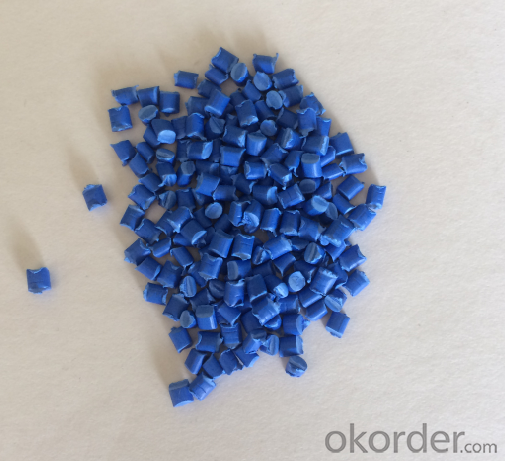
High Quality Standard Blowing masterbatch
- Loading Port:
- Ningbo
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 15000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications
Masterbatch is a solid or liquid additive for plastic used for coloring plastics.
Advantage:
1.This series color masterbatches are of high concentration pigment with bright colors.
2.When they are used in resins, it shows better dispersing and stablility performance.
3.Also the mixture has the highest mechanical intensity preservation rate.
4.A broad standard color range available from stock as well as tailor made products develop according to customer requirements.
Resin Suitability
1.Polyolefine : HDPE,LDPE,LLDPE,PP,EVA,TPE,PVC,etc.
2.Non-Polyolefine: PET, PBT, PC, PA, ABS,AS,PS,POM,etc.
Application Areas
1.Fiber ( Carpet, Textiles, Upholstery, etc.)
2.Film ( shopping bags, casting film, multilayer film, etc.)
3.Blow Molding ( Medical & Cosmetic container, Lubricant & Paint container, etc)
4.Extrusion Molding ( Sheet, Pipe, Wire & Cable, etc.)
5.Injection Molding ( Automotive, Electronic, Construction, House wares, Furniture, Toys, etc.)


- Q: (Explain what happens when a pigment molecule is struck by electromagnetic radiation in the visible light spectrum.)
- pigments are molecules that absorb electromagnetic radiation. For example, the chlorophyll pigment in plants absorbs blue and red light, which is why they reflect green light (since green is the color not absorbed). Another example is melanin, which is the pigment that darkens the skin of people. Melanin absorbs UV to protect the skin. A pigment molecule struck by EM radiation in the visible region may absorb some of the light depending on what pigment it is.
- Q: list 5 mineral pigments and 5 animals pigments and how its produced
- Mineral Pigments: Lazurite (Lapis Lazuli), Vivianite (Blue Ochre), Riebeckite, Glauconite, Malachite, Jarosite, Limonite, Hematite, Goethite, Celadonite and Shungite Animal Pigments: Tyrian Purple, made from the mucus of a Murex snail Carmine, made from an insect in central and south America, called Cochinilla Natural indigo, made from plants of the genera Indigofera Rose madder, a pigment derived from the plant Rubia tinctorum Gamboge, I think is a dark type of mustard (seeds) Alizarin occurs in the root of the common madder (Rubia tinctorum) and in various parts of Indian madder (Rubia cordifolia). And regarding how they are produced, well each one has it?s own methods. You may want to search each of those names and you can find information for each one. Hope this helps, Bella
- Q: Is gel food coloring a pigment or a dye?
- Dyes contain pigments, my friend. What is a pigment? They are like little beads. Very very tiny beads of the same color. Then if you spread these out, they give the thing a color. For example, the little green beads in leaves give it a green color. Pigment in our hair gives it a blonde/auburn/brown/black color. What is a dye? A dye is a liquid made up of water and pigments. The pigments are dissolved in water (well not really dissolve just that you cant see the beads) so that it's easier for us to use it. Everything that has a color is made up of pigments. So, gel food coloring is a thicker version of a dye that contains pigments.
- Q: I love the colours that pigments come in but I don't know how to use them. Is there any easy way?
- You can go to a store that sells makeup and ask them how to use it. They will even show you.
- Q: What does it mean when something is highly pigmented?
- PIGMENTED = A HIGH SATURATION OF COLOUR
- Q: Compare and contrast pigment color with the color seen from a light. What is the difference between mixing pigment colors and mixing light colors?
- Pigments are chemicals that selectively absorb and reflect different spectra of light. When a surface is painted with a pigment, light hitting the surface is reflected, minus some wavelengths. This subtraction of wavelengths produces the appearance of different colors. Most paints are a blend of several chemical pigments, intended to produce a reflection of a given color. Mixing pigments is subtractive. Mixing light is additive. Let's take the primary pigments, red, blue and yellow. Red pigment is red because the chemical it is made of absorbs (subtracts) blue and yellow light that falls on it and reflects only red light to your eye. Similarly, blue pigment is blue because it absorbs red and yellow light and reflects only blue. So when you mix the three primary pigments together, you produce something that absorbs all of the light falling on it in equal amounts and reflects nothing to your eye. Thus, it appears black. In contrast, when you mix only red and blue light, there isn't any yellow in it, so the resulting light appears purple (the complement of yellow). Likewise, if you mix red and yellow light it appears orange (the complement of blue). If you mix all three colors of light together (in equal amounts), the resulting light appears white because it contains all of the colors of the spectrum. This explanation is sound, although greatly simplified. The two summaries above are not my own, nor do I claim them as mine.
- Q: thinking about the main role of pigments in photosynthesis...? explain how the pigments in colored objects suc?
- photosynthetic pigment or antenna pigment is a pigment that is present in chloroplasts or photosynthetic bacteria and captures the light energy necessary for photosynthesis. Green plants have five closely-related photosynthetic pigments (in order of increasing polarity): Carotene - an orange pigment Xanthophyll - a yellow pigment Chlorophyll a - a blue-green pigment Chlorophyll b - a yellow-green pigment Phaeophytin a[1] - a gray-brown pigment Phaeophytin b[1] - a yellow-brown pigment Chlorophyll a is the most common of the six, present in every plant that performs photosynthesis. The reason that there are so many pigments is that each absorbs light more efficiently in a different part of the spectrum. Chlorophyll a absorbs well at a wavelength of about 400-450 nm and at 650-700 nm; chlorophyll b at 450-500 nm and at 600-650 nm. Xanthophyll absorbs well at 400-530 nm. However, none of the pigments absorbs well in the green-yellow region, which is responsible for the abundant green we see in nature.
- Q: what roles do pigments have in energy transfer?
- Pigments okorder /... When a photon of just the right amount of energy strikes an electron resonating in the pigment, the electron can absorb the photon and get promoted to a higher quantum level. The photon must have just the exact amount of energy to boost the electron from its current level to its new level or it cannot be absorbed. If the incoming photon is just right to promote an electron, in that pigment, the newly energized electron resonates along the bonds at the higher energy level where it can pass to the photosynthetic reaction center from the pigment array, to split water and take back an electron. Meanwhile the chlorophyll's electron passes to the electron transport chain to begin oxidative phophorylation.
- Q: Can somebody answer this in AP BIO language please
- A pigment molecule absorbs at specific wavelength(s), meaning that when light of a specific wavelength is incident to the molecule only certain wavelengths are absorbed while others are transmitted. The spectrophotometer emits monochromatic light (light of only one wavelength) which passes through the pigment molecule and a detector determines the amount of light that is either absorbed or transmitted by the sample. This is done at wavelengths from the UV (180-330 nm) to the visible (330-700 nm) and the light that is either transmitted or absorbed is detected by the spectrophotometer and is able to be graphed with absorbance representing the y-axis and wavelength representing the x-axis. The resultant graph will depict the absorption spectrum of that particular pigment molecule. Hope that helps.
- Q: We see pigments everywhere in products. They make a variety of things we see today. Where does it come from? Do they actually take a red rose pedal, grind the color and designate it as the color red?
- Pigments selectively reflect and absorb specific wavelengths in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum, which is roughly between 400 and 800 nm wavelength. When visible light is incident on a pigment parts of the spectrum are absorbed by certain chemical bonds that are found in conjugated systems or other components of the pigment, known as chromophores or colour centres. Other wavelengths or parts of the spectrum are reflected or scattered. Many pigments are charge-transfer complexes, such as transition metal compounds, but there are others that are organometallic compounds. These have wide light absorption bands that subtract most of the colours of the incident white light. The resulting reflected light spectrum creates the appearance of a colour. The difference between a pigment and a dye is that a pigment is insoluble in the substance that it is used to colour, therfore what you actually end up with is a suspension (e.g. blue pigment in polyethylene), whereas a dye soluble in a carrier so you end up with a solution of the dye, and the solvated dye molecules have an affinity to the surface of the substance that they are being used to colour (fabric dye molecules adsorb to the surfaces of the fibres that make up the fabric).
Send your message to us
High Quality Standard Blowing masterbatch
- Loading Port:
- Ningbo
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 15000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords