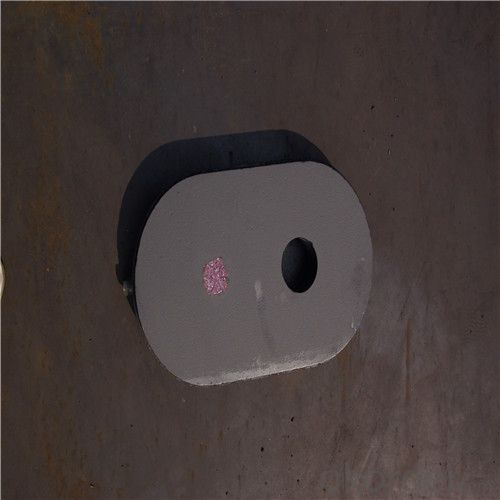
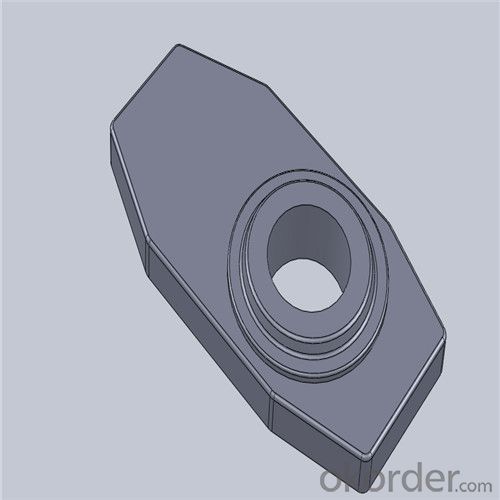
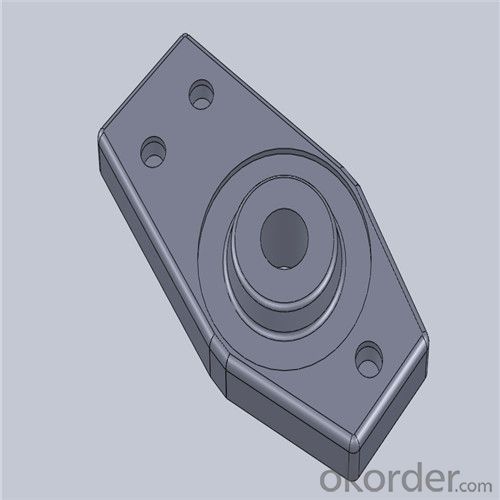
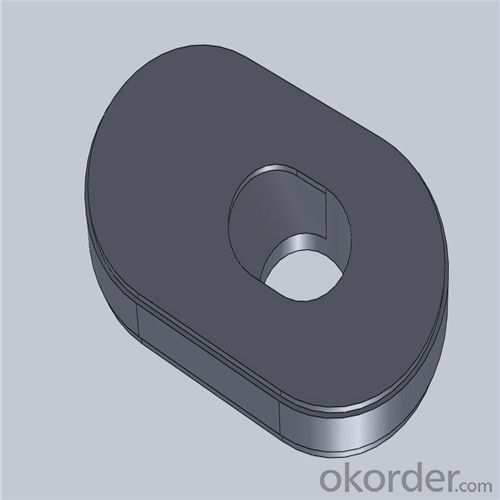
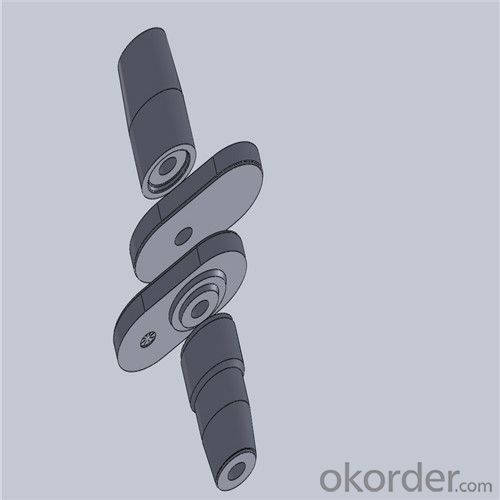
Monolithic Refractories High Performance & Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate Steel
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
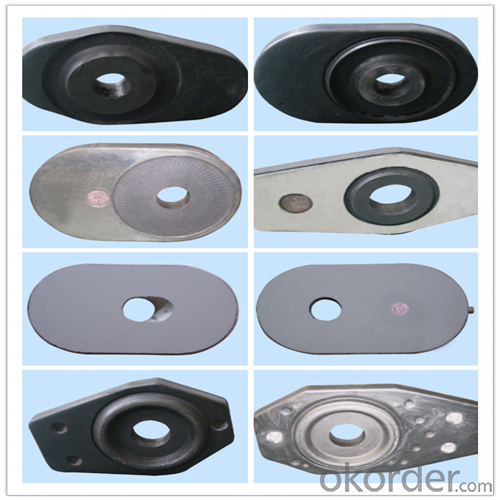
Quick Details for High Performance Refractory Ladle Slide Gate
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Shape: | Plate | Material: | Alumina Block |
| SiO2 Content (%): | N/A | Al2O3 Content (%): | 80-90% | MgO Content (%): | N/A |
| CaO Content (%): | N/A | Refractoriness (Degree): | 1770°< Refractoriness< 2000° | CrO Content (%): | N/A |
| SiC Content (%): | N/A | Model Number: | CS80 | Brand Name: | |
| Product name: | High performance refractory ladle slide gate | Model No.: | cs80 | Brand name: | CMAX |
| Quality: | Al-C or Al-Zr-C | Service life: | 4-6 heats | Apparent porosity: | 7% Max |
| Bulk density:: | 3.1 MIN | C.C.S: | 120MPA | MOQ: | 100 pcs for trial |
| Delivery time: | 60 working days upon receipt of deposit |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Inner carton packing, outer wooden case suitable for long term sea shipping |
| Delivery Detail: | three months working days upon receipt of deposit |
Specifications
Surface flatness less than 0.05mm
High mechanical strength
Erosion resistance
Oxidation resistance
Thermal shock stability
General Chemical Analysis for refractory ladle slide gate :
slide gate plate widely including Alumina carbon and Alumina Zirconia Carbon slide gate plate, MgO and MgO-spinel slide gate plate,nonoxides bonding slide gate plateand unburned slide gate plate.
Alumina -Zirconia-Carbon material
| Al-Zr-C Material | |||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) |
| 85 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
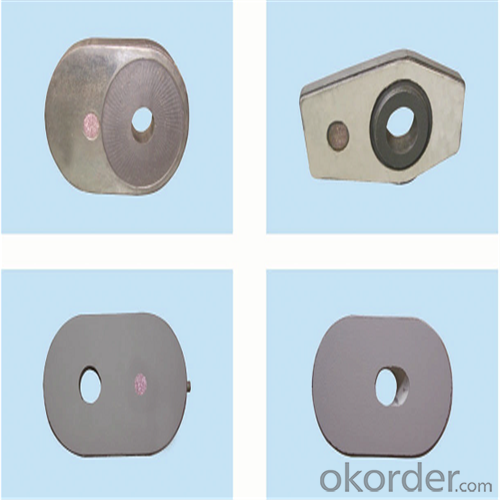
Composite type: Al-Zr-C for working line, outer Al-C material

| Al-Zr-C & Al-C Material | ||||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S | |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) | |
| Inner side (Working face) | 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| Outside | 90 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 3 | |


Other Products

About us


Sample is on your request.
Welcome to visit our factory~
- Q: How are monolithic refractories different from traditional brick refractories?
- Monolithic refractories differ from traditional brick refractories in terms of their composition and application method. While traditional brick refractories are made from individual bricks that are shaped and arranged to form a structure, monolithic refractories are a single, seamless material that is applied in a liquid or semi-liquid form and then cured or dried to form a solid mass. This allows monolithic refractories to be more versatile in terms of application, as they can be easily poured, sprayed, or troweled into complex shapes and installations. Additionally, monolithic refractories often offer better thermal insulation, higher resistance to thermal shock, and improved mechanical strength compared to traditional brick refractories.
- Q: What are the challenges in recycling monolithic refractories?
- One of the main challenges in recycling monolithic refractories is their composition. Monolithic refractories are typically made from a combination of different minerals, binders, and additives, which can make the separation and recovery of individual components difficult. Additionally, the high temperatures at which monolithic refractories are used can cause chemical reactions and physical changes that affect their recyclability. Furthermore, the presence of contaminants, such as metal oxides or impurities from the manufacturing process, can also pose challenges in the recycling process. Overall, developing efficient and cost-effective recycling methods for monolithic refractories requires addressing these challenges and finding innovative solutions.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories prevent slag penetration?
- Monolithic refractories prevent slag penetration by forming a dense and continuous protective layer on the surface of the refractory material. This layer acts as a barrier, preventing the molten slag from infiltrating and damaging the refractory.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the quality of iron and steel products?
- Enhancing the quality of iron and steel products is a crucial role played by monolithic refractories. These refractories consist of a single, solid structure that grants them high resistance against thermal and mechanical stresses. Their unique properties make them suitable for a range of high-temperature applications in the iron and steel industry. To start with, monolithic refractories excel in thermal insulation, maintaining a consistent temperature within furnaces and kilns. This temperature stability is vital for the proper heat treatment of iron and steel, ensuring ideal metallurgical properties and reducing the risk of defects. By preventing heat loss, monolithic refractories promote efficient energy utilization, resulting in cost savings and environmental benefits. In addition, monolithic refractories demonstrate remarkable endurance in the face of harsh operating conditions. The iron and steel manufacturing process involves extreme temperatures, aggressive chemical environments, and mechanical stresses. Monolithic refractories exhibit exceptional resistance to these conditions, ensuring durability and longevity. Their ability to resist thermal shock prevents cracking or spalling, which can lead to contamination and compromised product quality. Furthermore, monolithic refractories provide excellent corrosion resistance, shielding iron and steel products from chemical reactions with molten metal, slag, and other aggressive substances. This resistance not only preserves the integrity of the refractory lining but also prevents contamination of the metal, resulting in improved product quality. Monolithic refractories also offer flexibility in design and installation. They can be shaped, cast, or gunned into various complex geometries, allowing for customization based on the specific requirements of the iron and steel production process. This versatility ensures optimal lining performance, maximizing efficiency and product quality. In conclusion, monolithic refractories significantly contribute to the quality of iron and steel products. Their thermal insulation properties, resistance to harsh operating conditions, corrosion resistance, and design flexibility all play a vital role. By providing a reliable and durable lining in high-temperature applications, monolithic refractories help guarantee consistent and high-quality output in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: What are the specific requirements of monolithic refractories for ladle purging applications?
- The specific requirements of monolithic refractories for ladle purging applications include high thermal shock resistance, excellent erosion resistance, good slag resistance, and low porosity. Thermal shock resistance is crucial in ladle purging applications as the refractory material needs to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling. This is particularly important during ladle purging, where the ladle is exposed to high temperatures during molten metal pouring and then quickly cooled down during purging. Erosion resistance is another important requirement for monolithic refractories in ladle purging applications. The refractory material should be able to withstand the erosive action of molten metal streams and metalloids during purging. It should have a high resistance to chemical attack, preventing the material from deteriorating or eroding away. Slag resistance is also necessary for monolithic refractories used in ladle purging. The refractory material should have good resistance to the corrosive effects of slag, which can be present in ladles during purging. Slag can cause chemical reactions that can degrade the refractory material, leading to premature failure. Low porosity is an essential requirement for monolithic refractories in ladle purging applications. Low porosity ensures that the refractory material is impermeable to molten metal, preventing it from infiltrating the material and causing damage. This also helps to maintain the integrity and performance of the refractory lining during ladle purging. Overall, monolithic refractories for ladle purging applications need to exhibit high thermal shock resistance, excellent erosion resistance, good slag resistance, and low porosity to ensure the durability and longevity of the refractory lining in ladles during purging operations.
- Q: Can monolithic refractories be used for the lining of ladle refining furnaces and VOD converters?
- Yes, monolithic refractories can be used for the lining of ladle refining furnaces and VOD converters. Monolithic refractories are versatile and can be shaped and installed easily, making them suitable for lining various types of furnaces and converters, including ladle refining furnaces and VOD converters.
- Q: Can monolithic refractories be used for the lining of reheating furnaces and walking beam furnaces?
- Yes, monolithic refractories can be used for the lining of reheating furnaces and walking beam furnaces. Monolithic refractories are a type of refractory material that is characterized by its ability to be cast or gunned into place, rather than being made up of individual bricks or precast shapes. This makes them highly versatile and adaptable for various furnace applications, including reheating furnaces and walking beam furnaces. Reheating furnaces are used to heat metal products to a specific temperature before further processing, such as rolling or forging. The lining of these furnaces is subjected to high temperatures, thermal cycling, and mechanical stress. Monolithic refractories are well-suited for these conditions, as they have excellent thermal shock resistance and can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling. Walking beam furnaces are used in the steel industry for the continuous heating and transport of steel slabs or billets. These furnaces require a lining material that can withstand the abrasion and mechanical stress caused by the movement of the material. Monolithic refractories with high abrasion resistance and good mechanical strength are ideal for the lining of walking beam furnaces. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer other advantages such as easy installation, reduced downtime for repairs, and improved energy efficiency. They can be tailored to specific furnace designs and can be easily repaired or replaced when necessary. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are a suitable choice for the lining of reheating furnaces and walking beam furnaces due to their ability to withstand high temperatures, thermal cycling, mechanical stress, and abrasion. Their versatility, ease of installation, and repair make them a preferred option for these furnace applications.
- Q: What are the recommended installation techniques for monolithic refractories?
- The recommended installation techniques for monolithic refractories typically involve proper surface preparation, mixing of refractory materials, and precise application. It is crucial to clean and remove any loose debris from the substrate before installation. The refractory materials should be mixed thoroughly with the appropriate water content to achieve the desired consistency. It is recommended to use vibration or tamping techniques during application to remove air pockets and ensure proper compaction. Careful curing and drying processes should be followed to prevent thermal shock and achieve optimal performance.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the safety of iron and steel plants?
- The safety of iron and steel plants heavily relies on monolithic refractories. These refractories are specifically designed to withstand the harsh conditions commonly encountered in these industrial settings, including high temperatures, chemical attacks, and mechanical stresses. By using monolithic refractories, iron and steel plants can enjoy the following benefits: 1. Thermal resistance: Monolithic refractories excel in resisting extreme temperatures, preventing heat loss and ensuring the efficient operation of equipment and systems. This thermal insulation contributes to plant safety by reducing the risk of overheating, which can lead to equipment failure or catastrophic accidents. 2. Chemical resistance: Iron and steel plants involve the use of various chemicals, such as molten metal, slag, and corrosive gases. Monolithic refractories exhibit high resistance to these aggressive chemical environments, preventing corrosion, erosion, and material degradation. This resistance ensures the integrity of refractory linings, reducing the risk of leaks, spills, and contamination that could endanger workers and the environment. 3. Structural stability: Monolithic refractories provide excellent mechanical strength, offering stability to furnace linings, ladles, and other equipment. This stability is crucial for the safe operation of iron and steel plants, minimizing the risk of structural failure, collapse, or damage caused by mechanical stresses or heavy loads. 4. Quick repair and maintenance: Monolithic refractories offer easy installation and repair compared to traditional brick refractories. They can be poured, gunned, or rammed in place, allowing for swift repairs and maintenance. This rapid response to refractory failures or damages contributes to plant safety by minimizing downtime and preventing potential hazards associated with equipment malfunction. 5. Flexibility and adaptability: Monolithic refractories can be tailored to meet the specific needs of iron and steel plants. They can be customized in terms of composition, density, thermal conductivity, and other properties, ensuring optimal performance under varying operating conditions. This adaptability ensures that refractory linings are well-suited for the plant's processes, reducing the likelihood of accidents caused by inadequate refractory materials. In conclusion, monolithic refractories enhance the safety of iron and steel plants by providing thermal resistance, chemical resistance, structural stability, rapid repair capabilities, and flexibility. By utilizing these refractories, iron and steel plants can maintain a safe working environment, minimize the risk of accidents, and ensure the reliable operation of their equipment and systems.
- Q: What are the specific requirements of monolithic refractories for continuous casting applications?
- The specific requirements of monolithic refractories for continuous casting applications include high thermal shock resistance, excellent erosion resistance, good thermal conductivity, low shrinkage, and high refractoriness. These refractories must also have good flowability and workability to ensure easy installation and maintenance. Additionally, they should have a high degree of chemical stability to withstand the harsh conditions of molten metal and slag in continuous casting processes.
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories High Performance & Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate Steel
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords