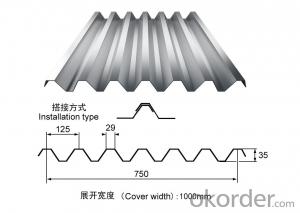
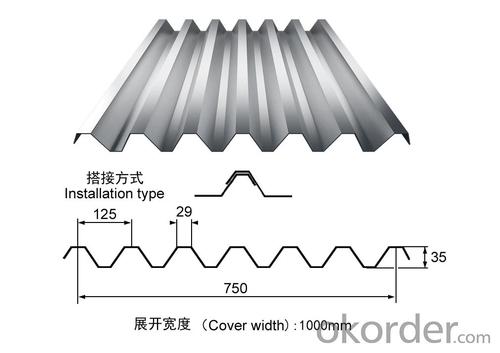
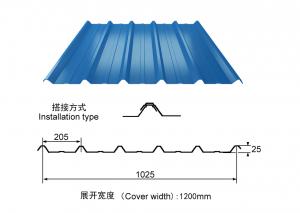
FDCORRIGATED SHEET
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
CORRIGATED SHEET 7210701000
Product Name:corrugated steel roofing sheet
Effective Width:650mm to 1250mm
Thickness:0.13mm-0.8mm
Material PPGI/PPGL steel coil
Coating:Z30-Z275,AZ30-AZ180
Color:white,blue or any RAL colors
length:1m-11.8m according to the container
top color coating:12um-25um
Back color coating:7um-10um
HRB:50-95
Base plate:PRE-PAINTED ALUZINC STEEL COIL,PRE-PAINTED GALVANIZED STEEL COIL
In continuous units in cold rolled steel strip, galvanized steel (electro galvanized and hot dip galvanized) as substrate, after surface pretreatment (degreasing and science processing), using the method of roll coating, coated with a layer or multi-layer liquid coating of plate, after baking and cooling income is the coating steel plate. Because the coating can have a variety of colors, on the habits of the coated steel sheet is called color coating steel plate. Because the coating is carried out before the sheet metal forming, in foreign countries which is called pre coating plate.
Color coated steel sheet is an organic coating coating on the steel surface, it has the advantages of beautiful appearance, bright color, high strength, good corrosion resistance, easy processing molding, but also allows the user to reduce costs, reduce pollution.
From the United States in 1935 to establish the first continuously coated steel line to begin, color coated steel plate has been widely applied, the current color coated plate varieties, about more than 600 kinds, the advantages of color coated sheet and organic polymer and steel plate of the two, which has good colorability, organic polymer molding, corrosion resistance and decorative, and steel plate with high strength and easy processing, can easily be punching cutting, bending, deep drawing processing. Made this makes organic coated steel sheet products have excellent practical, decorative, workability, durability.
- Q: What are the different types of steel sheet finishes for marine applications?
- Marine applications commonly employ several different types of steel sheet finishes to enhance durability and corrosion resistance in the face of constant exposure to moisture, saltwater, and harsh weather conditions. 1. Hot-dip galvanized: Among the most frequently used finishes for marine applications is hot-dip galvanization. This process involves coating the steel sheet with a layer of zinc, effectively safeguarding against corrosion. The zinc layer acts as a sacrificial barrier, preventing rust formation in the underlying steel. 2. Stainless steel: Highly resistant to corrosion, stainless steel sheets find widespread use in marine applications. These sheets are composed of a steel, chromium, and nickel alloy, providing exceptional strength and corrosion resistance. Different grades of stainless steel sheets are available, with 316 stainless steel being the most commonly utilized in marine environments. 3. Powder coating: Powder coating is a favored finish for steel sheets in marine applications. The process involves electrostatically applying a layer of powdered polymer to the steel sheet, which is then cured under heat to form a robust and durable coating. Powder coating offers good corrosion resistance and can be tailored in terms of color and texture. 4. Epoxy coating: To ensure superior protection against corrosion in marine environments, steel sheets are frequently treated with epoxy coatings. These coatings boast chemical resistance and excellent adhesion to the steel surface. Epoxy coatings are also renowned for their high impact and abrasion resistance. 5. Organic coating: Organic coatings, such as polyurethane or acrylic coatings, are employed to shield steel sheets in marine applications. These coatings create a protective barrier against corrosion and are commonly utilized in offshore structures, ships, and other marine equipment. It is important to consider various factors, including specific environmental conditions, budget, and desired aesthetics, when selecting a steel sheet finish for marine applications. Consulting with a professional or referring to industry standards and recommendations can aid in determining the most suitable finish for a particular marine application.
- Q: How do steel sheets perform in cryogenic environments?
- Steel sheets perform well in cryogenic environments. Cryogenic temperatures, typically below -150°C (-238°F), can cause materials to become brittle and lose their strength. However, steel is known for its excellent toughness and can withstand low temperatures without significant degradation. Steel sheets are commonly used in cryogenic applications due to their ability to maintain structural integrity and resist fracture. They exhibit good thermal conductivity, which allows them to effectively transfer heat from the environment and prevent cold spots that could compromise the material's strength. Furthermore, steel's low coefficient of thermal expansion minimizes the risk of dimensional changes caused by extreme temperature variations. This property is crucial in cryogenic environments where precision and stability are required. Additionally, steel resists embrittlement, a phenomenon that affects certain materials when exposed to cryogenic temperatures for extended periods. Some materials become more susceptible to fracture due to the diffusion of hydrogen or other gases into their lattice structure. Steel, however, has a high resistance to embrittlement, making it a reliable choice for cryogenic applications. In summary, steel sheets perform admirably in cryogenic environments. They maintain their structural integrity, resist embrittlement, and minimize dimensional changes, making them a suitable material for various applications in industries such as aerospace, energy, and research.
- Q: What are the different edge finishes available for steel sheets?
- There are several different edge finishes available for steel sheets, depending on the desired aesthetic and functional requirements. Some of the most common edge finishes for steel sheets include: 1. Mill Edge: This is the standard edge finish that comes directly from the steel mill. It is a rough, unfinished edge that has not been further processed or smoothed. It is typically used for applications where the edge appearance is not critical, such as in industrial or structural applications. 2. Trimmed Edge: In this edge finish, the rough mill edge is trimmed or sheared to remove any irregularities or burrs. It provides a cleaner and more uniform edge compared to the mill edge, making it suitable for applications where the edge appearance is important. 3. Deburred Edge: This edge finish involves removing any sharp or jagged edges through a deburring process. It provides a smooth and rounded edge, enhancing safety and reducing the risk of injury. Deburred edges are commonly used in applications where handling or contact with the edge is frequent, such as in automotive or appliance manufacturing. 4. Beveled Edge: A beveled edge is achieved by cutting or grinding an angle along the edge of the steel sheet. It creates a sloping or chamfered edge, which can improve the aesthetics and functionality of the sheet. Beveled edges are often used in architectural applications, as they can enhance the appearance and facilitate better jointing or welding. 5. Rolled Edge: This edge finish is created by rolling or bending the edge of the steel sheet to form a rounded or folded edge. Rolled edges provide a smooth and finished appearance, making them suitable for applications where the edge will be visible, such as in decorative or furniture manufacturing. 6. Hemmed Edge: Hemming involves folding the edge of the steel sheet over itself to create a double-layered edge. It provides a strong and finished edge that is resistant to fraying or unraveling. Hemmed edges are commonly used in applications where the edge will be exposed and require added durability, such as in roofing or sign manufacturing. These are just a few examples of the different edge finishes available for steel sheets. Each finish has its own unique characteristics and advantages, allowing for customization based on specific requirements and preferences.
- Q: What is the typical weight of steel sheets?
- The typical weight of steel sheets varies depending on their size, thickness, and type of steel being used. Generally, steel sheets can range in weight from a few pounds to several tons. For example, a standard 4x8 foot steel sheet with a thickness of 1/4 inch can weigh around 110 pounds, while a larger 10x10 foot sheet with a thickness of 1 inch can weigh over 1,000 pounds. It is important to note that these are just general estimates, and the weight can vary based on specific factors such as the alloy composition or any additional coatings applied to the steel sheets.
- Q: Are steel sheets suitable for outdoor furniture?
- Yes, steel sheets are suitable for outdoor furniture. Steel is known for its durability, strength, and resistance to weather and corrosion, making it an ideal material for outdoor use. Additionally, steel sheets can be easily shaped and welded to create various designs, making them versatile for different styles of outdoor furniture.
- Q: How do you determine the quality of steel sheets?
- One way to determine the quality of steel sheets is by examining their composition and properties. This can be done through various tests such as chemical analysis, mechanical testing, and visual inspection. Additionally, factors like the manufacturing process, certifications, and standards met by the steel manufacturer can also provide insights into the quality of the steel sheets.
- Q: How are steel sheets protected during welding?
- Shielding plays a crucial role in safeguarding steel sheets during welding. Its purpose is to shield the sheets from oxygen and other atmospheric contaminants that can lead to oxidation and impurities in the weld. Multiple methods are utilized to shield the steel sheets during welding. One commonly employed approach involves using a shielding gas, such as argon or carbon dioxide, which is directed towards the welding area to establish a protective atmosphere. This gas displaces the surrounding oxygen, effectively preventing it from reacting with the heated metal and causing oxidation. In addition to the use of shielding gas, another widely used method involves employing flux. Prior to welding, a substance known as flux is applied to the joint area of the steel sheets. Acting as a protective barrier, the flux creates a molten slag that covers the weld and provides shielding from the atmosphere. Flux can take the form of a powder, paste, or even a continuous wire feed during welding. Furthermore, certain welding techniques, like submerged arc welding, combine the use of both shielding gas and flux to offer optimal protection for the steel sheets. This technique involves the continuous feeding of granular flux along with the welding wire. As the flux melts, it forms a protective layer over the weld, while the shielding gas effectively prevents any atmospheric contamination. Overall, the safeguarding of steel sheets during welding is crucial for ensuring the weld's quality and integrity. Shielding methods, such as the use of shielding gas and flux, establish a protective environment that prevents the formation of oxidation, impurities, and other defects in the weld. Consequently, this results in a robust and long-lasting joint between the steel sheets.
- Q: Are the steel sheets suitable for electrical applications?
- Yes, steel sheets are suitable for electrical applications as they have good conductivity and can be easily shaped into desired forms for various electrical components.
- Q: How do steel sheets handle electromagnetic interference?
- Steel sheets can act as a shield against electromagnetic interference due to their high electrical conductivity and magnetic properties. They can effectively block or attenuate electromagnetic waves, reducing the impact of interference on electronic devices or systems.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for mezzanine flooring?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for mezzanine flooring. Steel sheets are commonly used for mezzanine flooring due to their durability, strength, and ability to support heavy loads. They provide a stable and safe platform for various applications in industrial and commercial settings.
Send your message to us
FDCORRIGATED SHEET
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords