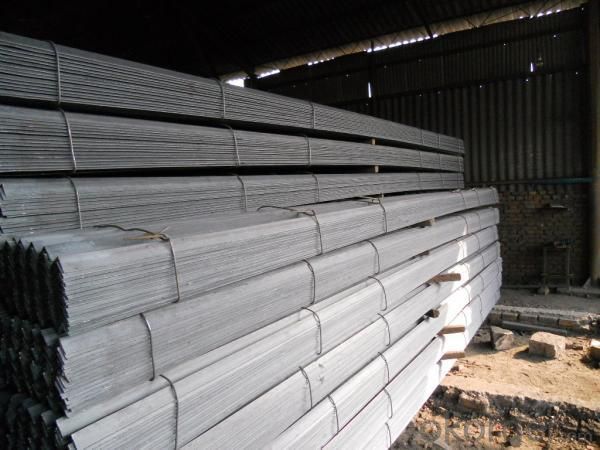
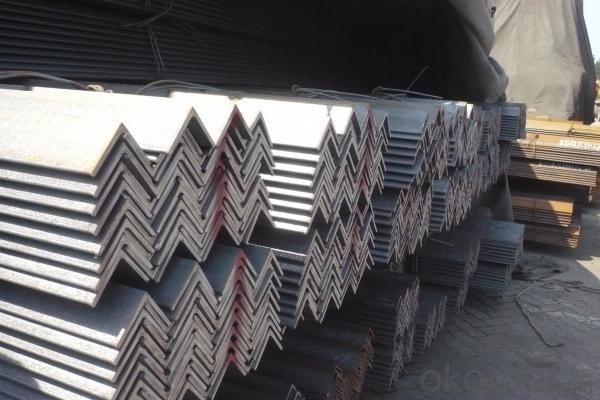
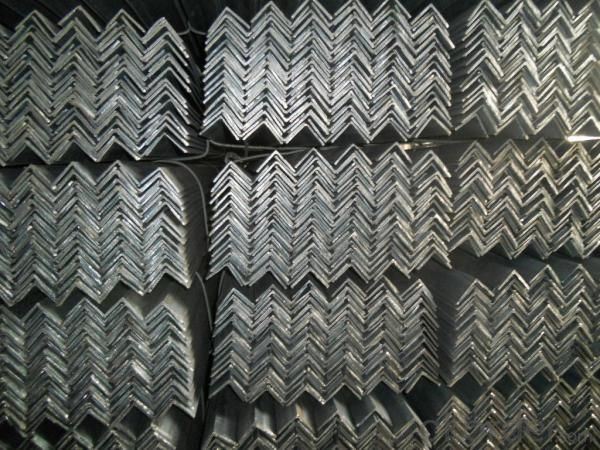
JIS SS400 Angle Steel
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25mts m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 80000-100000MTS/YEAR m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications of JIS SS400 Angle Steel
1.Standards:GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS
2.Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
3.Material: JIS G3192,SS400;SS540.
4. Payment terms:
1).100% irrevocable L/C at sight.
2).30% T/T prepaid and the balance against the copy of B/L.
3).30% T/T prepaid and the balance against L/C
5.Sizes:
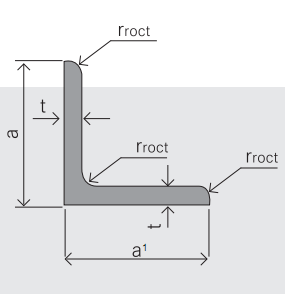
EQUAL ANGLES SIZES |
| ||
a(mm) | a1(mm) | thickness(mm) | length |
25 | 25 | 2.5---3.0 | 6M/12M |
30 | 30 | 2.5---4.0 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 2.5 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 3.0---5.0 | 6M/12M |
40 | 40 | 3.0---6.0 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3.7---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
60 | 60 | 5.0---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
63 | 63 | 6.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
65 | 65 | 5.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
70 | 70 | 6.0---7.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
75 | 75 | 5.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
80 | 80 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
90 | 90 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
100 | 100 | 6.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
120 | 120 | 8.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
125 | 125 | 8.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
130 | 130 | 9.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
140 | 140 | 10.0-16.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
150 | 150 | 10---15 | 6M/9M/12M |
160 | 160 | 10---16 | 6M/9M/12M |
180 | 180 | 12---18 | 6M/9M/12M |
200 | 200 | 14---20 | 6M/9M/12M |
5. Material Specifications:
Grade | Yield Strength,N/mm² | Extension Strength N/mm² | |||
Thickness of Steel,mm | |||||
≦16 | >16-≦40 | >40-≦100 | >100 | ||
SS330 | ≧205 | ≧195 | ≧175 | ≧165 | 330-430 |
SS400 | ≧245 | ≧235 | ≧215 | ≧205 | 400-510 |
SS490 | ≧285 | ≧275 | ≧255 | ≧245 | 490-610 |
SS540 | ≧400 | ≧390 | - | - | ≧540 |
Usage & Applications JIS SS400 Angle Steel
Trusses;
Transmission towers;
Telecommunication towers;
Bracing for general structures;
Stiffeners in structural use.
Packaging & Delivery of JIS SS400 Angle Steel
1. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
2. With bundles and load in 20 feet/40 feet container, or by bulk cargo, also we could do as customer's request.
3. Marks:
Color mark: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: There will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.
Production flow of JIS SS400 Angle Steel
Material prepare (billet) —heat up—rough rolling—precision rolling—cooling—packing—storage and transportation



- Q: How are steel angles priced?
- Steel angles are typically priced based on several factors. The first is the current market price of steel, which is influenced by factors such as supply and demand, global economic conditions, and fluctuations in raw material costs. Additionally, the size and dimensions of the steel angle can affect its price, with larger and thicker angles typically costing more. The grade and quality of the steel used in the angle also play a role in pricing. Higher-grade steel, such as stainless steel or alloy steel, tends to be more expensive due to its superior strength and corrosion resistance properties. Furthermore, the quantity of steel angles being purchased can impact the price. Bulk orders or larger quantities often qualify for volume discounts, which can reduce the overall cost per unit. Lastly, transportation and logistics costs can also be factored into the pricing of steel angles. Shipping distances, handling fees, and any additional services required for delivery can all contribute to the final price. Overall, the pricing of steel angles is determined by a combination of market conditions, size and dimensions, grade and quality, quantity ordered, and transportation costs. It is important to consider these factors when evaluating and comparing prices from different suppliers.
- Q: What are the different corrosion protection methods for steel angles?
- There are several corrosion protection methods for steel angles, including galvanization, powder coating, paint coating, and epoxy coating.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in electrical or telecommunications installations?
- Yes, steel angles can be used in electrical or telecommunications installations. Steel angles are commonly used in construction projects for their strength and durability. In electrical or telecommunications installations, steel angles can be used as support brackets for mounting equipment such as electrical panels, junction boxes, or communication cabinets. They provide a sturdy framework to secure and hold the equipment in place. Additionally, steel angles can be used to create cable trays and support structures for routing and organizing cables. The versatility and strength of steel angles make them a suitable choice for various applications in electrical and telecommunications installations.
- Q: What are the limitations of using steel angles?
- There are several limitations associated with the use of steel angles in various applications. Firstly, steel angles have a limited load-bearing capacity. The weight and pressure that can be safely supported by a steel angle are determined by its size, shape, and material composition. If the load exceeds the weight-bearing capacity of the angle, it can lead to structural failure or deformation. Secondly, steel angles are susceptible to corrosion. They are typically made of carbon steel, which can rust over time when exposed to moisture or corrosive environments. This corrosion weakens the structural integrity of the angle, reducing its lifespan and potentially compromising the overall stability of the structure it supports. Additionally, steel angles may have limitations in terms of their flexibility and versatility. Due to their fixed shape and size, they may not be suitable for applications that require intricate or complex designs. In such cases, alternative materials or fabrication methods may be more appropriate. Another limitation of steel angles is their limited resistance to fire. Steel, including steel angles, loses its strength and structural integrity at high temperatures. In the event of a fire, steel angles may not be able to withstand the heat and can deform or collapse, jeopardizing the safety of the structure and its occupants. Lastly, steel angles can be challenging to work with during installation or modification. Their rigid nature may require specialized tools, equipment, or expertise for cutting, drilling, or welding. This can add to the overall cost and time required for construction or renovation projects. Despite these limitations, steel angles remain widely used in various industries due to their affordability, durability, and versatility within their design limits. However, it is essential to consider these limitations and evaluate the specific requirements of each application to determine if steel angles are the most suitable choice.
- Q: What are the different methods for reinforcing steel angles?
- There are several methods for reinforcing steel angles, depending on the specific structural needs and design requirements. Some of the common methods include: 1. Welding: This is the most commonly used method for reinforcing steel angles. Welding involves joining two or more steel angles together using heat and pressure to create a strong and durable connection. It is important to ensure proper welding techniques and procedures are followed to maintain the integrity of the reinforcement. 2. Bolting: Another method for reinforcing steel angles is through the use of bolts. Bolts are inserted through holes in the angles and tightened to create a secure connection. This method is often used when the reinforcement needs to be adjustable or removable. 3. Riveting: Riveting is a traditional method for reinforcing steel angles. It involves inserting a pin or rivet through holes in the angles and securing it by deforming the end of the pin. This creates a strong and permanent connection between the angles. 4. Adhesive bonding: In some cases, adhesive bonding can be used to reinforce steel angles. This method involves applying a special adhesive to the surfaces of the angles and then pressing them together. The adhesive hardens and forms a strong bond between the angles. 5. Plate strengthening: When additional reinforcement is required, steel plates can be attached to the angles. These plates are typically welded or bolted to the angles to increase their strength and load-bearing capacity. 6. Reinforcing bars: Reinforcing bars, commonly known as rebar, can be used to reinforce steel angles. These bars are typically embedded into the concrete or masonry structure and extend into the angles to provide additional strength and support. It is important to consult with a structural engineer or design professional to determine the most appropriate method for reinforcing steel angles based on the specific project requirements and structural considerations.
- Q: What are the different standards and specifications for steel angles?
- There are several different standards and specifications for steel angles, which determine the physical and mechanical properties of the angles. Some of the most commonly used standards include: 1. ASTM A36/A36M: This is a standard specification for carbon structural steel, including angles. It specifies the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and other requirements for carbon steel angles. 2. ASTM A529/A529M: This specification covers high-strength carbon-manganese steel shapes, including angles. It outlines the composition, mechanical properties, and other specifications for these angles. 3. ASTM A572/A572M: This standard specification covers high-strength low-alloy columbium-vanadium structural steel shapes, including angles. It provides details on the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and other requirements for these angles. 4. ASTM A588/A588M: This specification covers high-strength low-alloy structural steel shapes, including angles, with improved atmospheric corrosion resistance. It specifies the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and other characteristics for these angles. 5. ASTM A709/A709M: This standard specification covers carbon and high-strength low-alloy structural steel shapes, including angles, for use in bridges. It provides information on the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and other specifications for these angles. 6. EN 10056: This European standard specifies the tolerances on shape, dimensions, and mass of hot-rolled structural steel equal and unequal angles. It also provides information on the mechanical properties and other requirements for these angles. 7. JIS G3192: This Japanese standard specifies the dimensions, mass, and permissible variations of hot-rolled steel sections, including angles. It outlines the mechanical properties and other specifications for these angles. These are just a few examples of the different standards and specifications for steel angles. It is important to consult the specific standard relevant to your project or application to ensure that the steel angles meet the required criteria.
- Q: What are the load-bearing capacities of steel angles?
- The load-bearing capacities of steel angles may differ due to various factors, such as the angle's size, thickness, and the type of steel used, as well as its specific application. Typically, steel angles are designed to offer structural support and can handle substantial loads. The load-bearing capacity of a steel angle is determined by its ability to withstand compression and tension forces, as well as its bending strength. These factors are influenced by the material properties of the steel, including its yield strength, tensile strength, and ductility. Steel angles find common usage in construction and engineering projects, where they are employed to support beams, frames, and structures. Engineers or designers usually specify the load-bearing capacity of a steel angle based on the project's specific requirements and the expected loads. Calculations and structural analysis, following engineering principles and standards, are typically carried out to determine the load-bearing capacity of a steel angle. These calculations take into account the angle's dimensions, support conditions, and the anticipated loads. To ensure that a steel angle's load-bearing capacity meets the necessary requirements for a given application, it is crucial to consult relevant engineering codes and standards provided by organizations such as the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) or British Standards Institution (BSI). In conclusion, the load-bearing capacities of steel angles can differ based on several factors. To accurately determine the load-bearing capacity of a specific steel angle for a given application, it is important to consult with a structural engineer or refer to appropriate engineering standards.
- Q: Can steel angles be used as supports for mechanical or HVAC ducts?
- Yes, steel angles can be used as supports for mechanical or HVAC ducts. Steel angles provide a strong and durable framework to securely hold and provide stability to the ductwork.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in the construction of railway bridges?
- Yes, steel angles can be used in the construction of railway bridges. They are often used as structural members to provide support and stability to the bridge structure. Steel angles offer strength, durability, and versatility, making them suitable for withstanding heavy loads and harsh environmental conditions typically encountered in railway bridge construction.
- Q: What is the typical length of a steel angle?
- The typical length of a steel angle can vary depending on the specific application or project requirements. However, standard lengths for steel angles often range from 10 to 20 feet.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Hebei, China |
| Year Established | 2003 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 500 Million |
| Main Markets | Southeast Asia; middle east; South Korea; Africa |
| Company Certifications | ISO 9001:2008 |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Tianjin |
| Export Percentage | 30%-45% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 11-20 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 10,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | 2 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM service offered |
| Product Price Range | high; average |
Send your message to us
JIS SS400 Angle Steel
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25mts m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 80000-100000MTS/YEAR m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






























