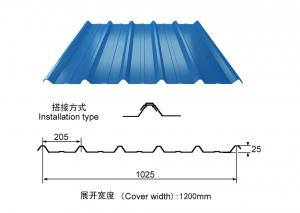
galvanized steel sheet
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 8000 m.t. m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
Grade: SGH340, DX51D and SGCC (customized)
Surface treatment: passivation, oiling, chromed, unoiled
Spangle types: minimal, zero and large
Thickness: 0.37 to 3.5mm
Width: greater than 1,000mm
Inner diameter: 508 to 610mm
Zinc coating: greater than 80g/m2
Applications:
Construction, home appliance, hardware and machinery
Standards:
JIS g3302 1998, ASTM a653 2003, EN10142 1990
EN10327 2004, AS1397 2001, GB2518-2004
Packing: export packing/sea worthy for international delivery
- Q: What is the difference between a painted and laminated steel sheet?
- Both a painted steel sheet and a laminated steel sheet belong to the category of steel sheets, but they offer distinct characteristics and applications. A painted steel sheet is a sheet of steel that has been coated with a layer of paint. This layer of paint serves two purposes: it protects against corrosion and enhances the sheet's appearance. The paint can be customized in terms of color and finish, allowing for versatility in design. Architectural applications, such as roofing, siding, and wall cladding, as well as the automotive and appliance industries, commonly utilize painted steel sheets. However, it is important to periodically maintain the paint layer to ensure its durability and appearance. On the other hand, a laminated steel sheet is created by bonding multiple layers of materials together. Typically, it consists of a steel core and one or more additional layers, such as plastic, polymer, or resin. The lamination process significantly strengthens and enhances the durability and performance of the steel sheet. These laminated steel sheets are highly resistant to impact, scratching, and chemical exposure, making them suitable for applications that require superior mechanical strength and protection. Industries such as transportation, construction, and industrial equipment manufacturing often utilize laminated steel sheets. Additionally, the laminate layers can provide added functionalities such as sound insulation, thermal insulation, or fire resistance. In conclusion, the main distinction between painted and laminated steel sheets lies in their composition and intended purpose. Painted steel sheets prioritize aesthetics and corrosion protection, while laminated steel sheets prioritize strength, durability, and specialized functionalities. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the given application.
- Q: How are steel sheets transported and stored?
- Steel sheets are typically transported and stored using specialized equipment and techniques. They are commonly transported in large trucks or shipping containers, secured with straps or chains to prevent movement during transit. When it comes to storage, steel sheets are often stacked on pallets or racks in dedicated storage areas. These storage areas are designed to handle the weight and dimensions of the sheets, ensuring proper organization and easy access when needed. Additionally, steel sheets may be covered or protected with materials such as plastic or tarpaulins to prevent corrosion or damage from environmental elements. Overall, careful handling, secure transportation, and proper storage methods are crucial to maintain the quality and integrity of steel sheets.
- Q: Can the steel sheets be used for metal stamping?
- Indeed, metal stamping can make use of steel sheets. Steel, renowned for its robustness and potency, is frequently employed as a material in metal stamping procedures. Generally, steel sheets are sliced into precise dimensions and shapes before being subjected to the stamping process, wherein a die and punch set are utilized to fashion the desired form onto the steel sheet. This technique enables the production of a diverse array of items, including automotive parts, household appliances, and industrial components.
- Q: What is the difference between a hot rolled and cold rolled galvanized steel sheet?
- The manufacturing process and resulting properties of a galvanized steel sheet differ between hot rolled and cold rolled. Hot rolled sheets are created by heating a large steel slab or billet above its recrystallization temperature, usually around 1700°F (926°C). This high temperature allows for easy shaping and forming of the steel into the desired thickness and dimensions. It also refines the grain structure and produces improved mechanical properties and a more uniform distribution of alloying elements. On the other hand, cold rolled sheets are manufactured at room temperature by passing the hot rolled sheet through rollers that compress and shape the material. This reduces the thickness of the sheet, increases its tensile strength, and improves its surface finish. Cold rolling also allows for tighter tolerances and more precise dimensions, making it suitable for applications that require high precision and consistency. In terms of properties, hot rolled sheets have a rougher surface finish due to the high temperature processing. However, they are generally more ductile and easier to form or bend compared to cold rolled sheets. Hot rolled sheets also have a slightly thicker oxide layer on the surface, providing additional corrosion resistance. On the other hand, cold rolled sheets have a smoother and more polished surface finish. They are typically thinner and have a higher strength-to-weight ratio compared to hot rolled sheets. The cold rolling process also results in a more homogeneous microstructure, improving the overall mechanical properties such as hardness and toughness. Ultimately, the choice between hot rolled and cold rolled galvanized steel sheets depends on the specific requirements of the application. Hot rolled sheets are often preferred for applications that require easy formability and a rougher surface finish, while cold rolled sheets are favored for their higher strength, tighter tolerances, and smoother surface finish.
- Q: What is the typical coefficient of thermal expansion of a steel sheet?
- The typical coefficient of thermal expansion of a steel sheet is around 10.8 x 10^-6 per degree Celsius.
- Q: How are steel sheets protected during storage in outdoor environments?
- Steel sheets are protected during storage in outdoor environments through the application of various protective measures. These measures may include the use of weather-resistant coatings, such as galvanization or paint, to prevent corrosion and rusting. Additionally, steel sheets can be stored on pallets or racks to minimize contact with the ground and reduce the risk of moisture accumulation. Covering the sheets with tarpaulins or using weatherproof storage containers further shields them from direct exposure to rain, snow, and sunlight. Regular inspections and maintenance are crucial to ensure the effectiveness of these protective measures and to address any potential issues promptly.
- Q: How do steel sheets perform in thermal expansion?
- Steel sheets have a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning they expand significantly when exposed to heat and contract when cooled. This property must be considered in applications where precise dimensional stability is required, as thermal expansion can lead to warping or distortion of the steel sheets.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used in the aerospace industry?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used in the aerospace industry.
- Q: How are steel sheets measured and sized?
- Steel sheets are commonly measured and sized based on their thickness, width, and length. Thickness is usually measured in gauge or millimeters, while width and length are measured in inches or millimeters. The size and dimensions of steel sheets can vary depending on the specific requirements of a project or application.
- Q: What are the different sheet metal finishing techniques for steel sheets?
- Some of the different sheet metal finishing techniques for steel sheets include deburring, grinding, polishing, sanding, and painting.
Send your message to us
galvanized steel sheet
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 8000 m.t. m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords