Structural Steel Angles
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications of Structural Steel Angles
1.Standards:GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS
2.Length:6m,9m,12m
3.Material:GBQ235B,Q345BorEquivalent;ASTMA36;EN10025,S235JR,S355JR;JISG3192,SS400;SS540.
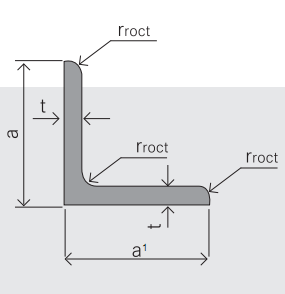 .
.
4.Sizes:
EQUAL ANGLES SIZES |
| ||
a(mm) | a1(mm) | thickness(mm) | length |
25 | 25 | 2.5---3.0 | 6M/12M |
30 | 30 | 2.5---4.0 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 2.5 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 3.0---5.0 | 6M/12M |
40 | 40 | 3.0---6.0 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3.7---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
60 | 60 | 5.0---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
63 | 63 | 6.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
65 | 65 | 5.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
70 | 70 | 6.0---7.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
75 | 75 | 5.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
80 | 80 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
90 | 90 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
100 | 100 | 6.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
120 | 120 | 8.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
125 | 125 | 8.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
130 | 130 | 9.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
140 | 140 | 10.0-16.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
150 | 150 | 10---15 | 6M/9M/12M |
160 | 160 | 10---16 | 6M/9M/12M |
180 | 180 | 12---18 | 6M/9M/12M |
200 | 200 | 14---20 | 6M/9M/12M |
5. Material details:
Alloy No | Grade | Element (%) | |||||
C | Mn | S | P | Si | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Q235 | B | 0.12—0.20 | 0.3—0.7 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.3 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Alloy No | Grade | Yielding strength point( Mpa) | |||||
Thickness (mm) | |||||||
≤16 | >16--40 | >40--60 | >60--100 | ||||
≥ | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Q235 | B | 235 | 225 | 215 | 205 | ||
Alloy No | Grade | Tensile strength (Mpa) | Elongation after fracture (%) | ||||
Thickness (mm) | |||||||
| ≤16 | >16--40 | >40--60 | >60--100 | |||
≥ | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Q235 | B | 375--500 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | |
Usage & Applications of Structural Steel Angles
Trusses;
Transmission towers;
Telecommunication towers;
Bracing for general structures;
Stiffeners in structural use.

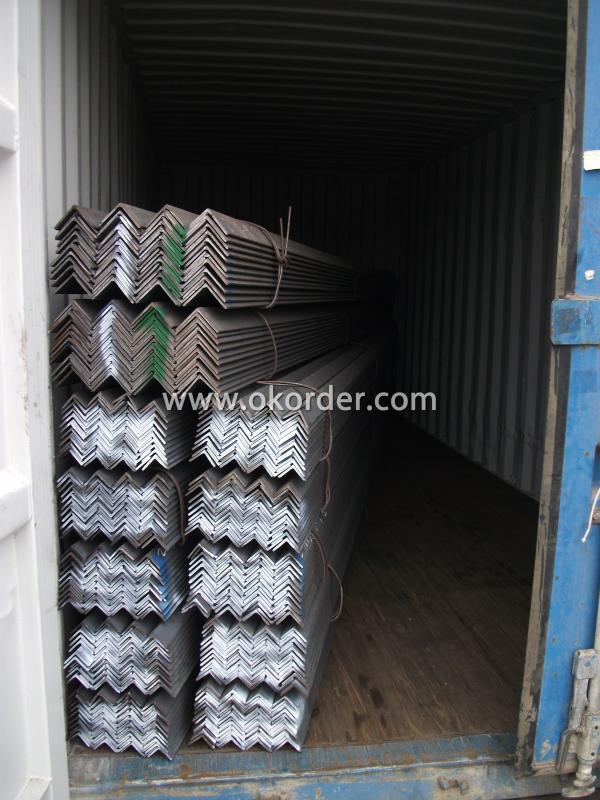
Packaging & Delivery of Structural Steel Angles
1. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
2. With bundles and load in 20 feet/40 feet container, or by bulk cargo, also we could do as customer's request.
3. Marks:
Color mark: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: There will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.

- Q: What are the factors to consider when choosing the appropriate steel angle size?
- When choosing the appropriate steel angle size, several factors need to be considered. These include the required load-bearing capacity, the structural design and stability requirements, the dimensions and shape of the application, the material strength and durability needed, and any specific industry standards or codes that govern the intended usage. Additionally, factors like cost, availability, and ease of installation may also influence the selection of the steel angle size.
- Q: What are the different methods of corrosion protection for steel angles?
- There are several methods of corrosion protection for steel angles, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. 1. Coatings: One of the most common methods is applying protective coatings on the steel angles. This can include paint, epoxy, or galvanization. Paint acts as a barrier between the steel and the environment, preventing moisture and oxygen from reaching the metal surface. Epoxy coatings provide a thicker and more durable layer, offering enhanced protection against corrosion. Galvanization involves applying a layer of zinc to the steel surface, which acts as a sacrificial barrier, corroding before the steel does. 2. Cathodic Protection: This method involves the use of an external electrical current to protect the steel angles. By connecting the steel to a more easily corroded metal, such as zinc or magnesium, and applying a direct current, the less noble metal corrodes instead of the steel. This method is particularly useful in marine or underground environments. 3. Alloying: Another way to protect steel angles from corrosion is through alloying. By adding small amounts of other metals, such as chromium or nickel, to the steel composition, the resulting alloy forms a protective oxide layer on the surface, which prevents further corrosion. Stainless steel is a common example of an alloy that offers excellent corrosion resistance. 4. Barrier Films: Applying a barrier film to the steel surface is another method to protect against corrosion. This involves applying a protective film, such as polyethylene or PVC, to create a physical barrier that prevents moisture and oxygen from reaching the steel. This method is commonly used in applications where the steel angles are exposed to harsh environments or chemicals. 5. Environmental Control: Controlling the environment in which the steel angles are placed can also help prevent corrosion. This includes minimizing exposure to moisture, humidity, and corrosive chemicals. Proper ventilation, regular cleaning, and maintaining a dry environment can all contribute to corrosion prevention. It is important to note that the best method of corrosion protection for steel angles depends on various factors, including the specific application, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. It is recommended to consult with corrosion experts or engineers to determine the most suitable method for a particular scenario.
- Q: What is the difference between equal and unequal steel angles?
- Equal and unequal steel angles are structural steel components that are commonly used in construction and industrial applications. The main difference between these two types of angles lies in their dimensions and properties. Equal steel angles, also known as L-shaped angles, have equal sides and equal angles between them. They are typically used to provide support and stability in various structures, such as buildings, bridges, and machinery. The equal sides of these angles allow for symmetrical distribution of load and provide balanced strength in all directions. This makes them ideal for applications where equal support is required on both sides. On the other hand, unequal steel angles have different side lengths and different angles between them. These angles are used when there is a need for uneven load distribution or when a specific angle is required for a particular application. The longer side of the angle is typically used for load-bearing purposes, while the shorter side may be used for additional support or as a connection point. Unequal angles are commonly used in the construction of frames, brackets, and supports where unequal load distribution is expected. In terms of properties, both equal and unequal steel angles are made from carbon steel, which provides good strength and durability. These angles are typically hot-rolled or cold-formed, depending on the manufacturing process. Hot-rolled angles are produced at high temperatures, resulting in a rough surface finish but improved mechanical properties. Cold-formed angles, on the other hand, are made by bending and shaping the steel at room temperature, resulting in a smoother surface finish but slightly lower mechanical properties. In summary, the main difference between equal and unequal steel angles lies in their dimensions and load distribution capabilities. Equal angles have equal sides and are used for symmetrical load distribution, while unequal angles have different side lengths and are used for uneven load distribution or specific angle requirements. Both types of angles are made from carbon steel and are commonly used in construction and industrial applications.
- Q: How do you determine the required length of a steel angle for a specific application?
- To determine the required length of a steel angle for a specific application, several factors need to be considered. 1. Load requirements: Begin by calculating the maximum load that the angle will need to bear. This includes both the weight of the object or structure it will support, as well as any additional live loads such as wind or snow. This load requirement will help determine the necessary strength and size of the angle. 2. Structural analysis: Perform a structural analysis of the intended application to determine the forces and stresses that will be placed on the steel angle. This analysis will help determine the required properties of the angle, such as its moment of inertia, section modulus, and bending capacity. 3. Material selection: Choose the appropriate steel material for the application based on its mechanical properties, such as yield strength, tensile strength, and ductility. Different grades of steel offer different levels of strength and durability, so selecting the right material is crucial for ensuring the angle can withstand the required loads. 4. Design codes and standards: Refer to applicable design codes and standards, such as those set by organizations like the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) or the Eurocode, to ensure compliance with industry regulations and guidelines. These codes provide specific formulas and procedures for calculating the required length and size of the angle based on the load and structural analysis. 5. Fabrication considerations: Consider any fabrication limitations or constraints that may affect the length of the steel angle. For example, standard lengths of steel angles may be available, so it may be necessary to select a length that is readily available or can be easily obtained through custom fabrication. 6. Consultation with professionals: If you are unsure about any aspect of determining the required length of a steel angle, it is advisable to consult with a structural engineer or a professional experienced in steel design. They can provide expert guidance and ensure that the angle is appropriately sized and designed for the specific application. By taking into account these factors and following a systematic approach, you can determine the required length of a steel angle that meets the specific requirements of your application.
- Q: Angle iron specifications 125 * 80 * 101 m multiple
- The angle iron can be made up of different force components according to the different structure, and can also be used as the connecting piece between the components. Widely used in a variety of architectural and engineering structures, such as beams, bridges, towers, hoisting and conveying machinery, ships, industrial furnace, reaction tower, container frame, cable bracket, power piping, busbar support installation, and warehouse shelves.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in the construction of power plants?
- Yes, steel angles can be used in the construction of power plants. They provide structural support and stability, making them suitable for various applications such as framing, bracing, and supporting equipment and machinery in power plants.
- Q: How do you store steel angles?
- Steel angles can be stored by stacking them horizontally on a flat and stable surface, ensuring that they are separated by wooden blocks or dunnage to prevent any damage or deformation. It is advisable to keep them in a dry and well-ventilated area to prevent rust or corrosion. Additionally, storing them indoors or under a weatherproof covering can provide further protection against environmental elements.
- Q: Can steel angles be used for retaining walls?
- Steel angles are a viable option for retaining walls. In construction, steel angles are commonly employed for a variety of purposes, including supporting structures and constructing retaining walls. They offer stability and strength to the wall, making them suitable for retaining soil or other substances. Steel angles can serve as the primary structural element or be combined with materials like concrete or timber to create a durable and robust retaining wall. The specific factors to consider in the design and engineering process would be the wall's height, load requirements, soil conditions, and local building codes. However, when properly designed and installed, steel angles can prove to be an effective choice for retaining walls.
- Q: Are steel angles heat-treated?
- Steel angles are indeed capable of undergoing heat treatment. To modify the physical and mechanical properties of the steel, controlled heating and cooling processes are employed in heat treatment. This can yield various desirable attributes, such as enhanced strength, hardness, toughness, or improved machinability. When it comes to heat treating steel angles, commonly employed techniques include annealing, quenching, tempering, or normalizing. The selection of a specific heat treatment method is contingent upon the desired final properties and the intended application of the steel angles.
- Q: How many meters is one angle steel?
- According to the specification number, the selection range of the domestic angle iron is 3 - 9m, 4 - 12M, 4 - 19m, 6 - 19m four scopes. The length of Japanese steel angle is chosen from 6 to 15m.
Send your message to us
Structural Steel Angles
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords



























