High Temperature Insulation Fiberglass Needle Mats
- Loading Port:
- Ningbo
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 500 m²
- Supply Capability:
- 300000 m²/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Description: Our high-quality Glass Fiber Mat is made by means of needle punching process with the mixed silicic acid glass fiber, that is chopped from long glass fiber. It is fire retardant, high temperatures resistant, good chemical and abrasion resistant, electrically and acoustically insulating and so on. The main applications are soundproof, heat resistant, heat protection, thermal insulation on pipes, insulator for high temperatures, or other industrial areas.
Features: high temperature, chemical, and abrasion resistance, fire retardant
Application: Fiberglass Mesh Cloth, resistant high temperatures
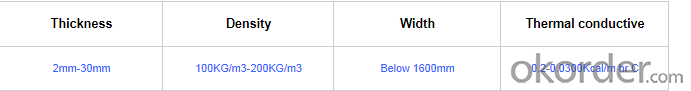
PRICE: USD2 per kilogram
UNIT: Kilogram
MOQ: 100 KGS
Width: 1m,1.2m,1.5m or customized
Yarn Type: E-glass
Standing temperature: up to 650℃
Product name: E Glass Needle Mat
Roll length: 50 meter or customized
Color: white
Weave Type:conventional
Alkali content: Alkali free
Processing service: cutting
Material: fiberglass
Thickness: 20mm or customized
Size: can be customized
Supply ability: 200000 Kilogram/Kilograms per Month
Packaging: Rolls packed In cartons loaded on pallets or according to customers' requirements.
Lead time: 7-30 days
Technology: nonwoven, laminating and needle-punched
- Q: What are the safety precautions when working with fiberglass fabric?
- When working with fiberglass fabric, it is important to take certain safety precautions to protect yourself from potential hazards. Here are some key safety measures to consider: 1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including goggles or safety glasses, a respirator or mask, gloves, and protective clothing. This will help minimize the risk of inhaling fiberglass particles, getting them in your eyes, or having direct skin contact. 2. Ventilation: Ensure that the work area is well-ventilated to prevent the accumulation of fiberglass dust or fumes. If working indoors, use exhaust fans or open windows to promote airflow and remove any airborne particles. 3. Dust Control: Minimize the generation of fiberglass dust by using wet methods, such as wetting the fabric before cutting or using a water mist to control airborne particles. Consider using a dust collection system or vacuum with a HEPA filter to capture any fiberglass dust that may be produced. 4. Cutting and Handling: When cutting fiberglass fabric, use appropriate tools such as shears or a rotary cutter to avoid fraying. Handle the fabric carefully to prevent the release of loose fibers into the air. If possible, use pre-cut fiberglass pieces to minimize the need for cutting on-site. 5. Cleanup: After completing the work, clean up any fiberglass dust or debris using a vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter. Avoid using compressed air or brooms, as they can disperse the particles into the air. Dispose of any waste material in accordance with local regulations. 6. Hygiene: Practice good personal hygiene by washing your hands and face thoroughly after working with fiberglass fabric. Launder any contaminated clothing separately to avoid cross-contamination. 7. Training: Ensure that all individuals working with fiberglass fabric are properly trained on the potential hazards, safety procedures, and the correct use of PPE. Regularly review and update safety protocols to promote a safe working environment. By following these safety precautions, you can minimize the risks associated with working with fiberglass fabric and protect your health and well-being.
- Q: Can fiberglass fabric be used for reinforcement in oil processing tanks?
- Yes, fiberglass fabric can be used for reinforcement in oil processing tanks. Fiberglass fabric is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and durability, making it an ideal material for reinforcing structures in harsh environments such as oil processing tanks. The fabric can be applied to the tanks either by wet lay-up or vacuum infusion process, ensuring proper adhesion and integration with the tank structure. Additionally, fiberglass fabric is non-conductive and non-magnetic, which makes it suitable for use in tanks containing flammable or sensitive materials. Overall, fiberglass fabric offers a cost-effective and reliable solution for reinforcing oil processing tanks.
- Q: Are fiberglass fabrics resistant to moisture or humidity?
- Fiberglass fabrics exhibit remarkable resistance to moisture and humidity due to their composition. Comprising delicate glass fibers, fiberglass possesses the ability to repel water and hinder the effortless passage of moisture. The non-porous structure of fiberglass prohibits the proliferation of mold or mildew, rendering it a superb material for scenarios frequently subject to moisture or humidity. Moreover, fiberglass fabrics endure substantial levels of moisture without compromising their durability or reliability, thereby establishing themselves as a dependable option across diverse sectors such as construction, marine, and automotive industries.
- Q: How does fiberglass fabric perform in peel strength?
- Fiberglass fabric typically performs well in peel strength due to its strong and durable nature. It exhibits good resistance to delamination or separation under applied forces, making it a reliable choice for applications where peel strength is important, such as in composite materials, automotive parts, and aerospace components.
- Q: What are the different fiberglass fabric finishes for antistatic properties?
- There are several different fiberglass fabric finishes that can provide antistatic properties. Some common finishes include carbon coating, metalized coating, and conductive polymer coating. These finishes help to dissipate static charges and prevent the buildup of static electricity on the fabric surface.
- Q: Is fiberglass fabric resistant to chemicals used in agriculture?
- Yes, fiberglass fabric is generally resistant to chemicals used in agriculture. Fiberglass is known for its excellent chemical resistance, making it a suitable material for various applications including those in the agricultural industry. It can withstand exposure to a wide range of chemicals commonly used in agriculture such as fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, and other agrochemicals. This chemical resistance ensures that the fabric remains durable and unaffected by the corrosive properties of these substances. Additionally, fiberglass fabric is also resistant to moisture, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures, making it a reliable choice for agricultural applications where exposure to harsh environmental conditions is common.
- Q: Can fiberglass fabric be used for making heat shields?
- Yes, fiberglass fabric can be used for making heat shields. Fiberglass fabric is known for its excellent heat resistance properties, making it an ideal material for heat shielding applications. It can withstand high temperatures without melting or deforming, providing a protective barrier against heat transfer. Additionally, fiberglass fabric is lightweight, flexible, and has good insulation properties, making it suitable for various heat shield applications, such as in automotive, aerospace, and industrial settings.
- Q: What are the different fiberglass fabric coatings for flame retardancy?
- There are several different coatings that can be applied to fiberglass fabric to enhance its flame retardant properties. Some of the commonly used coatings include: 1. Silicone: Silicone coatings are known for their excellent resistance to high temperatures and their ability to provide a protective layer against flames. They can withstand prolonged exposure to heat without degrading, making them ideal for applications that require long-term flame resistance. 2. Polyurethane: Polyurethane coatings are often used to provide a flexible and durable flame retardant layer on fiberglass fabric. They offer good resistance to abrasion and can withstand repeated exposure to flames without losing their effectiveness. 3. Acrylic: Acrylic coatings are lightweight and provide good resistance to both flames and chemicals. They are often used in applications where a balance between flame retardancy and flexibility is required, such as in protective clothing. 4. PVC: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) coatings are commonly used in the manufacturing of flame retardant fiberglass fabric. PVC coatings offer excellent flame resistance and are often applied to fabrics used in industrial settings and for protective purposes. It's important to note that the choice of coating depends on the specific requirements of the application. Factors such as desired level of flame retardancy, flexibility, durability, and cost will play a role in determining the most suitable coating for a particular use case.
- Q: How is fiberglass fabric cut?
- There are various ways to cut fiberglass fabric, depending on the desired outcome and the tools at hand. Scissors or a rotary cutter are commonly used for straight cuts and smaller pieces. However, for more intricate or precise cuts, it may be preferable to use a hot knife or a laser cutter. When using a hot knife, it heats up while cutting through the fiberglass fabric. This not only cuts the fabric but also seals the edges and prevents fraying. This method is particularly useful when dealing with thicker or heavier fiberglass materials. On the other hand, laser cutters utilize a focused beam of light to melt through the fabric, resulting in clean and precise cuts. This method is often employed in industrial settings where high accuracy and efficiency are necessary. Regardless of the chosen cutting method, it is crucial to wear appropriate safety gear, such as gloves and goggles, as fiberglass can cause irritation to the skin and eyes. Furthermore, working in a well-ventilated area is advisable to minimize exposure to fiberglass dust particles.
- Q: What are the different weave styles available for fiberglass fabric?
- Fiberglass fabric offers a variety of weave styles, each with its own distinct qualities and uses. Among the most popular are plain weave, twill weave, satin weave, and leno weave. 1. Plain weave, the most common style, features a straightforward over-under pattern. Warp yarns pass alternatively over and under weft yarns, resulting in a balanced and stable fabric. Its versatility makes it suitable for numerous applications. 2. Twill weave showcases a diagonal line pattern on the fabric surface. By passing the weft yarn over multiple warp yarns before going under one or more, twill weave fabrics offer superior strength and durability, making them perfect for high-performance applications. 3. Satin weave is known for its smooth and glossy appearance. The weft yarn passes over several warp yarns before going under one, creating a high number of floats and a silky texture. Satin weave fabrics are lightweight, flexible, and drape beautifully, making them ideal for achieving a refined and elegant finish. 4. Leno weave is a unique style that creates an open mesh structure. Adjacent warp yarns are twisted together and secured with a weft yarn, resulting in high porosity and excellent breathability. Leno weave fabrics are commonly used in filtration and composite reinforcement applications. These are just a few examples of the weave styles available for fiberglass fabric. The choice of weave depends on specific requirements, such as strength, weight, flexibility, and aesthetics.
Send your message to us
High Temperature Insulation Fiberglass Needle Mats
- Loading Port:
- Ningbo
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 500 m²
- Supply Capability:
- 300000 m²/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


























