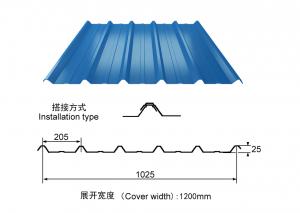
GALVANIZED CORRUGATION STEEL SHEET
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
GALVANIZED CORRUGATION STEEL SHEET
MATERIAL: FULL HARD, ZINC: 50G. CORRUGATION: 11NOS.
BUNDLE WEIGHT: 2-4MT, PACKAGE:SWAWORTHY PACKING
SIZE:0.19MM*665MM(750 BEFORE)*3000
- Q: What is the difference between a matte and glossy steel sheet?
- The main difference between a matte and glossy steel sheet lies in their surface finish. A matte steel sheet has a dull, non-reflective surface that diffuses light, resulting in a more muted appearance. On the other hand, a glossy steel sheet has a smooth, reflective surface that reflects light, giving it a shiny and polished look.
- Q: What is the process of applying anti-fingerprint coatings to steel sheets?
- The process of applying anti-fingerprint coatings to steel sheets typically involves several steps. Firstly, the steel sheets are thoroughly cleaned and degreased to ensure a smooth surface. This is typically done using solvents or alkaline cleaners. Next, the sheets are rinsed and dried to remove any remaining residue. Once clean, a primer or adhesion promoter may be applied to enhance the bonding between the steel and the anti-fingerprint coating. The anti-fingerprint coating is then applied onto the steel sheets using various methods such as spraying, dipping, or roll coating. The coating material is usually a combination of polymers, resins, and additives that provide the desired anti-fingerprint properties. After the coating is applied, the steel sheets are cured or dried, depending on the specific coating technology. This step ensures that the coating adheres properly to the surface and develops its anti-fingerprint characteristics. Lastly, the coated steel sheets may undergo quality checks and inspections to ensure that the coating thickness, appearance, and performance meet the desired standards. This can involve visual inspections, adhesion tests, and fingerprint resistance evaluations. Overall, the process of applying anti-fingerprint coatings to steel sheets involves cleaning, priming, coating, curing, and quality control measures to achieve a durable and effective anti-fingerprint surface on the steel.
- Q: What are the different storage methods for steel sheets?
- There are several different storage methods for steel sheets, including vertical storage racks, horizontal storage racks, cantilever racks, shelving systems, and pallet racking. Each method offers distinct advantages in terms of space utilization, ease of access, and efficient handling of the steel sheets. The choice of storage method depends on the size, weight, and quantity of steel sheets, as well as the available space and specific requirements of the facility.
- Q: What are the different sheet metal cutting techniques for steel sheets?
- Steel sheets can be cut using various techniques, specifically designed for this purpose. Here are some commonly employed methods: 1. Shearing: By applying a high force, a shear or a pair of blades is used to cut the steel sheet. This method is ideal for straight cuts and works with both thin and thick steel sheets. 2. Laser cutting: A high-powered laser beam is employed to slice through the steel sheet. This technique offers high precision and allows for intricate designs. It is suitable for thin and thick steel sheets. 3. Plasma cutting: Here, a plasma torch generates an electrically conductive jet of plasma to cut through the steel. This method is commonly used for thick steel sheets and provides fast cutting speeds. 4. Waterjet cutting: The steel sheet is cut using a high-pressure jet of water mixed with abrasive particles. Waterjet cutting is versatile and can handle different thicknesses of steel sheets. It is also suitable for cutting heat-sensitive materials. 5. Punching: A punch and die set are used to create holes or various shapes in the steel sheet. Punching is a cost-effective method for repetitive cuts and can be used with thin and thick steel sheets. 6. Abrasive cutting: Thin steel sheets can be ground through using an abrasive wheel or disc. This technique provides a smooth finish. Factors such as the steel sheet's thickness, required precision, design complexity, and material heat sensitivity determine the choice of cutting technique. Each method has its own advantages and limitations, so it is crucial to take these factors into account when selecting the appropriate method for cutting steel sheets.
- Q: What is the average price of a steel sheet?
- The average price of a steel sheet can vary depending on various factors such as size, thickness, quality, and market conditions. Therefore, it is difficult to provide an exact average price without specific details.
- Q: What is the difference between a galvanized and aluminized steel sheet?
- Galvanized steel and aluminized steel sheets are both widely used in various industries due to their durability and corrosion-resistant properties. However, there are distinct differences between the two. Galvanized steel sheets are coated with a layer of zinc to protect the underlying steel from rust and corrosion. This process, known as galvanization, involves immersing the steel sheet in a bath of molten zinc or applying a zinc-rich coating through electroplating. The zinc layer acts as a sacrificial barrier, meaning that it will corrode before the steel does, providing excellent protection against rust. Galvanized steel is commonly used in outdoor applications, such as roofing, fences, and automobile parts. On the other hand, aluminized steel sheets are coated with a layer of aluminum-silicon alloy. This process, known as aluminization, involves hot-dipping the steel sheet in a bath of molten aluminum or applying a thin layer of aluminum-silicon alloy through a continuous hot-dip process. The aluminum-silicon coating offers excellent heat resistance and corrosion resistance. Aluminized steel is commonly used in applications where high temperatures are present, such as automotive exhaust systems, heat exchangers, and ovens. In summary, the main difference between galvanized and aluminized steel sheets lies in the type of coating applied to the steel. Galvanized steel is coated with zinc, providing excellent rust protection, while aluminized steel is coated with an aluminum-silicon alloy, providing superior heat and corrosion resistance. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as the presence of high temperatures or the need for long-lasting rust protection.
- Q: How do steel sheets perform in terms of fire resistance?
- Steel sheets have excellent fire resistance properties. Due to their high melting point and low thermal conductivity, they can withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire. Additionally, steel sheets do not contribute to the fuel load of a fire, making them a reliable choice for fire-resistant structures.
- Q: How do steel sheets perform in cryogenic environments?
- In cryogenic environments, steel sheets prove to be highly effective. Cryogenic temperatures, which often fall below -150°C (-238°F), have the potential to render materials brittle and weaken their strength. Nevertheless, steel possesses remarkable toughness and can endure low temperatures without suffering significant deterioration. Due to their ability to uphold structural integrity and resist fracturing, steel sheets are frequently utilized in cryogenic applications. They exhibit commendable thermal conductivity, enabling efficient heat transfer from the surroundings and preventing the formation of cold spots that could compromise the material's strength. Furthermore, steel's low coefficient of thermal expansion diminishes the likelihood of dimensional alterations caused by extreme temperature fluctuations. This property is of vital importance in cryogenic environments where precision and stability are imperative. Moreover, steel exhibits resistance to embrittlement, a phenomenon that affects select materials when exposed to cryogenic temperatures for prolonged periods. Certain materials become more prone to fracturing due to the diffusion of hydrogen or other gases into their lattice structure. Conversely, steel displays a high resistance to embrittlement, rendering it a dependable choice for cryogenic applications. To sum up, steel sheets perform exceptionally well in cryogenic environments. They maintain their structural integrity, resist embrittlement, and minimize dimensional changes, making them a suitable material for various applications in industries such as aerospace, energy, and research.
- Q: How do steel sheets perform in terms of energy efficiency?
- Steel sheets have good energy efficiency properties due to their high thermal conductivity, which allows for efficient heat transfer. Additionally, steel sheets can be coated with insulating materials to further enhance their energy efficiency.
- Q: Are steel sheets suitable for roofing?
- Indeed, steel sheets make an ideal roofing material. Steel, being both sturdy and durable, can endure even the harshest weather conditions, including heavy rainfall, snow, and strong winds. Moreover, it boasts fire resistance, pest resistance, and rot resistance, making it a trustworthy option for long-lasting roofing solutions. In addition to these advantages, steel sheets are lightweight and simple to install, leading to reduced labor and installation expenses. Furthermore, they are available in a wide range of colors and finishes, enabling customization to suit the aesthetic of any structure. All in all, steel sheets offer exceptional protection and durability, which explains their popularity in roofing applications.
Send your message to us
GALVANIZED CORRUGATION STEEL SHEET
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords