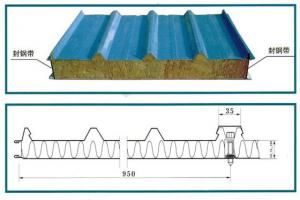
Section Steel Roll From China With High Quality
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 41000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Company Profile
CNBM International Corporation (CNBM International) is the most important trading platform of CNBM Group Corporation, a state-owned company under the direct supervision of State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council.
CNBM Group is integrated with four business segments: Manufacture, R&D,Sets of equipment and Logistics trading.Mill rolls are our main products.
CNBM International is highly recognized by its business partners and clients all over the world and has established good business relationship with the customers in over 120 countries and regions all over the world.
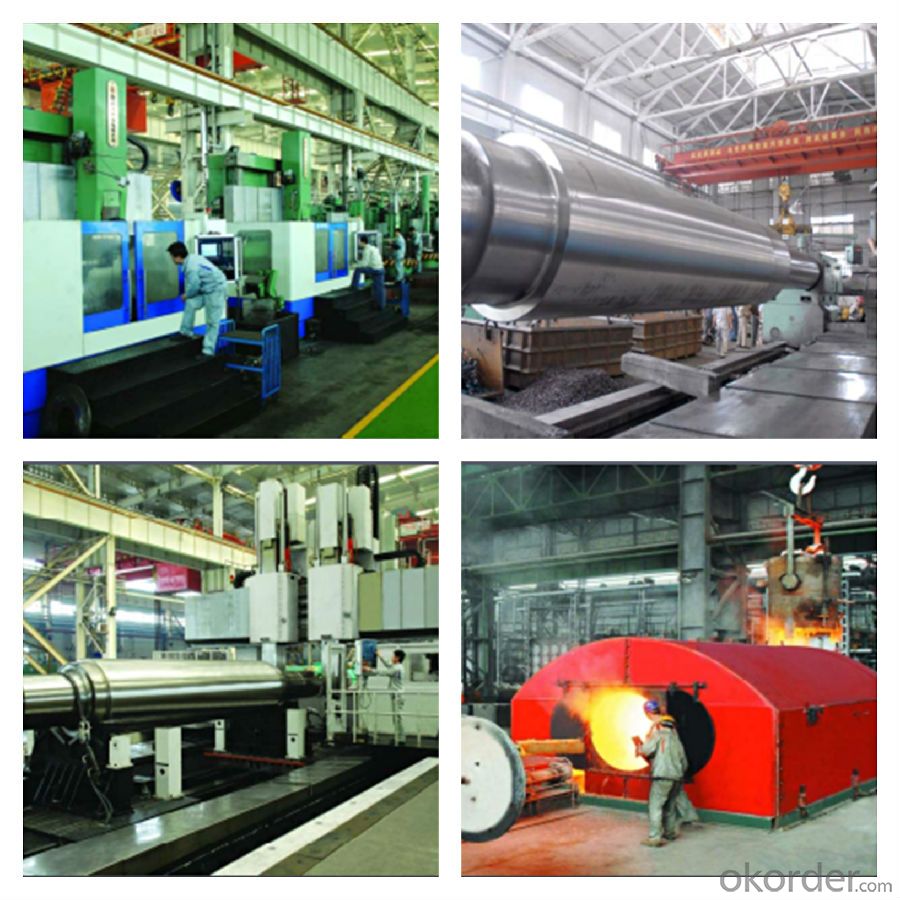
The product introduction of mill roll
Equipped with advanced technological facilities on melting, casting, forging, heat treating and mechanical machining, our factory has formed 9 professional complete roll manufacturing lines of cast steel, cast iron and forged steel rolls such as strip mill rolls, heavy section mill rolls, wire & bar rolls, special shaped rolls and small-sized cold rolls and specialized production lines of bloom and slab CCM, coke oven equipments and wind power products. Annual production capacity of mill rolls is 500,000 tons, metallurgical equipment is 80,000 tons.


Workshop
Workshop is the core of our company and undertakes all of scientific research work. The company specially produces and supplies all kinds of roll used for hot strip mill, cold strip mill, plate & heavy plate mill, large-sized section mill, universal mill etc.

Products & Specification
| Mill | Application | Material | Product Specification | ||
| Hot Strip Mill | Large-sized vertical roll | Special alloy cast roll, Adamite | All Sizes | ||
| Small-sized vertical roll | Adamite, HiCr iron | ||||
| Roughing work roll | Special alloy cast steel, Adamite, HiCr steel, Semi-HSS, HiCr iron | ||||
| Finish rolling | Early stand work roll | HiCr iron, HSS | |||
| Later stand work roll | ICDP, HSS | ||||
| Finishing back-up roll | Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000,W≤80t | |||
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000,W≤75t | ||||
| Temper rolling | Work roll | HiCr iron | All Sizes | ||
| Alloy forged steel | |||||
| Back-up roll | ICDP | ||||
| Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000, W≤80t | ||||
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000, W≤75t | ||||
| Mill | Application | Material | Product specification |
Cold strip mill & Single stand cold mill | Work roll | Alloy forged steel | All Sizes |
| Intermediate roll | Alloy forged steel | ||
| Temper roll | Alloy forged steel | ||
| Back-up roll | Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000,W≤80t | |
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000,W≤75t | ||
Largesized universal structural mill | Break-down roll | Special alloy cast steel, alloy nodular iron | All Sizes |
| Horizontal collar | High carbon adamite (duplex) | ||
| Vertical collar | High carbon adamite, HiCr iron | ||
| Edger roll Edger roll | High carbon adamite | ||
| Shaft | Alloy forged steel |
| Mill | Application | Marterial | Product Specification | |
| CSP | Vertical Roll | Adamite, Special alloy cast steel, HiCr iron | All Sizes | |
| Roughing work roll | Semi-HSS, HiCr Steel | |||
| Finish rolling | Early stand | HiCr iron, HSS | ||
| Later stand | ICDP, HSS | |||
| Roughing & Finishing back-up roll | Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000,W≤80t | ||
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000,W≤75t | |||
| Steckel Mill | Vertical roll | Adamite, Special alloy cast steel | All Sizes | |
| Roughing work roll | ICDP, HiCr iron | |||
| Finishing work roll | HiCr iron, ICDP | |||
| Back-up roll | Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000,W≤80t | ||
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000,W≤75t | |||
| Plate & Heavy plate mill | Rough rolling | 2-hi work roll | Special alloy cast steel, Tool steel | All Sizes |
| 4-hi work roll | HiCr iron, ICDP | |||
| Finishing work roll | HiCr iron, ICDP | |||
| Single stand work roll | HiCr iron, ICDP | |||
| Back-up roll | Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000,W≤80t | ||
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000,W≤75t | |||
Quality Control
The company has the most advanced experimental and testing equipments in global mill roll industry, including direct-reading spectrometer, spectrum analyzer , X-ray fluorescence analyzer, scanning electronic microscope, energy disperse spectroscopy, X-ray diffractometer, image analyzer, high/low temperature metallographic microscope, X-ray stress meter, brittleness temperature tester, thermal analogue machine, dilatometer, macro and micro hardness tester, OMNISCAM-1X automatic flaw detection, USN60 ultrasonic flaw detector, magnetic powder and non-destructive flaw detection etc,. The advanced inspection equipments and experimental methods provide guarantee for quality control and experiment on material, usability test and performance.
The factories of CNBM invested 2.3 billion RMB for large-scale
CNBM international Corporation has completed equipment and technology upgrade transformation, which was concentrated on three projects, production line of centrifugal casting rolls for hot strip and plate mill, forged roll for cold/hot strip mill, national class technology center and roll material lab. Through upgrade transformation, the following targets have been achideved:
(1)It becomes the world's biggest specialized mill roll maker with the largest production scale, the most complete specifications of products and the most extensive coverage of various rolls used on rolling mill.
(2) The technology of equipments has reached international leading level.
(3) "Mechanization, automation, intellectualization, digitization" of equipments obviously improve the quality control ability.
(4) New types of research instruments improve the R&D capacity of products.
Customers Visit

FAQ
Q:Are you a trading company or manufacturer?
A:CNBM is a large-scale central governmental industrial group with its own manufacturing sector, research and development sector, trading sector and logistics sector.
Q:I have some special requirement about specifications.
A:We have a well-rounded product range, which endows us with the capability of applying many special specifications. Please feel free to contact us with yours.
Q:Do you accept OEM service?
A:Yes, we do.
Q:What is your delivery time?
A:It depends on the size/complexity of your order and our own production schedule. Usually we provide a faster delivery than the industry's average.
Q:What is the payment term?
A:Our payment terms are negotiable.
Q:Can I have my own logo on the product?
A:Sure, we can apply your own logo on the products according to your requirement.
- Q: How are the cores placed in the mold cavity in metal casting machinery?
- In metal casting machinery, the cores are placed in the mold cavity using several techniques depending on the complexity of the casting design and the type of core material being used. One common method is called "core setting." In this process, the mold cavity is partially filled with sand or other mold material, and the core is then carefully placed in the desired position within the cavity. The remaining mold material is then added to completely enclose the core. This technique is typically used for simpler castings with relatively straightforward core shapes. For more complex castings with intricate core designs, a technique called "core assembly" is employed. In this method, the core is built in sections or segments, which are then assembled within the mold cavity to form the complete core shape. The individual core segments are aligned and secured using various techniques such as pins, clamps, or adhesive materials. This allows for greater flexibility in creating complex and detailed casting designs. In some cases, especially for large or heavy cores, mechanical devices such as cranes or robotic arms may be used to position the cores accurately within the mold cavity. This ensures precision and consistency in the placement of the cores, minimizing the chances of defects or inaccuracies in the final casting. Overall, the placement of cores in the mold cavity requires careful attention to detail, precision, and adherence to the casting design specifications. The method used will depend on factors such as the complexity of the casting design, the type of core material, and the capabilities of the metal casting machinery being used.
- Q: What are the different types of casting defects related to mold filling in metal casting machinery?
- There are several types of casting defects related to mold filling in metal casting machinery. These defects can occur during the process of pouring molten metal into the mold and can affect the overall quality and integrity of the final cast product. Some of the common casting defects related to mold filling include: 1. Incomplete filling: This defect occurs when the molten metal fails to completely fill the mold cavity, leaving voids or areas with insufficient metal. This can result in incomplete parts or weak sections in the final cast product. 2. Misruns: Misruns are defects that occur when the molten metal solidifies before completely filling the mold cavity. This can happen due to factors such as inadequate pouring temperature, improper gating system design, or insufficient molten metal volume. Misruns result in incomplete castings with incomplete shapes or sections. 3. Cold shuts: Cold shuts are defects that occur when two streams of molten metal fail to fuse properly during mold filling. This can happen due to inadequate gating or pouring practices, resulting in a weak or incomplete bond between the two metal streams. Cold shuts can lead to weak points or fractures in the final cast product. 4. Shrinkage cavities: Shrinkage cavities are defects that occur due to the contraction of molten metal during solidification. As the metal cools and solidifies, it undergoes a reduction in volume, causing shrinkage cavities to form. These defects can result in voids or cavities in the cast product, affecting its strength and structural integrity. 5. Porosity: Porosity is a defect characterized by the presence of small voids or gas pockets within the cast material. This defect can occur due to various factors, including the presence of trapped gases in the molten metal, inadequate venting in the mold, or improper gating design. Porosity can weaken the cast product and make it prone to failure under stress. 6. Inclusions: Inclusions are foreign materials that become trapped within the metal during the casting process. These can include sand, oxides, or other impurities that contaminate the molten metal. Inclusions can lead to weak points or defects in the cast product, affecting its overall quality. To minimize these casting defects related to mold filling, proper casting techniques, including proper design of gating systems, adequate pouring temperature, and appropriate mold venting, should be employed. Additionally, regular inspection and quality control measures should be implemented to identify and address any potential defects during the casting process.
- Q: How do you improve productivity and efficiency with automated metal casting machinery?
- Automated metal casting machinery offers numerous opportunities to enhance productivity and efficiency in the manufacturing process. Here are some key strategies to improve these aspects using automated metal casting machinery: 1. Streamline Workflows: Analyze the entire casting process and identify areas where automation can be introduced to streamline workflows. For instance, implementing robotic arms or conveyors can automate material handling, reducing human intervention and minimizing errors or delays. 2. Optimize Cycle Times: Automated machinery can significantly reduce cycle times as compared to manual casting. By fine-tuning the machine settings and optimizing the casting parameters, it is possible to achieve faster production rates without compromising quality. 3. Enhance Quality Control: Automated systems can integrate advanced sensors and monitoring technologies to ensure consistent quality control throughout the casting process. Real-time data analysis can detect any variations or defects, allowing for immediate intervention and corrective actions, thereby minimizing scrap and rework. 4. Implement Predictive Maintenance: Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the smooth operation of automated casting machinery. By leveraging sensor data and machine learning algorithms, it is possible to implement predictive maintenance practices. This helps identify potential issues before they lead to unplanned downtime, thereby improving overall equipment effectiveness and minimizing production interruptions. 5. Integrate Data Analytics: Collecting and analyzing data generated by the automated machinery can provide valuable insights into production performance, identifying bottlenecks, and opportunities for improvement. Leveraging data analytics can help optimize casting parameters, identify process inefficiencies, and make data-driven decisions to boost productivity and efficiency. 6. Continuous Training and Skill Development: While automated machinery reduces manual labor, it is essential to invest in training and upskilling the workforce to operate and maintain these advanced systems. This ensures that the workforce is proficient in utilizing the machinery to its full potential and can troubleshoot any technical issues effectively. 7. Collaboration and Integration: Integrating automated casting machinery with other manufacturing systems, such as inventory management, supply chain, and production planning, can further enhance productivity and efficiency. This enables seamless data exchange, synchronized workflows, and better coordination across various stages of the manufacturing process. By implementing these strategies, manufacturers can optimize productivity and efficiency in metal casting operations, reduce costs, improve product quality, and remain competitive in the market.
- Q: How does metal casting machinery handle the removal of castings from the mold?
- The process of shakeout is employed by metal casting machinery to extract castings from the mold. Shakeout can be accomplished through either mechanical or pneumatic means. In mechanical shakeout, the mold is positioned on a vibrating table or conveyor belt, which induces vibrations that aid in dislodging the sand or other mold material from the casting. As the mold is shaken, the castings detach from the mold and descend onto a designated collection area. This technique is commonly utilized for larger and weightier castings. On the contrary, pneumatic shakeout utilizes air or gas pressure to eliminate the mold material from the castings. This method entails directing a stream of compressed air or gas onto the mold, causing the mold to disintegrate and releasing the castings. Pneumatic shakeout is frequently employed for smaller and more intricate castings. Irrespective of the chosen method, it is crucial for the metal casting machinery to delicately and precisely handle the extraction of castings from the mold to prevent any damage. The machinery should be designed to exert an appropriate amount of force or pressure to separate the castings from the mold without causing any distortion or breakage. Furthermore, suitable handling mechanisms, such as grippers or conveyors, should be in place to safely transfer the castings from the mold to the subsequent stage of the manufacturing process.
- Q: How is the mold created using metal casting machinery?
- The mold is created using metal casting machinery by pouring molten metal into a pre-designed cavity called the mold. The mold is typically made of a heat-resistant material such as sand or clay, which is packed around a pattern or a replica of the desired metal object. The molten metal is then poured into the mold and allowed to cool and solidify. Once the metal has hardened, the mold is removed, leaving behind a solid metal object in the shape of the original pattern.
- Q: What are the different types of regulations and standards for metal casting machinery safety?
- There are several regulations and standards that govern the safety of metal casting machinery. These include the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations, which specify safety requirements for equipment and processes involved in metal casting. Additionally, standards such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) provide guidelines for the safe operation and maintenance of metal casting machinery. These regulations and standards cover areas such as machine guarding, electrical safety, ventilation, and fire prevention, among others, to ensure the safety of workers and prevent accidents in metal casting facilities.
- Q: What are the noise levels generated by metal casting machinery?
- The noise levels generated by metal casting machinery can vary depending on factors such as the specific equipment used, the casting process, and the surrounding environment. However, in general, metal casting machinery can produce high levels of noise due to the various mechanical processes involved, such as the movement of molds, the pouring of molten metal, and the operation of cooling systems. To ensure worker safety and comply with regulations, it is crucial to implement appropriate noise control measures, such as soundproof enclosures or personal protective equipment.
- Q: Can metal casting machinery handle the production of castings with tight tolerances?
- Yes, metal casting machinery can handle the production of castings with tight tolerances. With advancements in technology and precision casting techniques, modern metal casting machinery is capable of producing castings with high accuracy and tight tolerances. This is achieved through various measures, such as using advanced molds and pattern-making techniques, employing state-of-the-art machinery with computer numerical control (CNC) systems, and implementing rigorous quality control processes. Metal casting machinery allows for precise control over the entire casting process, including the selection of materials, the creation of molds, and the pouring of molten metal. CNC systems enable the machinery to precisely follow the design specifications, ensuring that the dimensions and tolerances of the castings are maintained within the required limits. Furthermore, the use of advanced molds and pattern-making techniques, such as 3D printing or additive manufacturing, allows for the production of intricate and complex castings with tight tolerances. These techniques enable the creation of highly accurate molds that can reproduce intricate details and geometries with high precision. Quality control processes are also crucial in ensuring that castings meet the required tolerances. This involves thorough inspections, measurements, and testing at various stages of the casting process. Advanced metrology tools, such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), are used to verify the dimensions and tolerances of the castings, guaranteeing their adherence to the specified requirements. In conclusion, metal casting machinery has evolved to meet the demands of producing castings with tight tolerances. With the use of advanced technology, precision casting techniques, and stringent quality control processes, metal casting machinery can handle the production of castings with high accuracy and tight tolerances.
- Q: What are the different types of ergonomic improvements implemented in metal casting machinery?
- Metal casting machinery has implemented a range of ergonomic improvements to prioritize the safety and comfort of workers. One prevalent enhancement is the integration of adjustable workstation height, enabling employees to customize their work surface to suit their individual needs. This adjustment reduces strain on the back, neck, and shoulders. Adjustable footrests are also commonly included to provide additional support and minimize leg and foot discomfort. Another significant ergonomic improvement involves the use of ergonomic controls and interfaces. This entails placing controls within easy reach and at an appropriate height, eliminating the need for excessive stretching or reaching. Controls are often designed with large, easy-to-read labels and intuitive interfaces to minimize the risk of user error and enhance overall efficiency. Additionally, ergonomic seating plays a crucial role in metal casting machinery. Ergonomic chairs are designed to offer proper support to the back, hips, and legs, decreasing the likelihood of musculoskeletal disorders and increasing worker comfort. These chairs frequently feature adjustable aspects such as backrest height, seat depth, and lumbar support to accommodate various body types and preferences. Moreover, ergonomic improvements encompass the utilization of anti-fatigue mats and flooring. These mats provide cushioning and support to workers who are required to stand for extended periods, reducing strain on their feet, legs, and lower back. Anti-fatigue flooring is designed to absorb shock and provide a more comfortable walking surface. Finally, proper lighting is an essential ergonomic improvement in metal casting machinery. Sufficient lighting is critical in minimizing eye strain and improving visibility, enabling workers to perform their tasks more effectively and reducing the risk of errors or accidents. In conclusion, the range of ergonomic improvements implemented in metal casting machinery aims to enhance the safety, comfort, and productivity of workers. These enhancements reduce the likelihood of work-related injuries and create a more user-friendly and efficient work environment.
- Q: Can metal casting machinery be used for casting different alloys?
- Yes, metal casting machinery can be used for casting different alloys. Metal casting machinery, such as foundry equipment and casting machines, are designed to accommodate different types of alloys and casting processes. The machinery allows for precise control over factors such as temperature, pressure, and mold design, which are essential for casting different alloys. Whether it is iron, steel, aluminum, copper, or other metals, the machinery can be adjusted and customized to meet the specific requirements of each alloy. Different alloys may have different melting points, shrinkage rates, and other characteristics, and the casting machinery can be modified accordingly to ensure optimal casting results. Moreover, the machinery can also be used for casting various shapes and sizes, providing flexibility in the production of different alloy components. Overall, metal casting machinery is versatile and adaptable, enabling the casting of different alloys in various applications.
Send your message to us
Section Steel Roll From China With High Quality
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 41000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches