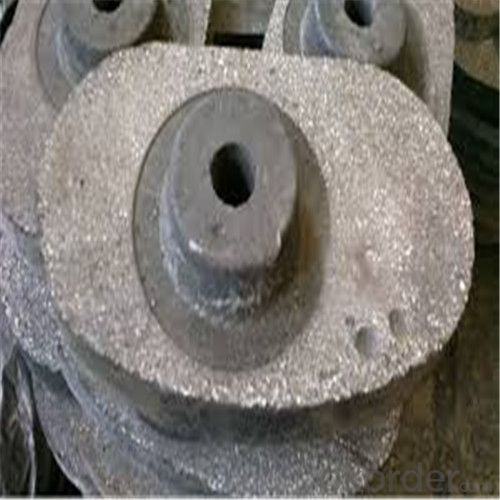
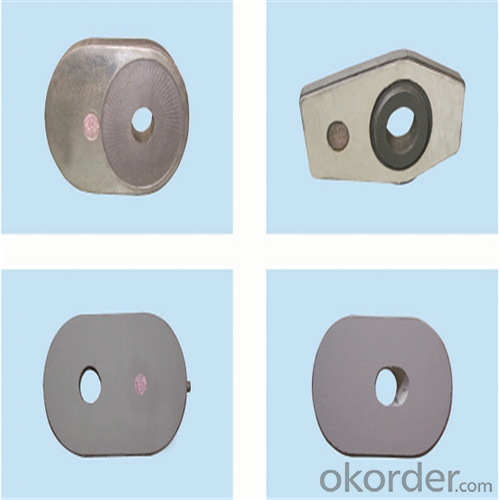
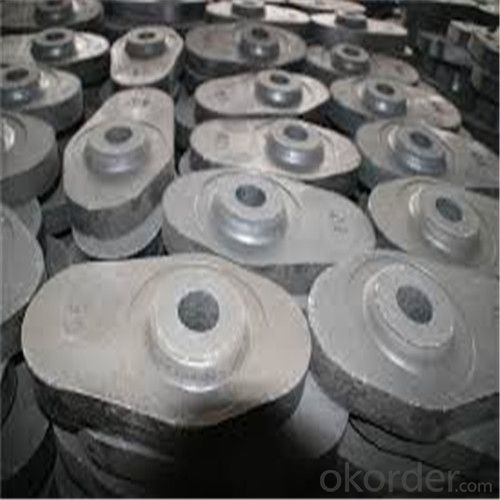
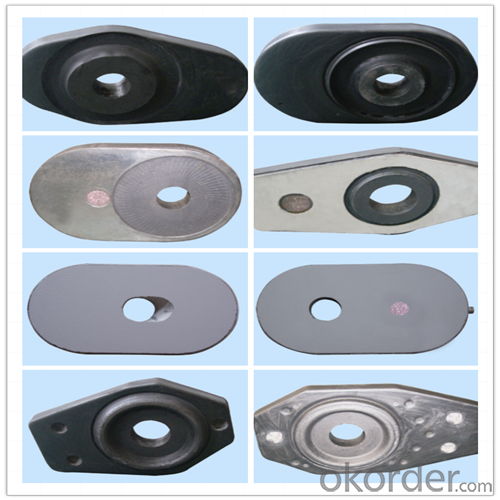
Monolithic Refractories High Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate for Iron and Steel Industry 2024
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for High Performance Refractory Ladle Slide Gate
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Shape: | Plate | Material: | Alumina Block |
| SiO2 Content (%): | N/A | Al2O3 Content (%): | 80-90% | MgO Content (%): | N/A |
| CaO Content (%): | N/A | Refractoriness (Degree): | 1770°< Refractoriness< 2000° | CrO Content (%): | N/A |
| SiC Content (%): | N/A | Model Number: | CS80 | Brand Name: | |
| Product name: | High performance refractory ladle slide gate | Model No.: | cs80 | Brand name: | CMAX |
| Quality: | Al-C or Al-Zr-C | Service life: | 4-6 heats | Apparent porosity: | 7% Max |
| Bulk density:: | 3.1 MIN | C.C.S: | 120MPA | MOQ: | 100 pcs for trial |
| Delivery time: | 60 working days upon receipt of deposit |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Inner carton packing, outer wooden case suitable for long term sea shipping |
| Delivery Detail: | three months working days upon receipt of deposit |
Specifications
Surface flatness less than 0.05mm
High mechanical strength
Erosion resistance
Oxidation resistance
Thermal shock stability
General Chemical Analysis for refractory ladle slide gate :
slide gate plate widely including Alumina carbon and Alumina Zirconia Carbon slide gate plate, MgO and MgO-spinel slide gate plate,nonoxides bonding slide gate plateand unburned slide gate plate.
Alumina -Zirconia-Carbon material
| Al-Zr-C Material | |||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) |
| 85 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
Composite type: Al-Zr-C for working line, outer Al-C material
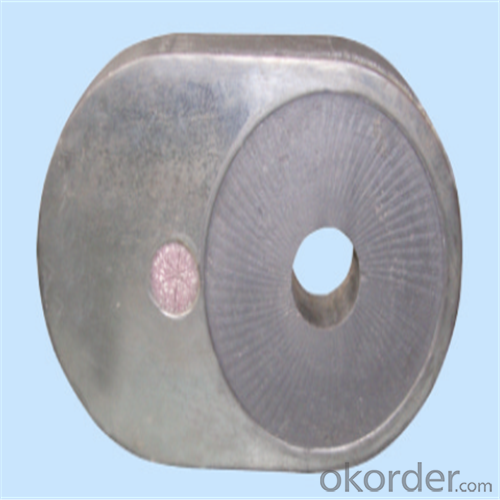
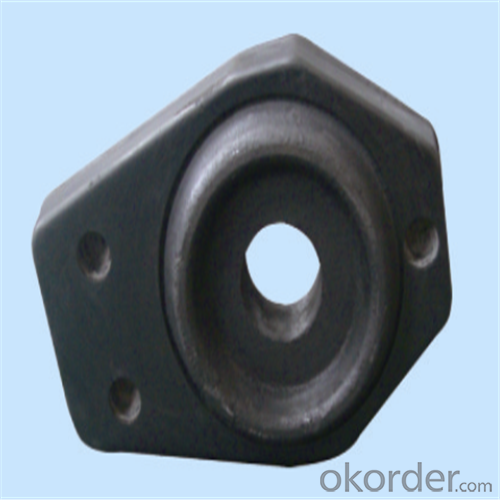
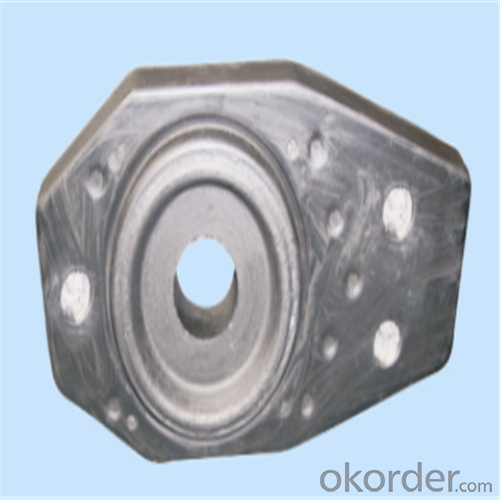



| Al-Zr-C & Al-C Material | ||||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S | |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) | |
| Inner side (Working face) | 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| Outside | 90 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 3 | |
Using the raw materials of tabular alumina, zirconia-corundum, carbon and other high-grade additives, after sintering to obtain characteristics of oxidation resistance, scour strength, erosion resistance, thermal shock resistance, shape stable and long service life, made our products the preferred materials for the large and medium-sized steel ladle, refining ladle, series of alloy steel ladle, and tundish. Our high performance sintering sliding gates include alumina carbon , Al2O3-ZrO2-C, etc, can meet the needs of different steel grade.
Other Products

About us


Sample is on your request.
Welcome to visit our factory~
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand the chemical attacks in copper smelting applications?
- Due to their unique properties and composition, monolithic refractories are capable of enduring chemical attacks in copper smelting applications. These refractories are specifically engineered to resist the harsh and corrosive environment found in copper smelting processes. To begin with, monolithic refractories are crafted from high-quality materials such as alumina, silica, and magnesia. These materials possess high melting points and chemical stability. Carefully selected, they are able to withstand the corrosive effects of copper smelting, including the presence of sulfur compounds and acidic gases. The refractory's composition also includes various additives and bonding agents that enhance its resistance to chemical attacks. In addition, monolithic refractories exhibit exceptional thermal shock resistance. This means they can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling. In copper smelting applications, where extreme temperatures are involved, this refractory quality is crucial in preventing the formation of cracks and ensuring long-term performance. Furthermore, monolithic refractories possess a dense and compact structure. This structure serves as an effective barrier against the infiltration of molten copper and other corrosive substances. By preventing the penetration of chemical attacks, the refractory lining's durability and longevity are ensured. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer superior erosion resistance. This is particularly important in copper smelting applications, where high-velocity gases and flows of molten metal can cause erosion of the refractory lining. The refractory's erosion resistance prevents the degradation of the lining and maintains its structural integrity. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are specially designed to withstand the chemical attacks encountered in copper smelting applications. Through the use of high-quality materials, the incorporation of additives, and the possession of excellent thermal shock resistance, density, and erosion resistance, these refractories provide a reliable and durable lining that can endure the harsh conditions of copper smelting processes.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories help in enhancing the durability of iron and steel furnaces?
- Monolithic refractories help enhance the durability of iron and steel furnaces by providing a high heat resistance and superior thermal insulation. They have the ability to withstand extreme temperatures, reducing the risk of thermal shock and cracking. Monolithic refractories also have excellent corrosion resistance, preventing chemical reactions with molten metal and slag. Their strong bonding properties ensure a tight seal, minimizing heat loss and improving energy efficiency. Overall, monolithic refractories contribute to the longevity and reliability of iron and steel furnaces by protecting them from the harsh conditions of high-temperature operations.
- Q: What are the key characteristics of monolithic refractories for electric arc furnace applications?
- Monolithic refractories designed for electric arc furnace applications possess several crucial qualities that render them suitable for the challenging conditions and extreme temperatures encountered in these environments. To begin with, monolithic refractories exhibit exceptional resistance to thermal shock. Electric arc furnaces operate at exceedingly high temperatures, and the rapid fluctuations in temperature during the melting and refining processes can subject the refractories to significant thermal stress. Monolithic refractories, however, are engineered to endure these thermal shocks without developing cracks or spalling, thereby guaranteeing the durability and performance of the lining. Moreover, monolithic refractories boast a high resistance to chemical attack. Electric arc furnaces involve the melting and refining of diverse metals and alloys, which can generate highly corrosive atmospheres. Monolithic refractories incorporate chemically inert materials and additives that bestow resistance against the corrosive impact of molten metals and slag, safeguarding the lining against chemical deterioration. Another noteworthy characteristic of monolithic refractories for electric arc furnace applications is their exceptional refractoriness. Refractoriness denotes a material's ability to retain its strength and integrity at elevated temperatures. Electric arc furnaces typically operate at temperatures surpassing 1500°C, and monolithic refractories are specifically engineered to endure these extreme conditions without experiencing substantial loss of properties or degradation. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer efficient thermal conductivity. This property facilitates efficient heat transfer throughout the lining, ensuring uniform heating and melting of the charge material. It also helps minimize the occurrence of hot spots and thermal gradients, which can result in uneven wear and premature failure of the lining. Lastly, monolithic refractories are renowned for their ease of installation and repair. Unlike traditional brick or block refractories, monolithic materials can be cast, sprayed, or rammed into place, eliminating the need for intricate masonry work. This not only saves time and labor but also enables convenient maintenance and repair of the lining, reducing downtime and enhancing overall furnace efficiency. In conclusion, monolithic refractories for electric arc furnace applications possess exceptional thermal shock resistance, high chemical resistance, high refractoriness, efficient thermal conductivity, and ease of installation and repair. These qualities render monolithic refractories ideal for withstanding the harsh conditions and demanding requirements of electric arc furnace operations.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall safety of iron and steel operations?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in ensuring the overall safety of iron and steel operations. These refractories are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, chemical reactions, and mechanical stresses, providing a protective barrier to the furnaces, ladles, and other equipment used in these operations. By maintaining the integrity of the refractory lining, monolithic refractories prevent leaks, minimize the risk of thermal shock, and reduce the chances of equipment failure or accidents. This helps to safeguard the workers, prevent damage to the infrastructure, and ensure the uninterrupted production of iron and steel, thus contributing to the overall safety of the operations.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories used in the repair and maintenance of ladles and tundishes?
- Monolithic refractories are used in the repair and maintenance of ladles and tundishes by providing a durable and heat-resistant lining. These refractories can be easily shaped and applied, allowing for quick repairs and preventing heat loss or leakage. They also offer excellent resistance to thermal shocks and chemical corrosion, ensuring a longer lifespan for ladles and tundishes. Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity and temperature control of these vessels, ultimately improving their overall performance and efficiency.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand the alkali attacks in cement kiln applications?
- Due to their unique composition and structure, monolithic refractories are capable of withstanding alkali attacks in cement kiln applications. Unlike traditional brick refractories, these refractories are made from a single material, resulting in a more uniform and dense structure. When exposed to alkali attacks in cement kilns, monolithic refractories create a barrier against the corrosive alkali substances by forming a protective layer on the surface. This protective layer is formed through reactions between the alkali substances and the refractory material, leading to the development of a stable compound that resists further attacks. Additionally, monolithic refractories possess high chemical resistance, allowing them to endure the aggressive conditions inside cement kilns. Their low porosity design minimizes the infiltration of alkali substances into the refractory material, reducing the risk of alkali attacks and extending the lifespan of the refractory lining. Furthermore, monolithic refractories are frequently manufactured using materials with elevated melting points, such as alumina, silica, and magnesia. These materials exhibit exceptional thermal stability, enabling the refractories to withstand the high temperatures in cement kilns without significant deterioration. This thermal stability is crucial in preventing the formation of cracks and spalling, which could permit alkali penetration and subsequent harm to the refractory lining. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are specifically engineered to resist alkali attacks in cement kiln applications by forming a protective layer, possessing high chemical resistance, and demonstrating excellent thermal stability. These characteristics make them an ideal choice for lining cement kilns, ensuring long-term performance and durability.
- Q: Can monolithic refractories be used for the lining of continuous casting tundishes and molds?
- Indeed, tundishes and molds used in continuous casting can utilize monolithic refractories for their lining. These refractories consist of a single, uniform structure, in contrast to traditional refractories that are composed of multiple bricks or tiles. The utilization of monolithic refractories offers various advantages in the lining of tundishes and molds during continuous casting procedures. Firstly, their monolithic nature allows for convenient installation and repair, as they can be cast or gunned into place, eliminating the need for intricate brickwork. Consequently, this reduces downtime and enhances productivity. Furthermore, monolithic refractories demonstrate exceptional resistance to thermal shock, which is critical for tundishes and molds that undergo rapid and extreme temperature fluctuations throughout the casting process. Their high thermal conductivity additionally ensures efficient heat transfer, facilitating uniform cooling and solidification of the cast metal. Additionally, monolithic refractories exhibit commendable resistance to chemical attack, ensuring prolonged performance even in the presence of molten metal and slag. Their low porosity further prevents metal penetration and the formation of cracks or spalling. In summary, monolithic refractories are a practical and efficient choice for lining continuous casting tundishes and molds, offering superior performance, ease of installation, and durability in the demanding conditions of the casting process.
- Q: What are the common failure mechanisms of monolithic refractories?
- Monolithic refractories commonly fail due to thermal spalling, chemical attack, erosion, and mechanical stress. Thermal spalling arises from abrupt temperature changes, causing the refractory material to crack and break. This can result from thermal shock or cyclic heating and cooling. Chemical attack occurs when aggressive chemicals or gases interact with the refractory material, degrading its lining. This can lead to the formation of new compounds or the dissolution of the refractory material, weakening its structure and reducing its resistance to further chemical attack. Erosion is another prevalent failure mechanism, particularly in scenarios where the refractory lining is exposed to high-speed gas or liquid flows. The abrasive action of the medium can gradually erode the refractory material, causing thinning and eventual failure of the lining. Mechanical stress, such as thermal expansion or contraction mismatch, can also lead to failure in monolithic refractories. Rapid temperature changes can result in differential expansion or contraction, leading to the development of cracks and fractures in the lining. To mitigate these failure mechanisms, several techniques can be utilized. These include careful material selection based on operating conditions, meticulous design to minimize thermal gradients, application of protective coatings, and regular inspection and maintenance to promptly detect and address signs of failure or degradation.
- Q: What are the recommended curing and drying procedures for monolithic refractories?
- The recommended curing and drying procedures for monolithic refractories typically involve a gradual heating process to ensure proper bonding and removal of any moisture. This process usually starts with a preheat at a low temperature to eliminate any residual water, followed by a controlled temperature increase over a specific duration to achieve the desired strength and stability. It is essential to follow the manufacturer's guidelines and consider the specific composition and thickness of the refractory material to ensure optimal curing and drying.
- Q: Can monolithic refractories be customized for specific iron and steel processing requirements?
- Indeed, monolithic refractories possess the capability to be personalized in order to satisfy the distinct demands of iron and steel processing. Renowned for their adaptability and versatility, monolithic refractories can be tailored to accommodate a wide range of applications. The formulation, tangible characteristics, and methods of installation can all be modified to cater to the specific necessities of iron and steel processing. For instance, the selection of raw materials employed in the production of monolithic refractories can be customized to endure the formidable temperatures and harsh chemical environments inherent in iron and steel processing. Diverse types of aggregates, binders, and additives can be chosen to augment the refractory's resistance against thermal shock, erosion, and corrosion. Moreover, the installation technique for monolithic refractories can be adjusted to suit the precise requirements of iron and steel processing. Whether it is gunning, casting, ramming, or spraying, the method of installation can be personalized to guarantee optimal performance and durability in the given application. Additionally, monolithic refractories can also be tailored to particular shapes and sizes to accommodate the various equipment and structures utilized in iron and steel processing. This facilitates a more precise and efficient lining of furnaces, ladles, tundishes, and other vessels, thereby enhancing overall productivity and performance in the process. In conclusion, monolithic refractories can be customized to cater to the distinct requirements of iron and steel processing by modifying their composition, tangible characteristics, installation techniques, and shape. This customization ensures that the refractories can withstand the extreme conditions encountered in these industries, resulting in improved performance, prolonged service life, and enhanced productivity.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories High Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate for Iron and Steel Industry 2024
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords