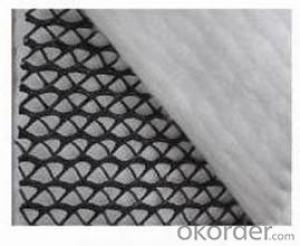
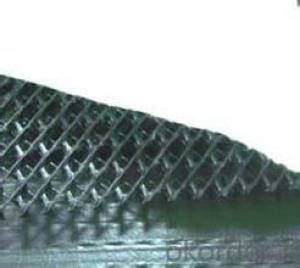
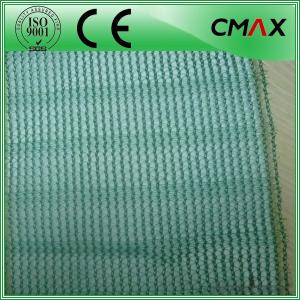
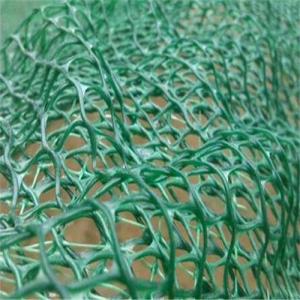
Geocomposite Drainage Net
Geocomposite Drainage Net Related Searches
Geogrid For Erosion Control Geogrid For Gravel Roads Geogrid For Gravel Driveway Geogrid For Roads Geogrid For Driveway Geogrid For Slopes Geogrid Machine Geocomposite Sheet Drain Best Geogrid Geocomposite Wall DrainHot Searches
Geocomposite Manufacturers Wholesale Liner Hdpe Geomembrane Wholesale Hdpe Geomembrana Hdpe Geomembrane Liner Manufacturers Hdpe Liner Cost Hdpe Pond Liner Specifications Geosynthetic Clay Liner Cost Landfill Liner Cost Geocomposite Manufacturers Geogrid Fabric For Sale Tensar Geogrid For Sale Geogrid For Sale Home Depot Geogrid Geogrid Home Depot Geogrid Fabric Near Me Geogrid Sizes Tensar Geogrid Distributors Tencate Geogrid Geogrid Near Me Geogrid Comparison ChartGeocomposite Drainage Net Supplier & Manufacturer from China
Okorder.com is a professional Geocomposite Drainage Net supplier & manufacturer, offers integrated one-stop services including real-time quoting and online cargo tracking. We are funded by CNBM Group, a Fortune 500 enterprise and the largest Geocomposite Drainage Net firm in China.Hot Products
FAQ
- No, earthwork products are not resistant to corrosion as they are typically made from materials such as soil, rocks, or concrete which can deteriorate over time due to environmental factors like moisture, air, and chemicals.
- Yes, sediment basins can be used for large-scale earthwork projects. Sediment basins are commonly used in construction projects to capture and control sediment runoff from disturbed areas. By collecting and retaining sediment-laden runoff, these basins help prevent sediment from being carried into nearby water bodies, thereby reducing environmental impacts. For large-scale earthwork projects that involve extensive soil excavation and grading, sediment basins can be strategically installed at key locations to effectively manage and control sediment runoff.
- There are several benefits of using earthwork products. Firstly, these products are highly durable and can withstand heavy loads, making them ideal for construction projects. Secondly, earthwork products are cost-effective as they can be sourced locally, reducing transportation costs. Additionally, these products are environmentally friendly as they are made from natural materials, minimizing their carbon footprint. Moreover, earthwork products are versatile and can be used for various applications such as erosion control, landscaping, and drainage systems. Overall, using earthwork products provides a sustainable and efficient solution for various construction and landscaping needs.
- Earthwork products, such as soil, rocks, and gravel, are generally resistant to weathering to some extent. However, their resistance may vary depending on the specific type of material and the prevailing weather conditions. While some earthwork products may be more durable and less prone to weathering, others may be more susceptible to erosion, degradation, or disintegration over time due to exposure to wind, rain, temperature changes, and other environmental factors. Therefore, it is important to consider the specific characteristics and composition of the earthwork product in question when assessing its resistance to weathering.
- What are the classification of civil engineering graduate students?
- Major professional basic courses and specialized courses / structural engineering, engineering mechanics and water conservancy projects
- There are various design options available for earthwork products, including different shapes, sizes, and materials. Some common design options include retaining walls, slope stabilization systems, drainage systems, erosion control products, and geosynthetic materials. These options can be customized to suit specific project requirements, ensuring efficient and effective earthwork solutions.
- Yes, earthwork products can be used in flood control projects. These products, such as engineered soil, geotextiles, and geogrids, can be utilized to build levees, embankments, and other structures that help mitigate and control flooding. These materials provide strength, stability, and erosion control, making them essential components in flood control measures.
- The load-bearing capacities of earthwork products vary depending on factors such as material type, compaction density, and design specifications. It is essential to consult engineering professionals or refer to product specifications to determine the specific load-bearing capacity of each earthwork product.