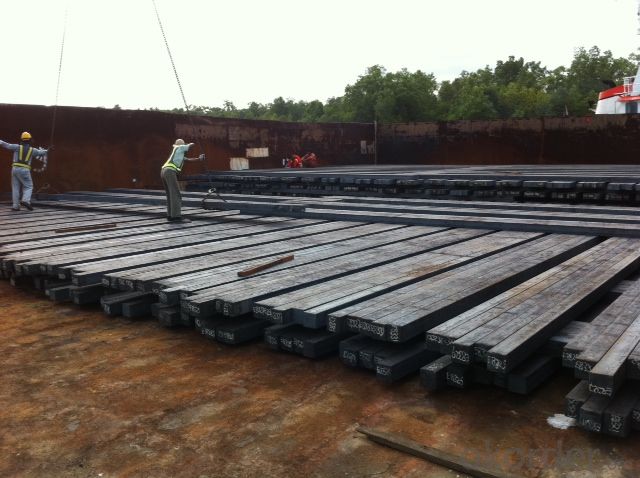
Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 175mm
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 175mm
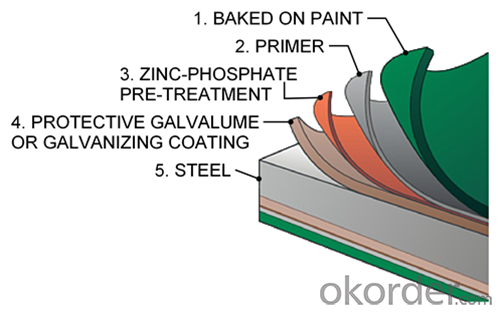
Description of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 175mm
Prepainted Rolled steel Coil is a kind of coated steel coil/sheet. With the cold rolled steel of different strength and thickness as substrate, it is produced through applying Al-Zn coat on both faces by hot dip process. In its coating, Al accounts for about 55%, Si 1.6%, while the remaining is Zn. Aluminum zinc coils enjoys both the physical protective feature and durability of Al and the electrochemical protective property of Zn. And its surface has bright silver color and regular embossed-like figure, which are highly decorative. RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing

Main Feature of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 175mm
1.Corrosion resistance: It mainly depends on the zinc protection. When the zinc being worn,
2. Heat resistance: steel sheet has excellent heat resistance, can withstand high temperatures over 300 centigrade, and is similar with aluminized steel high temperature oxidation resistance. It often used in chimney pipes, ovens, fluorescent lighting device and the device cover.
3. Heat reflective: Galvanized steel plate heat-reflective high rate is twice as galvanized steel, often used to make insulation materials. RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
Applications of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 175mm
1. Construction and building: roofing; ventilating duct; handrail; partition panel;etc.
2. Electric appliance: refrigerator; washing machine; refrigerator; DVD;etc.
3.Transportation: oil tank; gas tank;road sign; etc.
4.Agriculture constructions :barn; etc.RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
5.Others:vending machine; game machine; auto parts spare parts etc.

Specifications of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 175mm
Product | Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 175mm |
Material Grade | SGCC / SGCH / DX51D+AZ, etc |
Thickness | 0.5-3.0mm |
Width | 700-1500mm |
Tolerance | Thickness: +/-0.02mm , Width:+/-2mm |
Zinc-coating | AZ30-150g/m2 |
Technique | Raw material: Hot rolled steel coil --> Cold rolled_>hot dipped galvalume |
Surface | Dried, Chromated, Unoiled,RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing |
Spangle | Regular spangle , small spangle, zero spangle |
ID | 508MM 610MM |
Coil weight | 25MT max |
Export package | Cardboard inner sleeves, Waterproof paper, galvanized steel covered and steel strip packed |
FAQ of Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 175mm
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. What is the minimum order quantity ?
Our MOQ is 100 mt for each size each specification. Usually we can offer discount if can buy large QTY once. RAL Scale Z35 Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Construction Roofing
2. How long can we receive the product after ordering?
Our general delivery time is 30 days after confirmation, but so some special orders, we have offer special delivery time
3. How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system ,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
4. What is the payment?
We accept T/T, L/C
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of valves and fittings?
- Valves and fittings rely on steel billets, an essential raw material, for their production. These billets are solid steel forms, cast into specific shapes and sizes. The manufacturing process starts by heating the steel billets to a high temperature and passing them through rolling mills to achieve the desired form. This process refines the grain structure, enhancing the steel's strength, ductility, and overall quality. After shaping, the billets undergo further processing and machining to create various valve and fitting components, including bodies, bonnets, stems, and other essential parts. Precise machining ensures accurate dimensions and smooth surfaces, enabling proper assembly and functioning. Steel billets also provide crucial strength and durability to valves and fittings, as they are made from high-quality steel. This ensures that the final products can withstand the harsh operating conditions, pressure, and temperature variations they may encounter. Moreover, steel billets offer versatility in manufacturing, allowing the production of different types of valves and fittings, such as gate valves, ball valves, butterfly valves, and pipe fittings. This flexibility enables manufacturers to meet diverse industry requirements. In summary, steel billets serve as the primary raw material in the production of valves and fittings. Shaping, processing, and machining these billets result in high-quality components that offer strength, durability, and precision in the final products.
- Q: What are the different types of cutting processes used for shaping steel billets?
- There are several different types of cutting processes used for shaping steel billets. These processes include: 1. Bandsaw cutting: Bandsaw cutting is a widely used method for cutting steel billets. It involves using a continuous band of toothed metal blade to cut through the billet. Bandsaws are known for their ability to cut through thick sections of steel quickly and accurately. 2. Abrasive cutting: Abrasive cutting involves using an abrasive wheel or disc to cut through the steel billet. This method is commonly used for cutting smaller billets or for cutting shapes and contours into the billet. Abrasive cutting is known for its versatility and ability to produce smooth and precise cuts. 3. Plasma cutting: Plasma cutting is a thermal cutting process that uses a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to melt and remove the steel from the billet. This method is often used for cutting thick sections of steel or for cutting intricate shapes. Plasma cutting is known for its speed and ability to produce clean cuts. 4. Waterjet cutting: Waterjet cutting is a process that uses a high-pressure jet of water to cut through the steel billet. In some cases, abrasive particles may be added to the water to enhance the cutting ability. Waterjet cutting is known for its ability to cut through thick sections of steel without creating heat-affected zones or distortion. 5. Laser cutting: Laser cutting involves using a high-powered laser beam to melt and vaporize the steel billet. The laser beam is guided by computer controls to cut the desired shape. Laser cutting is known for its precision and ability to cut intricate shapes with minimal distortion. These are just a few examples of the different types of cutting processes used for shaping steel billets. Each process has its own advantages and is chosen based on factors such as the size of the billet, the desired shape, and the required accuracy.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of agricultural equipment?
- Steel billets are an integral component in the manufacturing process of agricultural equipment. These billets, which are essentially semi-finished steel products, serve as the raw material for producing various parts and components of agricultural machinery. One of the primary uses of steel billets in agricultural equipment manufacturing is for the construction of the frame or chassis of the equipment. The frame provides the structural integrity and support necessary to withstand the demanding conditions encountered in agricultural applications. Steel billets are often used due to their high strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, which are crucial qualities required for withstanding the heavy loads, vibrations, and exposure to harsh environments that agricultural machinery often faces. Additionally, steel billets are used in the production of other important components such as axles, gears, shafts, and blades. These components are critical for the proper functioning and performance of agricultural equipment. Steel billets are preferred for these applications due to their machinability, allowing them to be easily shaped and formed into the desired specifications and dimensions required for each component. Furthermore, steel billets are also utilized in the manufacturing of attachments and implements that are commonly used in agricultural operations. For instance, plows, harrows, cultivators, and seeders, all rely on steel billets to provide strength, durability, and resistance to wear and tear. These attachments are often subjected to demanding conditions and need to withstand the forces encountered during field operations. Overall, steel billets play a crucial role in the manufacturing of agricultural equipment by providing the necessary strength, durability, and functionality required for these machines to perform effectively in the agricultural sector. The use of steel billets ensures that the agricultural equipment can withstand the harsh conditions of farming operations, resulting in increased productivity, efficiency, and longevity of the machinery.
- Q: What is the drop per minute of the billet temperature at 850?
- Generally, the temperature decreases gradually during the rolling process (a small section of high speed wire has a temperature rising process), usually above 750 degrees
- Q: What are the different methods of steel billet casting?
- In the industry, various methods are commonly used for steel billet casting. These methods encompass continuous casting, ingot casting, and direct casting. Continuous casting stands as the most widely employed method for steel billet casting. In this process, molten steel is poured into a water-cooled mold, typically made of copper. As the steel cools and solidifies, a seamless billet is formed, which is subsequently cut into desired lengths. Continuous casting allows for high production rates and precise control over billet dimensions and quality. Ingot casting represents an alternative method for steel billet casting. It involves pouring molten steel into individual molds to create ingots. These ingots are then allowed to solidify before being reheated and hot rolled into billets. Ingot casting is often utilized for small-scale production or for specialty steel alloys that require specific compositions. Direct casting, also known as strand casting, emerges as a newer method for steel billet casting, eliminating the need for solidification and reheating processes. In this method, molten steel is directly poured into billets through a series of water-cooled copper molds. The billets are subsequently cooled and cut to the desired lengths. Direct casting offers advantages such as reduced energy consumption and improved yield by eliminating the intermediate steps of ingot casting. Ultimately, the selection of the steel billet casting method relies on factors like production volume, desired quality, and specific requirements of the steel alloy being produced. Each method possesses its own advantages and limitations, and choosing the appropriate method is vital for ensuring efficient and cost-effective steel billet production.
- Q: What are the main factors affecting the dimensional tolerances of steel billets?
- Various factors can influence the dimensional tolerances of steel billets. The manufacturing process itself is one of the main factors. The method employed to produce the billets, whether it be casting or hot rolling, can impact the final dimensions. Casting processes, for instance, can introduce variations in the cooling rate, thereby affecting the overall shape and size of the billets. Another crucial factor is the initial quality of the raw material. The composition and homogeneity of the steel utilized in billet production can contribute to dimensional variations. Impurities or uneven distribution of alloying elements can result in inconsistencies in the size and shape of the billets. The temperature maintained during the manufacturing process is also significant. High temperatures have the potential to cause thermal expansion, leading to dimensional changes in the billets. Proper control of cooling rates and the cooling process is vital to maintaining the desired tolerances. The design and condition of the manufacturing equipment can also impact dimensional tolerances. Adequate maintenance and calibration of machinery are essential to ensure consistent and accurate production. Lastly, external factors like handling and transportation can affect the dimensional tolerances of steel billets. Improper handling or rough transportation conditions can result in physical deformations or damage to the billets, leading to variations in their dimensions. In summary, achieving the desired dimensional accuracy in steel billets necessitates attention to factors such as the manufacturing process, raw material quality, temperature control, equipment condition, and handling and transportation practices.
- Q: What are the different methods of steel billet surface etching?
- There are several methods of steel billet surface etching, including chemical etching, electrochemical etching, and laser etching. Chemical etching involves immersing the billet in a solution that reacts with the surface to remove a thin layer of material. Electrochemical etching uses an electric current to dissolve the surface of the billet in a controlled manner. Laser etching uses a high-powered laser to selectively remove material from the surface, creating a permanent etched pattern. These methods offer different levels of precision, depth control, and speed, allowing for various applications in steel manufacturing and surface treatment.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of automotive components?
- Steel billets are an essential raw material used in the manufacturing of automotive components. These billets are semi-finished products that are shaped into various forms to create the necessary components. Firstly, steel billets are heated to a specific temperature to make them malleable and easier to work with. Once they reach the desired temperature, they are placed into a mold or die and subjected to intense pressure to shape them into the desired form. This process is known as forging. Automotive components such as engine parts, gears, axles, and suspension components require high strength and durability. Steel billets are preferred for these applications due to their excellent mechanical properties, including high tensile strength, toughness, and wear resistance. After the forging process, the shaped billets are further processed through various techniques such as machining, heat treatment, and surface finishing to achieve the final specifications required by automotive manufacturers. These processes ensure that the components meet the necessary performance standards, dimensional accuracy, and surface quality. The use of steel billets in the manufacturing of automotive components offers several advantages. Steel is readily available, cost-effective, and has a high recycling rate, making it an environmentally friendly choice. Additionally, steel's versatility allows for a wide range of component designs and customization options to meet specific automotive requirements. In conclusion, steel billets play a crucial role in the manufacturing of automotive components. Their malleability and excellent mechanical properties make them an ideal raw material for forging processes, enabling the production of high-strength and durable components used in various automotive applications.
- Q: How are steel billets used in the production of sheet metal?
- Steel billets are used in the production of sheet metal through a process known as rolling. Rolling is a technique that involves passing steel billets through a series of rollers to reduce their thickness and create a flat sheet. The first step in the process is to heat the steel billets to a specific temperature to make them more malleable. Once heated, the billets are then fed into a rolling mill, where they pass through a series of rollers that gradually decrease the thickness of the steel. As the billets are rolled, they are compressed and elongated, resulting in a thinner and longer piece of steel. This process is repeated multiple times, with each pass reducing the thickness of the steel sheet. Once the desired thickness is achieved, the sheet is cooled and cut into specific lengths. The final product is a flat sheet of sheet metal that can be further processed and used in various industries, such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing. Steel billets play a crucial role in the production of sheet metal as they provide the raw material from which the sheets are formed. Their malleability and ability to withstand the rolling process make them an ideal choice for creating thin and durable sheet metal.
- Q: How do steel billets contribute to the overall vibration resistance of a structure?
- Steel billets contribute to the overall vibration resistance of a structure by providing a strong and rigid framework. The high strength and stiffness of steel billets help to absorb and distribute dynamic loads, reducing the amplitude and impact of vibrations. This structural stability minimizes the risk of fatigue and damage caused by vibrations, ensuring the long-term integrity and durability of the structure.
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Steel Billet 3SP Standard 175mm
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






























