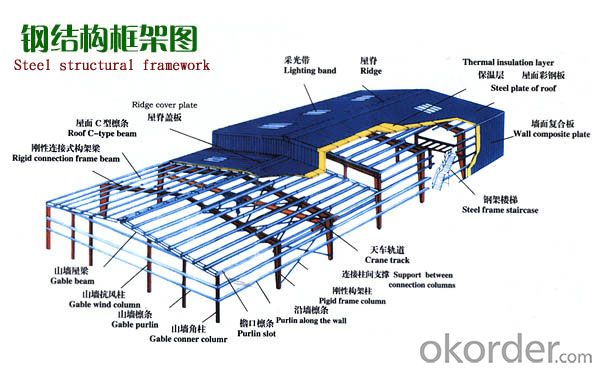
Cheap Steel Structure Warehouse
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications
Steel Structure
We can design,fabricate and install all kinds of steel structure buildings.
Item Name: Steel Structure
Size: Length,Width and height according to customer's requirements.
Material: Q235 and Q345.
Surafce: hot dip galvanize or Painted
Drawings: We can make the quotation according to customer's drawing.
We can also make the design and quotation according to customer's requirements.
We can offer all the detailed drawings for installation and fabrication.
Packing: Decided by buyer.
Load in to 40ft GP,20ft GP or 40HQ or 40OT.
Carbon structural steel: Q195, Q215, Q235, Q255, Q275, etc.
High-strength low-alloy structural steel
Quality carbon structural steel and alloy structural steel
Special purpose steel
- Q: What is the difference between hot-rolled and cold-formed steel structures?
- Hot-rolled and cold-formed steel structures differ in several key aspects. Firstly, the manufacturing process for each type of steel structure is distinct. Hot-rolled steel structures are produced by heating the steel billets to extremely high temperatures and then rolling them into the desired shape. This process results in a more malleable and ductile steel, allowing for a wider range of shapes and sizes to be produced. On the other hand, cold-formed steel structures are made by bending or forming the steel at room temperature. This process involves passing the steel through a series of rollers to achieve the desired cross-sectional shape. Cold-formed steel structures typically have a thinner gauge compared to hot-rolled structures and are primarily used for lightweight applications. Another significant difference is the mechanical properties of the two types of steel. Hot-rolled steel structures exhibit higher tensile strength and yield strength compared to cold-formed steel structures. This enhanced strength is due to the heat treatment during the manufacturing process, which aligns the grain structure and increases the overall strength of the steel. Furthermore, hot-rolled steel structures have better resistance to corrosion and fire compared to cold-formed steel structures. The high-temperature treatment during manufacturing forms a protective oxide layer on the surface of hot-rolled steel, which acts as a barrier against corrosion. Cold-formed steel structures, however, require additional measures such as coatings or galvanization to enhance their corrosion resistance. In terms of cost, cold-formed steel structures are typically more economical compared to hot-rolled steel structures. The simpler manufacturing process and the use of thinner gauge steel contribute to reduced material and labor costs for cold-formed structures. Overall, the choice between hot-rolled and cold-formed steel structures depends on the specific application and design requirements. Hot-rolled steel structures offer greater strength and versatility but are generally more expensive. Cold-formed steel structures, while lighter and more cost-effective, may be limited in terms of load-bearing capacity and corrosion resistance.
- Q: What are the guidelines for the maintenance and inspection of steel structures?
- The maintenance and inspection of steel structures is crucial to ensure their longevity, safety, and structural integrity. Here are some guidelines that can be followed for this purpose: 1. Regular Inspections: Schedule regular inspections of the steel structures by qualified professionals. These inspections should be conducted at least once a year, but the frequency may vary depending on the usage, location, and condition of the structure. 2. Visual Examination: Perform a visual examination of the entire structure to identify any visible signs of damage, such as corrosion, cracks, or deformation. Look for changes in color, texture, or appearance of the steel surfaces. 3. Corrosion Protection: Implement effective corrosion protection measures to prevent the degradation of steel. This can include applying protective coatings, such as paint or galvanization, to the steel surfaces. Regularly inspect these coatings for any signs of wear or damage and repair or reapply as necessary. 4. Structural Stability: Assess the structural stability of the steel components by checking for signs of movement, distortion, or misalignment. Look for any loose connections, bolts, or fasteners, and tighten or replace them as needed. 5. Load Capacity Verification: Regularly verify the load capacity of the steel structures to ensure they can withstand the intended loads. This can be done through calculations, stress analysis, or load testing, depending on the complexity and criticality of the structure. 6. Environmental Factors: Consider the environmental factors that may affect the steel structures, such as exposure to moisture, chemicals, extreme temperatures, or seismic activity. Implement appropriate measures to mitigate these risks, such as proper drainage, insulation, or earthquake-resistant design. 7. Documentation: Maintain detailed records of all inspections, maintenance activities, repairs, and modifications performed on the steel structures. This documentation will help track the history of the structure and provide valuable information for future inspections and maintenance. 8. Professional Expertise: Engage experienced and qualified professionals for the maintenance and inspection of steel structures. They should have the necessary expertise, knowledge, and equipment to identify and address any potential issues effectively. Remember, adhering to these guidelines is essential, but it is also important to consult relevant codes, standards, and regulations specific to your region or industry. Regular maintenance and inspections will not only extend the lifespan of steel structures but also ensure the safety of the people and assets relying on them.
- Q: How do steel structures provide resistance against wind-borne debris impact?
- Steel structures possess inherent strength and durability, enabling them to withstand wind-borne debris impact. The material itself, steel, is highly robust with a high tensile strength, allowing it to endure significant external forces. In the case of wind-borne debris, steel structures are specifically designed to absorb the impact and distribute the load, resulting in minimal damage. One notable characteristic of steel structures is their capacity to flex and deform without breaking. This flexibility enables the structure to absorb and disperse the energy produced by wind-borne debris impact. Steel beams and columns are engineered to bend and twist, effectively reducing the force exerted on the structure. This capability prevents disastrous failure and ensures the structural integrity of the building. Furthermore, steel structures can be customized with specific features that enhance their resistance against wind-borne debris impact. These features encompass reinforced connections like bolted or welded joints, which provide additional strength and stability. By reinforcing critical areas, steel structures are better equipped to withstand the impact of airborne debris. Moreover, the use of steel in construction permits the utilization of advanced design techniques. Computer-aided simulations and wind tunnel testing allow engineers to accurately evaluate the potential impact of wind-borne debris and design structures accordingly. This precise analysis aids in determining the necessary thickness, shape, and positioning of steel elements to optimize their resistance to impact. In conclusion, steel structures offer exceptional resistance against wind-borne debris impact due to their strength, flexibility, and advanced design capabilities. By leveraging these attributes, steel structures guarantee the safety of occupants and safeguard against potential damage caused by severe weather conditions.
- Q: What are the necessary safety measures for steel structure construction?
- Some necessary safety measures for steel structure construction include conducting thorough risk assessments, providing appropriate personal protective equipment to workers, ensuring proper training and supervision, implementing fall protection systems, regularly inspecting equipment and materials, and following all relevant safety regulations and protocols. Additionally, maintaining clear communication channels and promoting a safety-conscious culture among workers is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring a safe construction site.
- Q: How are steel structures designed for different educational systems?
- Steel structures for different educational systems are designed based on a combination of factors including local building codes, safety regulations, architectural requirements, and the specific needs of the educational institution. These designs typically incorporate features such as large open spaces for classrooms, laboratories, and recreational areas, as well as strong structural elements to ensure durability and longevity. Additionally, the designs may also prioritize energy efficiency, accessibility, and flexibility to accommodate potential future expansions or modifications.
- Q: How are steel structures designed for recreational facilities such as sports stadiums and theme parks?
- Steel structures for recreational facilities such as sports stadiums and theme parks are designed by taking into account various factors such as the intended use, capacity requirements, safety regulations, and aesthetic considerations. Structural engineers analyze the load-bearing capacity, durability, and flexibility of steel to create designs that can withstand the forces exerted by large crowds, extreme weather conditions, and dynamic movements. Advanced computer modeling and simulation techniques are often used to optimize the design and ensure structural integrity. Additionally, collaboration between architects, engineers, and construction teams is essential to create functional and visually appealing steel structures for these recreational facilities.
- Q: How are steel structures designed for efficient transportation and logistics?
- Steel structures are designed for efficient transportation and logistics through careful planning and consideration of various factors. One key aspect is the use of modular and prefabricated components. By breaking down the structure into smaller modules, it becomes easier to transport and assemble them at the desired location. These modules are designed to fit together seamlessly, ensuring efficient transportation and logistics. Furthermore, steel structures are designed to be lightweight yet sturdy. This reduces the overall weight of the structure, thereby minimizing transportation costs. The use of advanced engineering techniques and materials helps in achieving this balance between strength and weight. In addition, steel structures are often designed with ease of assembly in mind. This means that they can be quickly and efficiently erected at the desired location. This is particularly important for transportation and logistics purposes, as it reduces the overall time required for construction and minimizes disruptions to the surrounding area. Moreover, steel structures can be designed to be easily disassembled and relocated if necessary. This flexibility is beneficial for transportation and logistics purposes, as it allows for the structure to be moved to a different location if the need arises. This is especially useful in industries where rapid deployment or frequent relocation of facilities is required. Lastly, steel structures can incorporate various features to enhance transportation and logistics efficiency. For example, they can be designed with integrated loading docks, ramps, and other specialized features to facilitate the movement of goods and materials. Additionally, the design can include provisions for the installation of overhead cranes or other lifting equipment, enabling efficient handling and storage of heavy items. Overall, steel structures are meticulously designed to ensure efficient transportation and logistics. From modular components and lightweight materials to ease of assembly and disassembly, these structures are carefully crafted to minimize costs and time associated with transportation, while maximizing flexibility and functionality.
- Q: What are the different types of steel canopies and awnings used in buildings?
- There are several different types of steel canopies and awnings that are commonly used in buildings. These structures provide shade and protection from the elements, while also adding aesthetic appeal to the overall design of the building. Here are some of the most popular types: 1. Cantilevered Canopies: These canopies are supported by a single beam or column, extending outwards from the building without any additional support. Cantilevered canopies are often used in commercial buildings, providing shade for entrances, walkways, or outdoor seating areas. 2. Tensile Membrane Canopies: Tensile membrane canopies are made of a flexible fabric material that is stretched over a steel frame. These canopies can be custom-designed to create unique shapes and forms, offering a visually striking addition to the building. They are commonly used in stadiums, outdoor event spaces, or as car park covers. 3. Louvered Canopies: Louvered canopies consist of adjustable horizontal slats that can be opened or closed to control the amount of sunlight or rain that enters the space below. These canopies are ideal for areas where flexible shading is desired, such as outdoor patios or restaurant terraces. 4. Walkway Canopies: Walkway canopies are designed to provide shelter and protection for pedestrians moving between different sections of a building or across open spaces. These canopies are often used in educational institutions, hospitals, or office complexes to ensure people can move comfortably regardless of weather conditions. 5. Entrance Canopies: Entrance canopies are typically located above the main entrances of buildings, providing shelter for visitors and protecting the entrance area from rain or snow. These canopies can be simple in design, such as a flat metal roof with supporting columns, or they can be more elaborate with curved or angular shapes. 6. Window Awnings: Window awnings are smaller-scale structures that are mounted above windows to provide shade and reduce heat gain inside the building. These awnings can be fixed or retractable, allowing occupants to adjust the level of shading as needed. Each type of steel canopy or awning serves its own purpose and offers unique benefits. Whether it's providing shade, protecting entrances, or enhancing the architectural design, these structures play an essential role in enhancing the functionality and visual appeal of buildings.
- Q: Why steel buildings have the best seismic performance?
- Steel material of isotropic, homogeneous, flexible, able to withstand seismic moment repeatedly without brittle failure; loss of stability time is obvious, is conducive to escape;
- Q: How are steel trusses designed and sized?
- Steel trusses are designed and sized using a combination of engineering principles, computer-aided design software, and industry codes and standards. The design process involves considering the specific requirements of the structure, such as the span, load conditions, and desired aesthetics. Factors like material properties, shape, and member connections are taken into account to ensure the truss can safely support the applied loads while minimizing deflection and stress. The sizing of steel trusses involves optimizing the dimensions and cross-sectional properties of the individual members to achieve the desired strength and stability. This is done by analyzing the internal forces and moments within the truss, often utilizing finite element analysis to accurately model the complex behavior of the structure.
Send your message to us
Cheap Steel Structure Warehouse
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords