excellent hot-dip galvanized/ aluzinc steel sheet in good quality
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Description:
1.Mateials:SGCC,DX51D / DX52D /S250,280GD
2.Size:width:600-1250mm(900mm,1215mm,1250mm,1000mm the most common)
thickness:0.15-2.0mm
length:1000-6000mm,as your require
3.Zinc coating :60-180g( as required)
4.Coil id:508mm
5.Coil weight: 3-5MT(as required)
6. Surface:regular/mini/zero spangle, chromated, skin pass, dry etc.
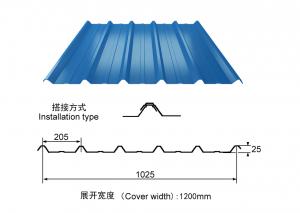
Applications of our Galvalume Coil:
Galvalume Coil widely used for roofing products, It is also the ideal base material for Prepainted Steel Coil.
1. roofing
2. gutters
3. unexposed automotive parts
4. appliances
5. furniture
6. outdoor cabinetry
Production of cold formed corrugated sheets and profiles for roofing, cladding, decking, tiles, sandwich walls, rainwater protective systems, air conditioning duct as well as electrical appliances and engineering.
We can ensure that stable quality standards are maintained, strictly meeting both market requirements and customers’ expectations. Our products enjoy an excellent reputation and have been exported to Europe, South-America, the Middle-East, Southeast-Asia, Africa and Russia etc.. We sincerely hope to establish good and long-term business relationship with your esteemed company.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for architectural applications?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for architectural applications. Steel sheets are versatile and can be used for various architectural purposes such as roofing, cladding, and structural components. They offer strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal, making them a popular choice in modern architecture.
- Q: Are steel sheets suitable for data center infrastructure?
- Yes, steel sheets are suitable for data center infrastructure. Steel is a strong and durable material that can provide the necessary structural integrity and support for data center equipment and systems. It is commonly used for server racks, cabinets, enclosures, and other components within data centers. Steel sheets offer stability, protection, and easy customization options, making them a reliable choice for data center infrastructure.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used in construction?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used in construction. They are commonly used for various applications such as roofing, siding, structural framing, and cladding in both residential and commercial buildings due to their strength, durability, and versatility.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for roofing purposes?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for roofing purposes. Steel roofing sheets are commonly used in commercial and industrial buildings, as well as residential homes. They are known for their durability, longevity, and resistance to harsh weather conditions such as rain, snow, and wind. Steel sheets are available in various profiles and finishes, allowing for customization to suit different architectural styles and design preferences. Additionally, steel roofing is lightweight, fire-resistant, and often made from recycled materials, making it an environmentally friendly roofing option. Overall, steel sheets are a popular choice for roofing due to their strength, versatility, and aesthetic appeal.
- Q: How are steel sheets priced?
- Steel sheets are priced based on factors such as the type and grade of steel, thickness, size, market demand, and prevailing market conditions. Prices can also be influenced by the cost of raw materials and production processes involved.
- Q: What are the different thickness options for steel sheets?
- The thickness options for steel sheets can vary depending on the specific type and application, but common options range from very thin sheets around 0.4 mm (0.0157 inches) to thick sheets up to 25 mm (0.9843 inches) or even thicker for certain industrial uses.
- Q: Can steel sheets be customized in terms of thickness?
- Yes, steel sheets can be customized in terms of thickness. Steel sheets are manufactured in various thicknesses to cater to different applications and requirements. The thickness of a steel sheet can be customized during the manufacturing process according to the specific needs of the customer. This customization allows for versatility and flexibility in using steel sheets for a wide range of purposes, from construction and automotive industries to manufacturing and fabrication processes. Customizing the thickness of steel sheets ensures that they meet the specific strength, durability, and structural requirements of the project at hand.
- Q: Are steel sheets resistant to UV rays?
- No, steel sheets are not inherently resistant to UV rays. Steel can be vulnerable to UV damage, which can cause it to fade, discolor, or even corrode over time. However, the extent of the damage will depend on various factors such as the type of steel, the thickness of the sheet, the specific UV exposure, and the presence of protective coatings. To enhance the UV resistance of steel sheets, manufacturers often apply coatings such as paint, powder coatings, or galvanized finishes that can provide some level of protection against UV rays. It is important to consult with steel suppliers or manufacturers to determine the specific UV resistance capabilities of the steel sheets being used and to consider additional protective measures if necessary.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used in the energy sector?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used in the energy sector. Steel is a versatile material that offers several advantages for various applications in the energy industry. It is commonly used in the construction of power plants, transmission towers, and infrastructure for renewable energy sources such as wind turbines and solar panels. In power plants, steel sheets are used in the fabrication of boilers, turbines, and other components. Steel's high strength and durability make it suitable for withstanding the high temperatures and pressures involved in power generation processes. It also offers resistance to corrosion and erosion, ensuring the longevity of critical equipment. Steel sheets are also utilized in the construction of transmission towers and substations. These structures support power transmission lines and facilitate the efficient flow of electricity across long distances. Steel's strong mechanical properties make it an ideal choice for these applications, as it can withstand the weight and stresses imposed by power transmission infrastructure. Furthermore, steel sheets are vital in the manufacturing of wind turbines and solar panels. In wind turbines, steel is used for the tower structure, which must be strong enough to support the weight of the rotor and withstand the loads from wind forces. Additionally, steel sheets are used in the construction of solar panel frames, providing rigidity and stability for the photovoltaic modules. Overall, steel sheets are widely used in the energy sector due to their strength, durability, and resistance to various environmental factors. The versatility of steel makes it a reliable choice for a range of applications, helping to support the generation and transmission of energy in both conventional and renewable energy sources.
- Q: What is the standard size of a steel sheet?
- The standard size of a steel sheet can vary depending on the specific application and industry. However, in general, steel sheets are commonly available in standard sizes such as 4 feet by 8 feet (1.2 meters by 2.4 meters) or 5 feet by 10 feet (1.5 meters by 3 meters). These dimensions are widely used in construction, manufacturing, and fabrication processes. It is important to note that customized sizes can also be obtained based on the requirements of a particular project or customer.
Send your message to us
excellent hot-dip galvanized/ aluzinc steel sheet in good quality
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords