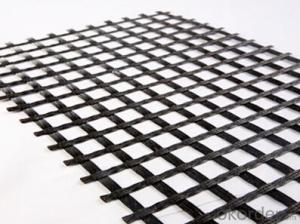
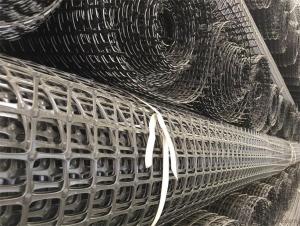
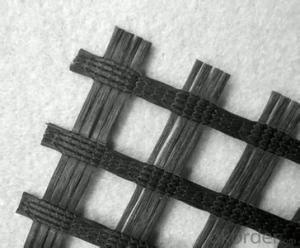
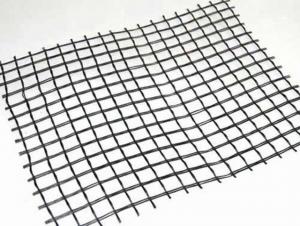
Tensar Interax Geogrid
Tensar Interax Geogrid Related Searches
Tensar Triax Geogrid Interax Geogrid Tenax Geogrid Tensar Triaxial Geogrid Tensar Uniaxial Geogrid Tensar Biaxial Geogrid Geogrid Tensar Tensar Ux Geogrid Tensar Structural Geogrid Tensar Triax Tx170 Geogrid Tensar Triax Tx7 Geogrid Triaxial Geogrid Tensar Tensar Triax Tx140 Geogrid Tensar Type 2 Geogrid Tensar Triax Tx130s Geogrid Tensar Triax Tx5 Geogrid Tensar Bx1100 Geogrid Tensar Triax Tx 140 Geogrid Tensar Bx1100 Biaxial Geogrid Triax Geogrid Tensar Triax 160 Geogrid Tensar Geogrid Calculator Tensar Triax Tx160 Geogrid Tensar Geogrid Reinforcement Tensar Bx1200 Biaxial Geogrid Tensar Bx 1200 Geogrid Tensar Geogrid Bx1100 Tensar Bx1200 Geogrid Tensar Tx140 Geogrid Tensar Tx7 GeogridTensar Interax Geogrid Supplier & Manufacturer from China
Tensar Interax Geogrid is a high-performance geosynthetic product designed to enhance the load-bearing capacity and stability of various civil engineering applications. It is engineered with a unique, bi-directional aperture structure that provides exceptional tensile strength and dimensional stability, making it ideal for applications such as road construction, slope reinforcement, and soil stabilization. The product is known for its durability and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions, ensuring long-lasting performance in a wide range of projects.The Tensar Interax Geogrid is widely used in civil engineering projects due to its ability to reinforce soil and improve load distribution. It is particularly effective in applications where increased stability and reduced settlement are required, such as in the construction of embankments, retaining walls, and foundations. Additionally, it can be used in coastal and riverbank protection projects to prevent erosion and maintain structural integrity. The versatility of the Tensar Interax Geogrid makes it a valuable asset in the field of geotechnical engineering, offering a cost-effective and efficient solution for a variety of challenges.
Okorder.com is a leading wholesale supplier of Tensar Interax Geogrid, offering a vast inventory to meet the needs of various projects and applications. As a reliable source for this high-quality geosynthetic product, Okorder.com ensures that customers have access to the materials they need to complete their projects successfully. With a commitment to providing exceptional customer service and support, Okorder.com stands out as a trusted supplier for Tensar Interax Geogrid and other geotechnical products.
Hot Products