Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG630MX-E Solar Inverter
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 unit
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 unit/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
1. Structure of Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG630MX-E Description
A solar inverter, or PV inverter, or Solar converter, converts the variable direct current (DC) output of a photovoltaic (PV) solar panel into
autility frequency alternating current (AC) that can be fed into a commercial electrical grid or used by a local, off-grid electrical network.
It is acritical BOS–component in a photovoltaic system, allowing the use of ordinary AC-powered equipment.
Solar inverters have special functions adapted for use with photovoltaic arrays, including maximum power point tracking and anti-islanding protection.
Suitable for 50Hz/60Hz grid, could be used in Asia, Australia and Europe.
2. Main Features of the Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG630MX-E
• LVRT (Zero-voltage Ride-through)
• Active power continuously adjustable (0~100%)
• Reactive power control with power factor from 0.9 lagging to 0.9 leading
• DC input voltage up to 1000V
• Latest 32 bit DSP chip, advanced digital lock-in technique, more quickly and precisely
• -30℃~+55℃ continuously operating at rated power
• Continuously and stably working in high altitude environment
• Auxiliary heater (Optional)
3. Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG630MX-E Images

4. Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG630MX-E Specification
Input Side Data | |
Max. PV input power | 713KW |
Max. PV input voltage | 1000V |
Startup voltage | 635V |
Min. operation voltage | 615V |
Max. PV input current | 1160A |
MPP voltage range | 615~850V |
No. of DC inputs | 8 |
Output Side Data | |
Nominal AC output power | 630kVA |
Max. AC output apparent power | 700KVA |
Max. AC output current | 1010A |
THD | < 3 % (Nominal power) |
Nominal AC voltage | 400V |
AC voltage range | 320V~460V |
Nominal grid frequency | 50/60Hz |
Grid frequency range | 47~52/57~62Hz |
Power factor | >0.99@default value at nominal power, (adj. 0.9 overexited ~0.9 underexited) |
Isolated transformer | No |
DC current injection | <0.5 %In |
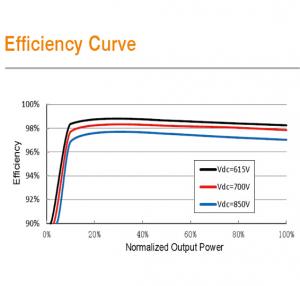
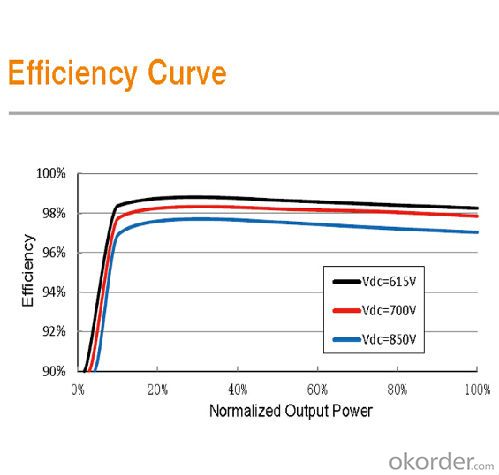
Efficiency | |
Max. efficiency | 98.60% |
Max. European efficiency | 98.50% |
Protection | |
Input side disconnection device | DC load switch |
Output side disconnection device | AC load Switch |
DC overvoltage protection | Yes |
AC overvoltage protection | Yes |
Grid monitoring | Yes |
Ground fault monitoring | Yes |
Over temperature protection | Yes |
Insulation monitoring | Yes |
Surge arrester for auxiliary supply | Yes |
General Data | |
Dimensions(W×H×D) | 1606×2304×860mm |
Weight | 1700kg |
Operating ambient temperature range | -30~65℃(>55℃ derating) |
Night power consumption | <100W |
External auxiliary supply voltage | 400V |
Cooling method | Temperature controlled air-cooling |
Ingress protection rating | IP21 |
Allowable relative humidity range | 0~95% no condensing |
Max. operating altitude | 6000m (>3000m derating) |
Fresh air consumption | 4500 m3/h |
Display | Colored touch screen |
Communication | RS485/Modbus, Ethernet(Opt.) |
5. FAQ of Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG630MX-E
Q1. What is the difference between inverter and solar inverter?
A1. Inverter only has AC inpput, but solar inverter both connect to AC input and solar panel, it saves more power
Q2. What is the difference between MPPT&PWM?
A2. MPPT has higher efficiency, it can track the max power point and won't waste energy.
- Q:Can a solar inverter be used with a smart home automation system?
- Certainly! A smart home automation system can indeed work together with a solar inverter. Nowadays, many solar inverters come with communication capabilities built-in, like Wi-Fi or Ethernet connectivity. This means that they can easily be integrated into a smart home automation system. This integration allows homeowners to remotely monitor and control their solar power production and usage using a smartphone app or a central control panel. By having a smart home automation system, users can keep track of real-time energy generation, make adjustments to settings, and receive notifications about system performance or any potential issues. This integration not only enhances the convenience and efficiency of managing solar power but also enables better optimization and synchronization with other smart devices and appliances in the household.
- Q:Can a solar inverter be used with different types of backup power configurations?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with different types of backup power configurations. Solar inverters are designed to convert the DC power generated by solar panels into AC power that can be used to power electrical devices and appliances. They can be integrated with various backup power systems such as batteries, generators, or grid connections to provide uninterrupted power supply during periods of low solar generation or power outages. The versatility of solar inverters allows for flexibility in choosing and combining backup power sources based on specific needs and preferences.
- Q:What is the maximum AC voltage that a solar inverter can provide?
- The maximum AC voltage that a solar inverter can provide typically depends on the specific model and its specifications. However, in general, most solar inverters are designed to produce a maximum AC voltage of around 240 volts in residential installations and up to 480 volts in commercial or utility-scale installations.
- Q:Photovoltaic grid-connected inverter problem
- The first zero line is the AC output. Any AC output of the inverter will have zero line, whether it is isolated or non-isolated. Isolation is the safety of high voltage inverters and regulators. 50KW above the inverter almost with the transformer.
- Q:Are there any disadvantages of using a solar inverter?
- Yes, there are some disadvantages of using a solar inverter. One major disadvantage is the initial cost of purchasing and installing the inverter, which can be relatively high. Additionally, solar inverters are susceptible to damage from power surges or lightning strikes, which can result in costly repairs. Furthermore, solar inverters require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance, which can add to the overall cost. Lastly, solar inverters can produce a humming noise during operation, which may be a nuisance in certain environments.
- Q:Can a solar inverter be used with a solar tracker system?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with a solar tracker system. In fact, using a solar inverter with a solar tracker system can enhance the overall efficiency and performance of the system. The solar inverter converts the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power electrical appliances or be fed into the grid. This AC power can then be easily integrated with the solar tracker system to continuously adjust the position and alignment of the solar panels to maximize their exposure to sunlight. Overall, combining a solar inverter with a solar tracker system can optimize the energy generation and increase the overall output of the solar power system.
- Q:What is the maximum number of parallel inverters that can be connected?
- The maximum number of parallel inverters that can be connected depends on various factors such as the power rating, capacity, and design of the inverters, as well as the electrical system they are being connected to. It is best to consult the manufacturer's specifications and guidelines to determine the maximum number of parallel inverters that can be safely connected.
- Q:What is the role of a solar inverter in power factor correction?
- The role of a solar inverter in power factor correction is to convert the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used by the electrical grid. In doing so, the solar inverter ensures that the AC power being fed into the grid has a power factor close to unity, which means it is efficient and does not cause any unnecessary strain on the electrical system. This helps to improve the overall power quality and efficiency of the solar energy system.
- Q:Can a solar inverter be used with a single solar panel?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with a single solar panel. The purpose of a solar inverter is to convert the direct current (DC) produced by the solar panel into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power electrical devices or be fed into the electrical grid. Even with a single solar panel, the inverter can still perform this function effectively.
- Q:Generally a large grid-connected photovoltaic power plant will have several inverters
- The use of a high-power grid-connected inverter into the grid, the need for line design is relatively simple, because the DC and AC lines are separated, the use of convergence box to summarize, DC bus and then into the grid inverter
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG630MX-E Solar Inverter
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 unit
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 unit/month
Offcanvas right
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords