0.6/1kV XLPE Insulation Flame Retardant Power Cables
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
1. Application
This product is apply to AC rated voltage 0.6/1kV circuit, for the use of power transmission and distribution,suitable for the situation which requires flame retardant.
2、Type and Specification
Voltage Class | 0.6/1 kV |
Type | Z-YJV62、Z-YJLV62、Z-YJV63、Z-YJLV63、 Z-YJV72 Z-YJLV72、Z-YJV73、Z-YJLV73、 Z-YJV72、Z-YJLV72 Z-YJV73、Z-YJLV73、Z-YJV、Z-YJLV、Z-YJV22、Z-YJLV22 Z-YJV32、Z-YJLV32、Z-YJV42、Z-YJLV42 |
Size Range(mm2)
1 core:1.5~1000;
2、3、4 cores:1.5~500;
5、3+1、3+2、4+1 cores:4~500;
Executive Standard
GB/T 19666-2005、GB/T 12706-2008
3. Operational Performance
a. Cable conductor allowed long-term working temperature not exceeding 90 ℃.
When short circuit happened (the duration no longer than 5 seconds), the maximum temperature of cable conductor is not exceeding 250℃.
b. When laying cable, the ambient temperature should not be lower than 0℃,if not the cable need to be preheated. The bending radius of three cores unarmored cable should not be less than 15 times of outer diameter of cable, 12 times for armored cable. The bending radius of single core unarmored cable should not be less than 20 times of outer diameter of the cable, 15 times for armored cable.
c. Cable DC resistance should comply with GB/T3956-1997.
d. The laying of cable is not limited by the level drops.
e. Power frequency voltage withstanding test: U0 under 3.6kV,2.5 U0+2kV/5min no breakdown.
f. Partial discharge test: discharge capacity under 1.73U0 isnot more than 10pC.
e. Flame retardant characteristics:
Flame retardant cable should withstand group burning test specified in GB/T18380.3-2001.
4、Cable structure diagram
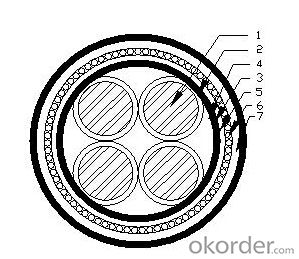
1-Conductor 2-Insulation 3-Taped covering 4-Filling
5-Innersheath 6-Armour 7-Outer sheath
- Q: Suppose load is 100KW, length 50m, how to calculate cable size. If we know current Is any easy mathod to calculate cable size.
- There are two issues to consider, cable heating and voltage drop. Of the two, voltage drop is by far the easiest. You need to determine what the allowable voltage drop in you cable is. The voltage drop is just I x R where I is the current and R is teh round trip cable resistance. The specification of 100 kW isn't enough. If its a high tension 100 kV line, the current is only 1 amp and a run of 16 AWG wire would deliver about 99,999 volts out of the original 100,000 volts to your load. If its a 100 volt system then a 4 AWG wire would only deliver only 20 volts to the load. The formula for wire resistance (in AWG) is that 10 AWG has 0.001 ohm/ft. Each increase of 1 in the gauge increases resistance by the cube root of 2 (about 25%). You calculate by picking what voltage drop you can live with, for the known current figure the resistance, knowing the length figure the resistance per foot, and then pick the AWG using the above. The second concern is wire heating. Although you could do the heat transfer calculations, instead look up the allowable ampacity for any wire in an electrical engineers or NEC handbook.
- Q: The power company are doing some work on our road. and are going to be moving the terminal thing on the side of our house (2nd floor side wall) where the electric comes to the house and feeds both ours and next door (semi-detached). We have seen some dwellings that have a long UPVC bright orange plastic pipe covering the cable for a few meters and wondered why they do this?
- It is to protect the cable and people and animals. It stops animals chewing and protects in case of hitting the cable.
- Q: lost my original 7A cable and the uk wire is 2.5A
- The PS3 Slim's power supply is rated at 250W which works out to be just under 2.5A @ 110v. Since the PS3 only draws around 100W it should be OK. If you were using an Older PS3 then it would require more power and would not be safe with a 2.5A cable. Since a new cable wouldn't cost much you should probably invest in a better one anyway.
- Q: I have my old 350 power supply cable but i got a new 520 one. do i have to use the defuly 520 power suppl cable? i use my old cabbke
- The cable merely supplies the power to the PSU. You're confusing the wattage of the PSU (350/520W) with the supply voltage (110/120/240v). The cable will work perfectly with either one?
- Q: Can A bad battery or power cable cause a laptop to Blue Screen?Is there anyway to pinpoint the actual cause?
- No its usually because of hard drive failure if your talking about THE BLUE SCREEN OF DEATH
- Q: What is the best tool or method in your opinion to locate cable damage causing current leak on several cables supplying outdoor lighting as detected by a tripping GFCI breaker. (Or water in a light obviously). Is there a meter that can measure that directly with the power off?
- I usually have one of my kids lick their finger and run it along the cable. a lightbulb in the mouth helps.
- Q: I just need the console. No controllers, power cables, AV cables, Ethernet cables, Hard Drive, and so on.I checked Google, but the only offers I can find are OKorder and RRoD'd 360s on OKorder. Do any retail stores sell just the console? Or will I have to trust nobody will send me a broken console?
- you only want the console weird, without a hardrive? Try a pawnshop a place where people go to give things that are missing or don't want anymore, a place where you could sell anything
- Q: My power cable says it is plug in but will not charge it. What is wrong?
- It could be your cable or power supply unit went bad. Or, your power socket on the main board went south. The good thing about laptops is that the power supply unit is external and easy to swap out.
- Q: A power cable of copper is stretched straight between two fixed towers. If the temperature decreases, the cable tends to contract; the amount of contraction for a free copper cable is 0.0017% per degree celsius. Show that the stretched cable will snap if its temperature decreases by 128°C.Ignore the weight of the cable and assume Hooke's law is obeyed until the cable breaks. Young's modulus for copper is 11.0 x 10^10 N/m^2 and the ultimate tensile strength of copper is 2.4 x 10^8 N/m^2.
- Change in length=(coefficient of expansion)(original length)(change T)= (.0017)(chose your favoret length, I chose 100)( -128 because T is decreeing)=-21.76 Strain = (change in length)/(original length)= 21.76/100= .2176Pa (for simplicity's sake I dropped the negative, rember the wire is in tension) Stress = (youngs modulus)(strain)= (11?10^10)(.2176)= 2.3936?10^10 Pa The UTS (2.4?10^8)<(2.39?10^10) so there is definitely necking and because of the difference most likely there was failure long ago.
- Q: I have a USB powered external hard drive. The cable that came with it has to plug-ins for the PC. I know the fat one provides power so I use that one. I would like to know what the other skinny one is for.I have seen other people plug both in when using it and it worked fine for them. I am using just the fat one and it works fine for me. I would just like to know the reason for having both on a cable.
- The Fat one is the Main one. If your computer is provide most power the HDD needed. That would be just fine. Just like on your case. The Skinny one is the Extended for getting extended power needed. Thus if some computer could not recognize your device, mostly caused by unable to get some power. You could plugged it both to get suitable power for your device.
Send your message to us
0.6/1kV XLPE Insulation Flame Retardant Power Cables
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
























