinability, enhanced lubricity, and better chip formation during machining processes. Leaded steel also exhibits increased resistance to wear and galling, making it suitable for applications in which friction and sliding contact occur. Additionally, leaded steel has good corrosion resistance and can be easily welded and formed. However, it is important to note that leaded steel should be handled with caution due to the potential health hazards associated with lead exposure.
- Q: What are the main applications of special steel in the power storage industry?
- Special steel has various applications in the power storage industry, primarily in the production of battery components and infrastructure. It is widely utilized in the manufacturing of battery cases, frames, and terminals due to its high strength, corrosion resistance, and electrical conductivity properties. Additionally, special steel is used in the construction of power storage facilities and equipment, such as racks and supports, ensuring durability and reliability of the infrastructure. Overall, the main applications of special steel in the power storage industry revolve around enhancing the performance, longevity, and safety of batteries and power storage systems.
- Q: What are the properties of high-strength tool steel?
- High-strength tool steel possesses excellent hardness, wear resistance, and toughness. It has the ability to retain its sharpness, withstand high temperatures, and resist deformation. This type of steel is also known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications in industries such as manufacturing and construction.
- Q: What are the applications of special steel in the nuclear industry?
- Special steel is extensively used in the nuclear industry due to its exceptional properties. It is primarily employed in the construction of reactor vessels, containment structures, and fuel storage systems. Its high strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures make it an ideal material for these critical components. Additionally, special steel is also utilized in the production of nuclear fuel rods, shielding materials, and various other components that require excellent mechanical properties and resistance to radiation damage.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the oil and gas aftermarket industry?
- Special steel plays a crucial role in the oil and gas aftermarket industry by offering enhanced performance, durability, and resistance to extreme conditions. It is used in various components such as pipes, valves, fittings, and drilling equipment, ensuring efficient and reliable operations in harsh environments. The unique properties of special steel, including high strength, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance, enable the industry to achieve increased productivity, improved safety, and extended equipment lifespan.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the production of gearboxes?
- Yes, special steel can be used in the production of gearboxes. Special steel alloys such as alloy steel or stainless steel provide enhanced strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion, making them ideal for manufacturing high-performance gearboxes that can withstand heavy loads and harsh operating conditions.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to sustainable construction?
- Special steel contributes to sustainable construction in several ways. Firstly, it has a significantly longer lifespan compared to other construction materials, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. This leads to reduced resource consumption and waste generation. Additionally, special steel is highly durable and resistant to corrosion, making it an ideal choice for structures in harsh environments, such as bridges or offshore wind farms. This longevity and resilience reduce the environmental impact associated with the maintenance and replacement of infrastructure. Furthermore, special steel can be recycled and reused multiple times without losing its properties, reducing the demand for virgin materials and minimizing the carbon footprint of construction projects. Overall, the use of special steel in construction helps promote sustainability by increasing the lifespan of structures, reducing resource consumption, and minimizing waste generation.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to weight reduction in manufacturing?
- Special steel contributes to weight reduction in manufacturing through its unique properties and characteristics. Special steels are designed to have high strength-to-weight ratios, allowing manufacturers to use less material while still achieving the desired strength and performance. This results in lighter and more efficient products without compromising their structural integrity. Additionally, special steels can be processed into complex shapes, enabling the production of intricate components that are both lightweight and strong. Overall, the use of special steel in manufacturing helps reduce the overall weight of products, leading to improved fuel efficiency, lower transportation costs, and increased sustainability.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the agricultural sector?
- Indeed, the agricultural sector can utilize special steel. Special steel pertains to steel alloys crafted and engineered to possess distinct and superior characteristics. These qualities encompass heightened strength, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and heat resistance, among others. Within the realm of agriculture, numerous applications can highly benefit from special steel. One notable application involves the production of agricultural machinery and equipment. Components like blades, cutting edges, plowshares, and tillage tools necessitate the ability to endure substantial loads, abrasion, and harsh environmental conditions. By employing special steel, with its superior strength and wear resistance, the lifespan of these components can be significantly extended. Consequently, maintenance and replacement costs for farmers are reduced. Furthermore, special steel can play a role in constructing storage facilities and infrastructure within the agricultural sector. Structures such as grain silos, barns, and livestock shelters often demand materials capable of resisting corrosion caused by moisture, chemicals, and animal waste. Special steel alloys, equipped with enhanced corrosion resistance properties, offer a durable and enduring solution. This enables farmers to store their crops and livestock in a secure and reliable environment. Moreover, special steel can be employed in fabricating irrigation systems and pipelines. These systems necessitate materials capable of enduring exposure to water, soil, and fertilizers without degradation or corrosion. Special steel grades, like stainless steel, boasting excellent corrosion resistance, can be utilized to ensure the longevity and efficiency of irrigation systems. This reduces water wastage and fosters enhanced agricultural productivity. In conclusion, the agricultural sector can indeed employ special steel, thanks to its exceptional qualities such as strength, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and heat resistance. Its applications span from the manufacturing of agricultural machinery and equipment to the construction of storage facilities and irrigation systems. Embracing special steel allows farmers to enjoy heightened durability, reduced maintenance costs, and improved efficiency, thereby contributing to the growth and sustainability of the agricultural sector.
- Q: How does the cost of special steel compare to regular steel?
- The cost of special steel is generally higher compared to regular steel. Special steel is specifically designed and produced to possess exceptional properties and characteristics that regular steel does not have. It undergoes additional processes such as alloying, heat treatment, or specialized manufacturing techniques to enhance its strength, durability, corrosion resistance, and other desirable attributes. These added steps in production increase the overall cost of special steel. On the other hand, regular steel is more readily available and is produced on a larger scale. It is often used for general purposes and applications where high-performance qualities are not required. Regular steel is relatively cheaper due to its lower production costs and wider availability in the market. However, it is important to note that the cost comparison between special steel and regular steel can vary depending on various factors such as the specific type of steel, the quantity being purchased, market conditions, and any additional customization required. Therefore, it is advisable to consult with steel suppliers or specialists to get accurate pricing information based on specific requirements.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Guangdong, China |
| Year Established | 2005 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 100 Million |
| Main Markets | korea, India, Malaysia, Brazil, Germany, Belgium, Middle East |
| Company Certifications |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Guangzhou |
| Export Percentage | 50%-80% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 21-100 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | 23,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | 1 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM servise offered |
| Product Price Range | high; average |
Send your message to us
Japanese Standard Bearing Steel
- Loading Port:
- Guangzhou
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25MT m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 600000 Tons/Year m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























